- Home
- ADC Development
- Antibody Discovery for ADC Development
- Tumor Surface Protein Specific Antibody Discovery
- Anti-Mucin16 Antibody Discovery
Anti-Mucin16 Antibody Discovery Service
Empowered by advanced technology platforms and experienced technical personnel, the technical division at Creative Biolabs is dedicated to serving as your antibody development and characterizations. Mucin16 (MUC16) is a tumor-associated antigen that is cleaved from the surface of ovarian cancer cells and shed into blood providing a useful biomarker for monitoring growth of ovarian cancer. Based on the shedding mechanism of MUC16, Creative Biolabs now offers a comprehensive set of antibody development services against tumor cell surface protein MUC16 to assist our clients to conduct their project.
Mucin16
MUC16, a high molecular weight (MW) cell surface glycoprotein containing both O-linked and N-linked oligosaccharides, is not detected in the epithelium of normal ovaries but is highly expressed on the ovarian tumor cell surface, suggesting a physiologic role in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Its biological functions include cytolytic inhibition of human natural killer cells, facilitation of tumor cell to mesothelial cell adhesive interaction and modulation of tumor cell growth. MUC16 has been shown to interact strongly with mesothelin (MSLN) and the interaction between tumor cell surface MUC16 and mesothelial cell membrane-bound MSLN facilitates the initial adhesion and subsequent implantation and peritoneal spread that characterize EOC metastasis.
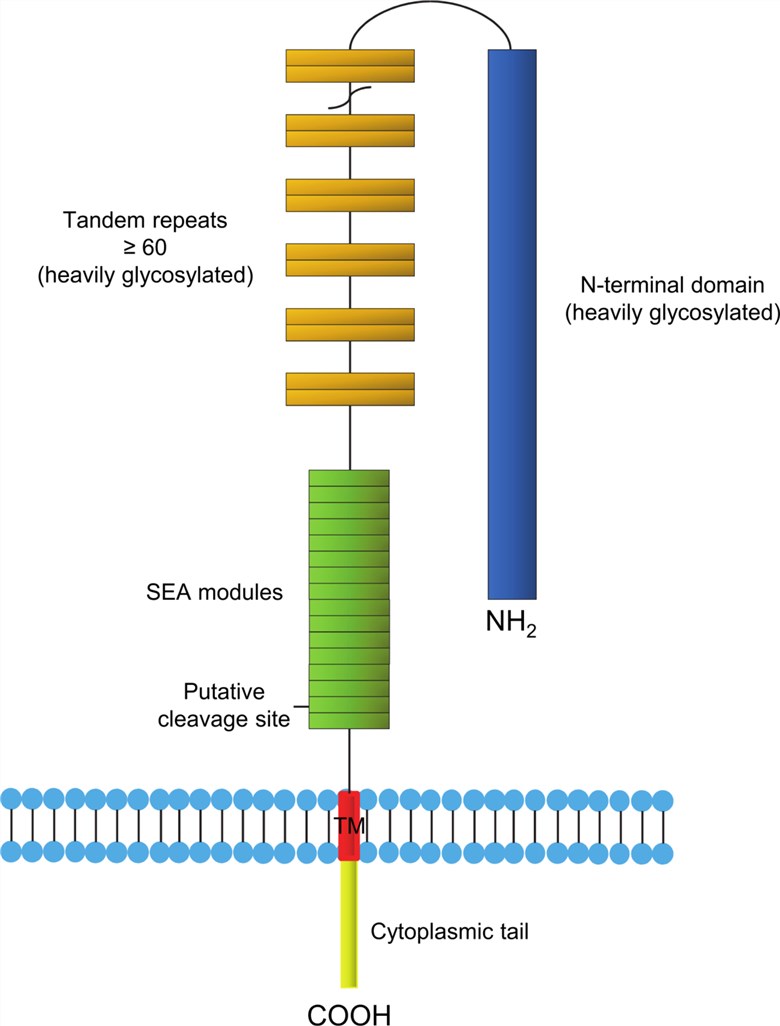 Fig.1 Schematic structure of MUC16.1,2
Fig.1 Schematic structure of MUC16.1,2
Shedding
MUC16 is shed from the tumor surface via a proteinase-dependent mechanism, catalyzed by a membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). Proteolytic clearing of MUC16 may then expose integrins for high-affinity cell binding to peritoneal tissues, thereby anchoring metastatic lesions for subsequent proliferation within the collagen-rich sub-mesothelial matrix. Shedding generates a cell associated carboxyl-terminal fragment of MUC16 (MUC16-Cter) with potential oncogenic functions. MUC16-Cter, with an approximately MW of 17KDa, is capable of imparting tumorigenic and metastatic phenotypes to pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
Antibody Strategies against Mucin16
Owing to the clinical importance of MUC16, antibody-based therapeutic approaches using antibodies against the tandem repeat domains of MUC16 have been the modus operandi for MUC16 targeted therapy but met with very limited success, such as Oregovomab and Abagovomab. One of the major reasons is that these antibodies bind to the shed CA125, it is highly likely that these antibodies do not reach cancer cell at all.
Additional antibodies towards MUC16-Cter including the membrane proximal 12 residues will be critical for therapeutic targeting using MUC16. The antibodies for the MUC16-Cter that remains associated with the tumor cells can be exploited to design MUC16 based immunotherapeutic modalities such as antibody-drug conjugate (ADC).
Besides, preventing MUC16 shedding should be considered an alternative approach to the existing MUC16 based therapeutics for three reasons. First, preventing MUC16 cleavage by antibodies would increase the cell surface representation of MUC16, which will enhance the efficacy of antibody-based therapeutics such as Oregovomab and Abagovomab. Second, antibodies also could be conjugated with drugs to form ADC, which will be internalized into an ovarian tumor cell and release drugs to kill cells. Third, since nuclear localization of MUC16 is cleavage-dependent, abrogation of MUC16 cleavage would reduce the nuclear functions of MUC16-Cter. We, therefore, believe using ADC that prevent MUC16 cleavage or bind to the MUC16-Cter will both result in better therapeutic efficiency.
Creative Biolabs has gained significant knowledge of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) preparation. We are more than happy to share our experience and help our customers with this tragically important step in antibody development. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Rancourt, Claudine, et al. "The role of MUC16 mucin (CA125) in the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer." Ovarian cancer: basic science perspective. Volume 1 (2012): 67-84.
- Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
