Introduction of AQP4
Aquaporin-4, also known as AQP4, is the main water channel of the central nervous system encoded by the AQP4 gene in humans. AQP4 is highly concentrated in the human body primarily at the end of astrocytes, where it participates in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) functional unit. Additionally, AQP4 is also expressed in epithelial cells of many organs throughout the body, such as the kidney, intestine, salivary glands, sensory organs, and skeletal muscles. The structure of AQP4 is characterized by six-transmembrane domains and five connecting loops to form the channel.
| Basic Information of AQP4 | |
| Protein Name | Aquaporin-4 |
| Gene Name | AQP4 |
| Aliases | Mercurial-insensitive water channel, MIWC, WCH4 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | P55087 |
| Transmembrane Times | 6 |
| Length (aa) | 323 |
| Sequence | MGRQKELVSRCGEMLHIRYRLLRQALAECLGTLILVMFGCGSVAQVVLSRGTHGGFLTINLAFGFAVTLGILIAGQVSGAHLNPAVTFAMCFLAREPWIKLPIYTLAQTLGAFLGAGIVFGLYYDAIWHFADNQLFVSGPNGTAGIFATYPSGHLDMINGFFDQFIGTASLIVCVLAIVDPYNNPVPRGLEAFTVGLVVLVIGTSMGFNSGYAVNPARDFGPRLFTALAGWGSAVFTTGQHWWWVPIVSPLLGSIAGVFVYQLMIGCHLEQPPPSNEEENVKLAHVKHKEQI |
Function of AQP4 Membrane Protein
The most well-known function of AQP4 is to provide fast water transportation as well as maintain homeostatic balance within the CNS. It has been recognized that AQP4 can be used as a key molecule in the interaction between astrocytes and brain microvascular endothelial cells to regulate water movement, waste removal, fine-tuning of potassium homeostasis, as well as cell adhesion. Moreover, AQP4 has been considered as a critical contributor to neuroinflammation, which is expressed mainly in the foot processes of pericapillary astrocytes at the blood-brain border (BBB) and brain-cerebrospinal fluid border, and controls the movement of water in the brain. AQP4 is reported to be associated with the pathology of brain edema, which is a disease caused by brain-water imbalance. In addition, the altered AQP4 expression is thought to play a key role in neuroinflammation during brain injury.
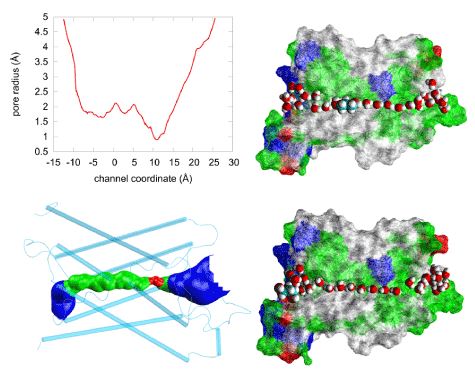 Fig.1 Steric fitness of 1,3-propanediol (PDO) inside AQP4. (Yu, 2016)
Fig.1 Steric fitness of 1,3-propanediol (PDO) inside AQP4. (Yu, 2016)
Application of AQP4 Membrane Protein in Literature
This article demonstrates that AQP4 deficiency may relax the proinflammatory cytokine release from astrocytes through SPHK1/MAPK/AKT pathway. It improves our understanding of AQP4 in neuroinflammatory events, highlighting a novel profile of SPHK1 as a potential target for the treatment of CNS inflammation.
This article reveals that immunization with the neuromyelitis optica (NMO) autoantigen AQP4 through augmented inflammatory response can increase disease severity in EAMG mice, which may explain exacerbation or increased susceptibility of patients with one autoimmune disease to develop the additional autoimmune syndrome.
In this study, the authors use a rat model of hydrocephalus to demonstrate that AQP4 is over-expressed in hydrocephalus and silencing AQP4 can aggravate the hydrocephalus, indicating that AQP4 plays a protective role against hydrocephalus.
This article demonstrates that AQP4 deletion can protect the blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity by reducing inflammatory responses, which is realized by the upregulation of PPAR-γ expression and attenuation of proinflammatory cytokine release. So, the authors suggest that the reduction of AQP4 may be protective in acute severe hypoglycemia.
The authors use a rat ischemic stroke (IS) model to reveal that increasing the Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) activity can improve brain edema, infarct volumes, and reduce neurological impairment, which is related to 4-HNE clearance and AQP4 down-regulation.
AQP4 Preparation Options
We provide custom membrane protein preparation services for worldwide customers. Leveraging by our advanced Magic™ membrane protein production platform, we are able to provide target membrane protein in multiple active formats. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-AQP4 antibody development services.
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality membrane protein preparation service to facilitate the development of worldwide customer’s research. During the past years, we have successfully established a powerful Magic™ membrane protein platform which enables us to provide a series of membrane protein preparation services. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.