The Androgen Receptor (AR) is categorized as a ligand-dependent steroid hormone nuclear receptor. Upon the entry of free testosterone into the cell, it is metabolized into a more potent 5-alpha-dihydrotestosterone metabolite (5-DHT). 5-DHT or testosterone supplants the heat shock proteins within the AR, binding with importin-alpha, this catalyzes the translocation of AR to the cellular nucleus. Within the nucleus, the receptor dimer binds with the androgen response element, which subsequently recruits co-activator proteins to enhance transcription, thereby instigating a cellular response. Furthermore, it is through the alteration of amino acid side chain orientations and positions that AR accommodates a multitude of distinctive small molecule ligands, enabling a range of biological functions to be conducted.
Disruption of AR functions results in complications in males such as the inability to undergo proper sexual differentiation or the development of complete androgen insensitivity syndrome. In addition, inactivated AR has been identified as a significant participant in the onset of prostate cancer.
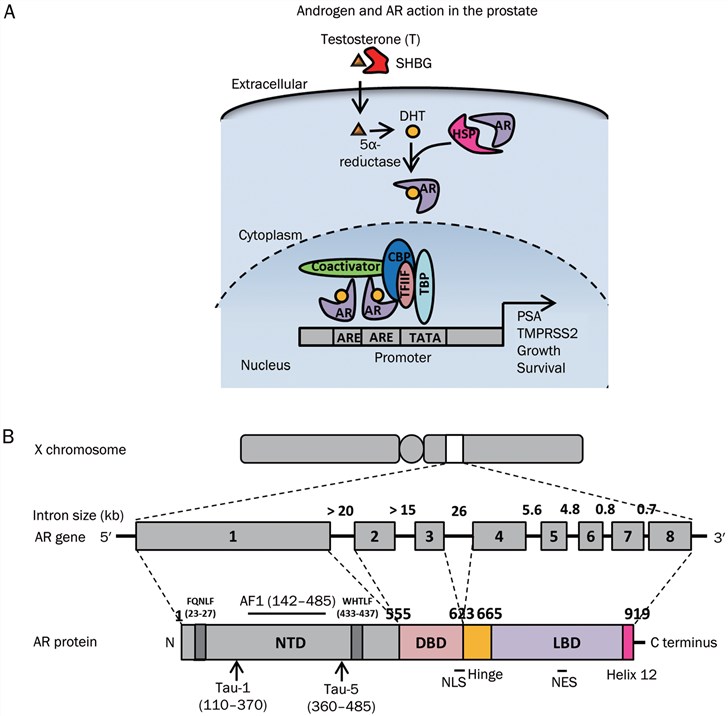 Fig.1 AR protein and action.1
Fig.1 AR protein and action.1
Reference
-
Eileen, Li, et al. " Androgen receptor: structure, role in prostate cancer and drug discovery." Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 36 (2015): 3-23.


 Fig.1 AR protein and action.1
Fig.1 AR protein and action.1


