As a well-established company in the bio-industry, Creative Biolabs offers a full range of in vitro diagnostics (IVD) services. Guaranteed to perform within the specified time frame, and the quality of various disease research is always maintained to the end. Our laboratory services have many advanced microsphere-based nucleic acid assays, such as microsphere-based single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) assays, to support customer's needs in the fast-growing disease diagnosis projects.
Introduction to Microsphere-based Liquid Arrays
In the past few years of studies, the identification of biomarkers or serotypes for many infectious diseases has become the cornerstone of our understanding of disease epidemiology. Meanwhile, the epitope mapping of different antigens also plays an important role in immunogenicity evaluation. As a result, a wide variety of microsphere-based liquid arrays have been generated for determining different antigen types and representing antigen epitopes.
Moreover, microsphere-based liquid arrays have been broadly used in genomic research, such as SNP genotyping, gene expression profiling, disease biomarker identification, as well as early drug screening. In general, a wide variety of microsphere beads (approximately 4-6μm in diameter) are used to prepare arrays. Each type of microsphere bead is labeled differently according to its unique optical characteristics, such as fluorescence. Depending on the color and unique wavelength of each fluorescence tag, multiple gene mutations can be detected simultaneously. Besides, the microspheres are easily suspended in the liquid array and exhibit favorable dynamics during the detection process.
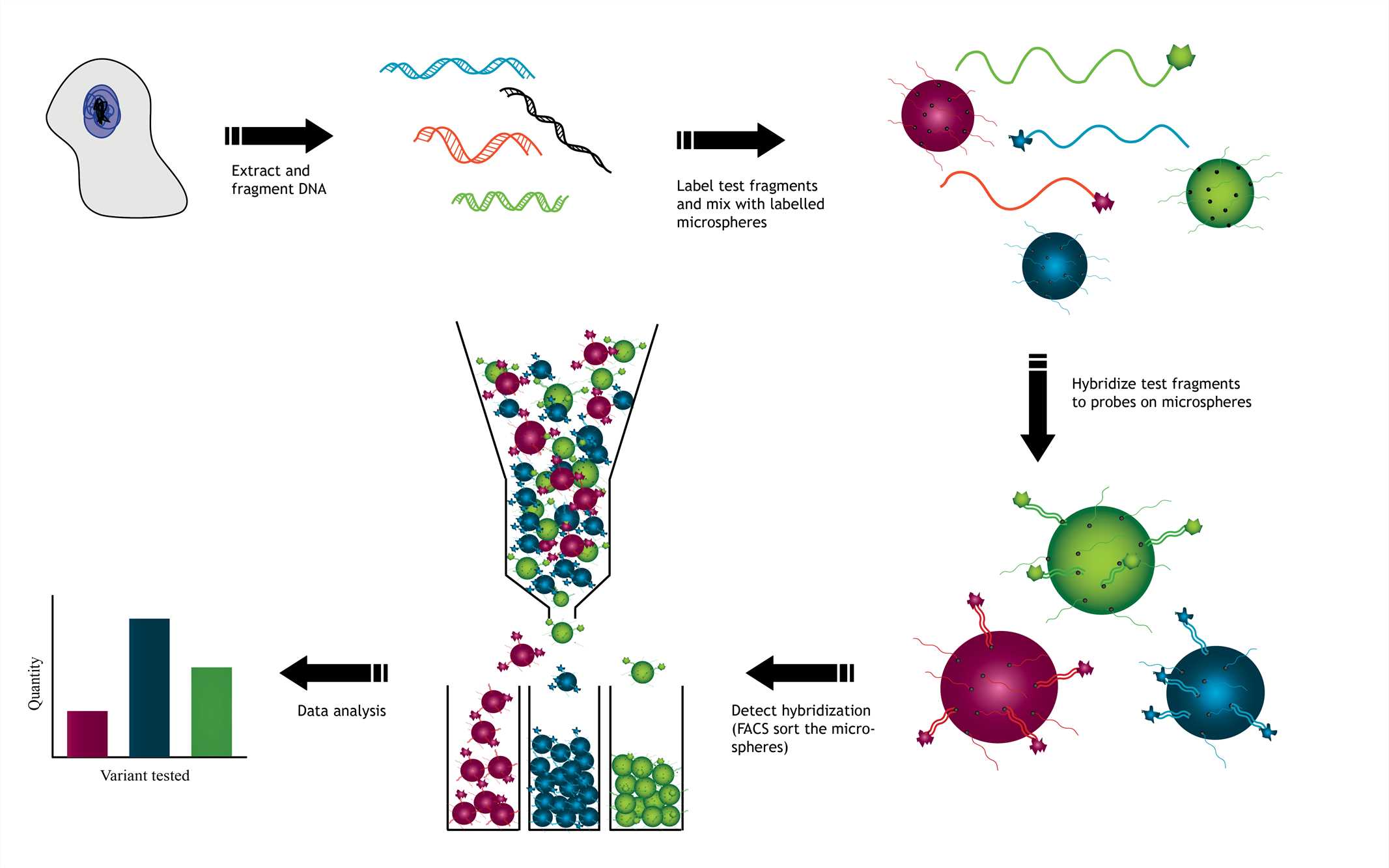 Fig.1 Microsphere-based array technology with DNA hybridization model. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Microsphere-based array technology with DNA hybridization model. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Microsphere-based Nucleic Acid Assays
Currently, in vitro disease diagnosis is one of the long-term challenges in the biomedical industry. To solve the difficulties of traditional IVD approaches, microsphere-based nucleic acid assays have been regarded as effective strategies for determining DNA markers in various disease types.
With the commitment of being your best drug discovery partner, Creative Biolabs has established a panel of microsphere-based nucleic acid assays for our clients to screen, sequence, and/or quantitate a nucleic acid of interest. The data derived from our studies have indicated that our assays are a series of rapid, accurate, high-throughput, and large-scale testing methods for analyzing nucleic acid samples. For instance, a battery of nucleic acid assays has been designed for incubating fluorescent tags cDNA or DNA oligonucleotide probes to specifically labeled microspheres. The abundance of each target in different samples can be further determined by collecting and analyzing different fluorescent signals.
Why Choose Us?
Nowadays, Creative Biolabs has established the utmost efficient integrated microsphere-based nucleic acid assays solutions to innovate and accelerate your disease diagnosis and treatment. Our platform is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and highly experienced staff is available to assist in all areas of nucleic acid studies. We have integrated high-quality services that are based in America and span the entire development chain all over the world.
- High-density microsphere-based liquid arrays
- Thousands of copies of a unique oligonucleotide probe sequence
- Flexible combination of microsphere sensing elements, arrays, and microsphere pools
- The interrogation of very small sample volumes
- Strict signal-to-noise ratio monitoring
Creative Biolabs is a leading drug development company, providing a wide spectrum of microsphere-based nucleic acid assays from disease diagnosis. With our one-stop IVD solution platform, we are ready to help you tackle your toughest research challenge. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for closer communication to learn how we can be involved in your project. Separate services or integrated end-to-end solutions are all welcomed.
Published Data
1. Development of a New Microsphere-Based Gene Expression Assay
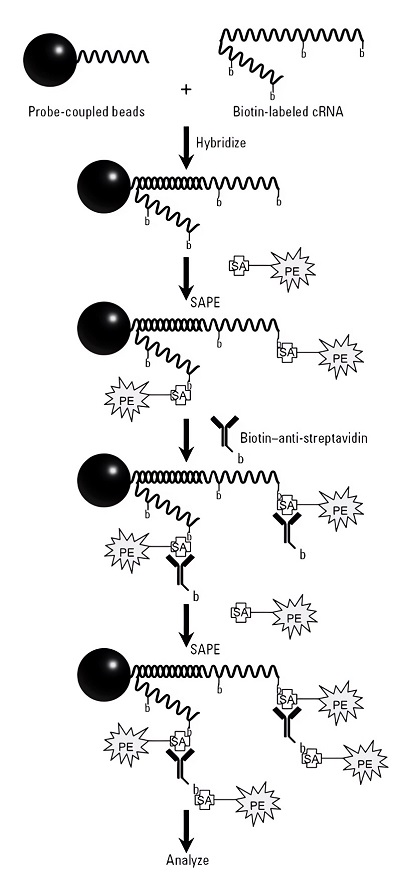 Fig.2 Workflow of the microsphere-based high-throughput gene expression assay.1
Fig.2 Workflow of the microsphere-based high-throughput gene expression assay.1
This study developed a high-throughput gene expression profiling assay to assess the effects of estrogen exposure in prepubertal rats. The assay, based on bead-based technology, involved covalently attaching carefully selected oligonucleotides to fluorescently coded microspheres, which were then hybridized to biotinylated cRNA, followed by signal amplification, enabling rapid, sensitive, and multiplexed analysis. Researchers created an RNA expression profiling system specific to 17 estrogen-responsive transcripts and three controls, allowing the simultaneous evaluation of up to 100 distinct analytes in a single sample using a 96-well plate format. This system demonstrated improved sensitivity compared to existing microsphere-based assays, with detection levels down to 1 amol. It also offered better sensitivity and precision than microarray technology, requiring as little as 2.5 μg starting cRNA. The assay provides higher throughput and reduced costs compared to microarrays, with a trade-off in the number of transcripts analyzed.
2. A Peptide Nucleic Acid Bead Array Technology for The Detection of Bacillus cereus
 Fig.3 Schematic of acpcPNA-based bead array method.2
Fig.3 Schematic of acpcPNA-based bead array method.2
This study developed a robust method for detecting Bacillus cereus using pyrrolidinyl peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) as probes in a bead array with multiplex and high-throughput capabilities. PNAs with prolyl-2-aminocyclopentanecarboxylic acid (ACPC) backbone, with sequences targeting groEL, motB, and 16S rRNA, were covalently attached to fluorescently barcoded beads for the detection of these B. cereus genes. The acpcPNA-based bead array demonstrated high selectivity, with detectable signals only in the presence of B. cereus and not other species. The assay's sensitivity was 0.038, 0.183, and 0.179 ng for groEL, motB, and 16S rRNA, respectively, outperforming its DNA counterpart, which validated the superior binding affinity of acpcPNA. The method's robustness was validated by testing spiked milk and pickled mustard greens, showing minimal interference from food matrices. This acpcPNA-based bead array offers a reliable alternative nucleic acid-based method for detecting foodborne pathogens.
References
- Naciff, Jorge M., et al. "Design of a microsphere-based high-throughput gene expression assay to determine estrogenic potential." Environmental health perspectives 113.9 (2005): 1164-1171. Distributed under Open Access license PDM 1.0, without modification.
- Noppakuadrittidej, Prae, et al. "Development of peptide nucleic acid-based bead array technology for Bacillus cereus detection." Scientific Reports 13.1 (2023): 12482. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.