Advances in optical imaging technologies have stimulated the development of near-infrared (NIR) fluorescently labeled targeted probes for use in molecular imaging. As sdAbs have already proven to be excellent candidates for molecular imaging, Creative Biolabs has taken lots of effort to design NIR-conjugated sdAbs targeting various protein markers for in vivo imaging and to evaluate the effect of dye and dye conjugation chemistry on their pharmacokinetics during development. We now provide customized NIR dyes-conjugated sdAb development services to support your in vivo research use.
Near-infrared Fluorescence Imaging
NIR fluorescence imaging is widely used for tracking antibodies and biomolecules in vivo. Clinical and preclinical applications include intraoperative imaging, tracking therapeutics, and fluorescent labeling as a surrogate for subsequent radiolabeling. NIR fluorescence provides high contrast between target and background tissues by improving tissue penetration and minimizes tissue autofluorescence. It is non-damaging radiation and less toxic for in vivo monitoring of biologic processes. Besides, it can be easily conjugated to sdAb by random labeling and site-specific methods.
SdAbs have better imaging pharmacokinetics since they are rapidly excreted by kidneys and constitute an ideal tool for diagnostic applications in various disease areas, including infectious, inflammatory neurodegenerative diseases and tumors. Furthermore, NIR fluorescence (NIRF) imaging is becoming a noninvasive alternative to radionuclide imaging for joints in small animals. NIR dye labeled sdAbs were documented for tumor imaging and tumor surgery imaging. Besides, sdAbs can also be used for in vivo NIRF targeting of T cells. Cellular imaging of immune cells such as T cells, B cells and antigen-presenting cells has provided important information on immune homeostasis, immune responses and autoimmune diseases. Depending on the research fields, our technique team also provides Customized Labeled Nano-tracer as Imaging Tools services towards different targets involved in cancer, inflammation, immune checkpoints or tumor extra environment.
Case
IRDye800CW or IRdye680RD were conjugated either randomly (via lysine) or site-specifically (via C-terminal cysteine) to the anti-HER2 sdAb. After verification of purity and functionality, the biodistribution and tumor targeting of the NIR-sdAbs were assessed in HER2-positive and -negative xenografted mice. The study revealed that NIR fluorescent labeling of sdAbs allows rapid, specific, and high contrast in vivo tumor imaging.
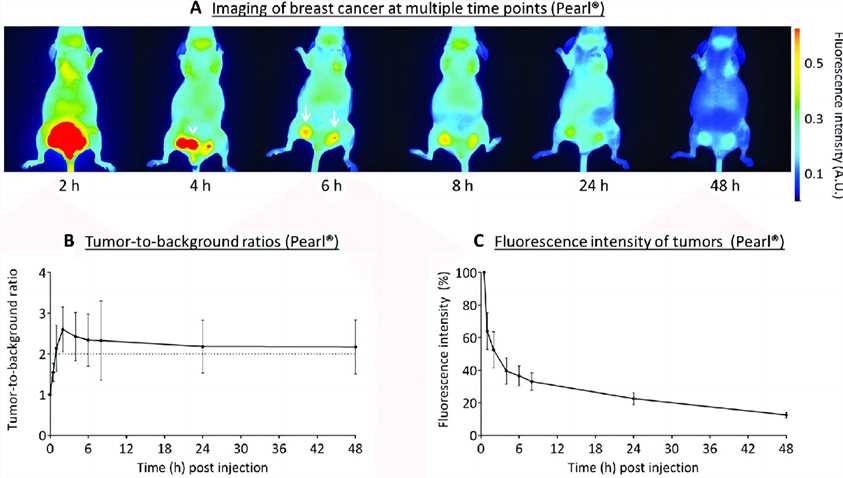 Fig.1 NIR imaging of breast cancer.1,4
Fig.1 NIR imaging of breast cancer.1,4
In the last 20 years, sdAbs have been proposed as a new class of antibody-derived agents for molecular imaging because of their unique features regarding affinity, specificity, and rapid pharmacokinetics, ensuring good uptake in the targeted tissues and high target-to-background ratios. Creative Biolabs is professional in antibody generation. We will take full advantage of our experience and advanced technology to provide high-quality products for our clients. If you are interested in our customized labeled nano-tracer development services, please directly contact us for more information.
Published Data
1. Small Molecule Targeted Near-Infrared Dye Conjugate for In Vivo Imaging of LHRH Receptor-Positive Cancers
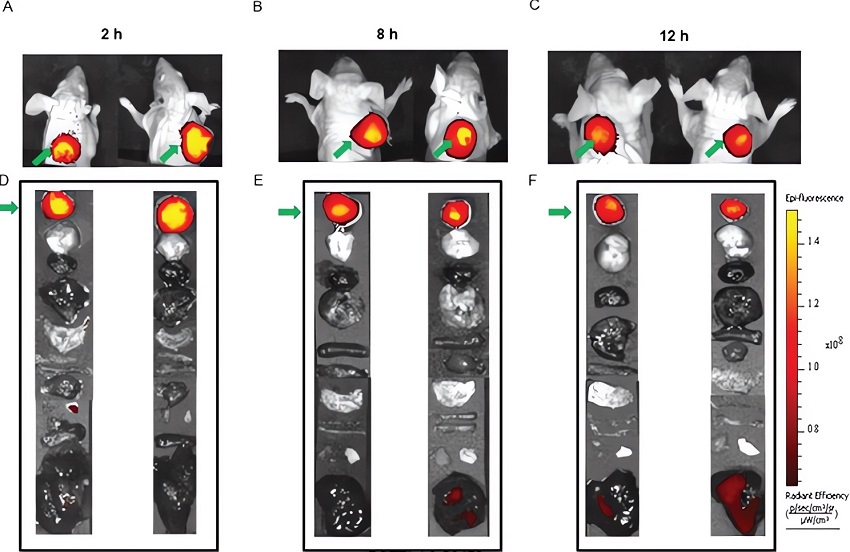 Fig.2 Time course imaging of MDA-MB-231 tumor with BOEPL-targeted NIR dye conjugates.3,4
Fig.2 Time course imaging of MDA-MB-231 tumor with BOEPL-targeted NIR dye conjugates.3,4
This study introduced a small molecule non-peptidic ligand, BOEPL, targeting the luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone receptor (LHRH-R) for the delivery of payloads to LHRH-R-positive tumors. The researchers conjugated BOEPL to a NIR dye using various linkers. In vitro, these conjugates exhibited binding affinities in the low nanomolar range, while in vivo, they displayed selective receptor-mediated uptake within tumor tissues. Tumor uptake could be blocked by excess unlabeled conjugate, with dye retention observed for up to 12 hours post-injection. Importantly, BOEPL-targeted NIR dye conjugates showed minimal uptake in non-malignant tissues, with any brief accumulation in the kidneys attributed to normal clearance processes. These results indicated that BOEPL-targeted NIR dye conjugates could serve as effective agents for fluorescence-guided surgery, enabling more precise removal of LHRH-R-positive cancerous tissues. Additionally, they demonstrated the feasibility of using BOEPL for payload delivery to LHRH-R-positive tumors in vivo.
References
- Boonstra, Martin C., et al. "Real-time near-infrared fluorescence imaging using cRGD-ZW800-1 for intraoperative visualization of multiple cancer types." Oncotarget 8.13 (2017): 21054.
- Matlashov, Mikhail E., et al. "A set of monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins for multicolor imaging across scales." Nature communications 11.1 (2020): 239.
- Roy, Jyoti, Miranda Kaake, and Philip S. Low. "Small molecule targeted NIR dye conjugate for imaging LHRH receptor positive cancers." Oncotarget 10.2 (2019): 152.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.