DNA Topoisomerases
Majority of clinically used antifungals suffer from various drawbacks in terms of toxicity, efficacy and cost, and their frequent use has led to the emergence of resistant strains. Hence, there is a great demand for novel antifungals belonging to a wide range of structural classes, selectively acting on novel targets with fewer side effects. To promote the antifungal drug discovery research, Creative Biolabs is offering high-quality contract research services for the discovery of effective antifungal agents targeting DNA topoisomerases.
Introduction of DNA Topoisomerases
DNA topoisomerases are enzymes that change the topological structure of cccDNA during the process of DNA replication, transcription, recombination, and genomic stability maintenance. They have shown to be valuable targets for therapeutic agents such as antibacterial agents (e.g., fluoroquinolones targeting bacterial type II topoisomerases) and anti-cancer agents (e.g., camptothecin targeting human topoisomerases). These drugs inhibit the enzymes in a unique way so that they can be converted into cellular poisons that leads to cell death. Since DNA topoisomerases are ubiquitous enzymes that are found in various living organisms including pathogenic fungi, the potential of these enzymes as novel antifungal drug discovery targets has been tested in some studies.
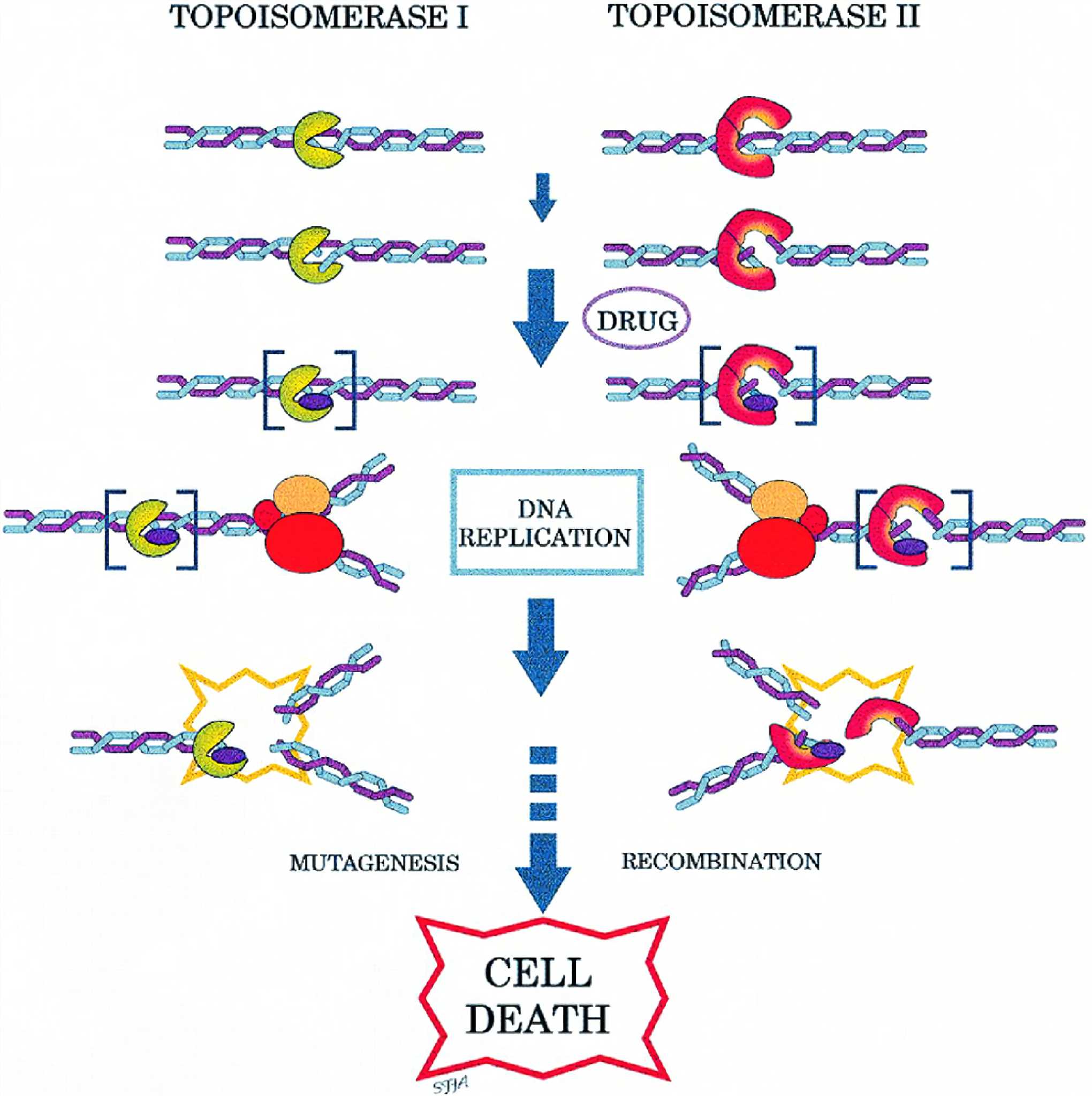 Fig. 1 Mechanism of DNA topoisomerase inhibitors.1
Fig. 1 Mechanism of DNA topoisomerase inhibitors.1
Features of our Services
Creative Biolabs offers the largest and most diverse portfolio of standard and custom-specific drug discovery solutions to suit your novel discovery goals. You can choose from our antifungal drug discovery service packages or individual service modules including target identification and validation, Hit identification, Hit to lead, Lead optimization, and IND enabling. Moreover, our services are characterized by:
- Structure-based antifungal drug discovery against diverse potential targets
- Expert scientists and staff with keen project and program management skills
- Robust, efficient processes combined with quality systems and on-time delivery of reports
- Individualized technical support and best after-sale services
As a well-recognized service provider for drug discovery and development, Creative Biolabs is fully competent and dedicated to providing our clients with the most high-quality services. For more information about our services, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
- Froelich-Ammon, S.; Osheroff, N. Topoisomerase Poisons: Harnessing the Dark Side of Enzyme Mechanism. Journal of Biological chemistry. 1995, 270(37): 21429-21432. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
