Protein Elongation Factors (EF2)
This limited antifungal drugs and drug resistance highlights the urgent need for the discovery of novel antifungal drugs. Creative Biolabs has successfully launched an innovative antifungal drug discovery platform with customized services to discover antifungal drugs and understand the mechanism of action. Here is an introduction about protein elongation factors (EF2), which can be served as potential targets for antifungal drug discovery.
Introduction of Protein Elongation Factors
EF2 promotes translocation, such as displacement of nascent peptidyl-tRNA from the A site to the P site and movement of the ribosome along the mRNA, all of which are accompanied by a conformational change in the ribosome from the pretranslocational to the posttranslocational state. The protein sequence of EF2 has been highly conserved throughout evolution, while Saccharomyces cerevisiae EF2 sharing 66% identity and 85% homology to human EF2. Despite this high degree of similarity, a class of tetracyclic diterpene glycoside natural products, the sordarins, have now been identified as selective inhibitors of EF2 function in fungal protein synthesis.
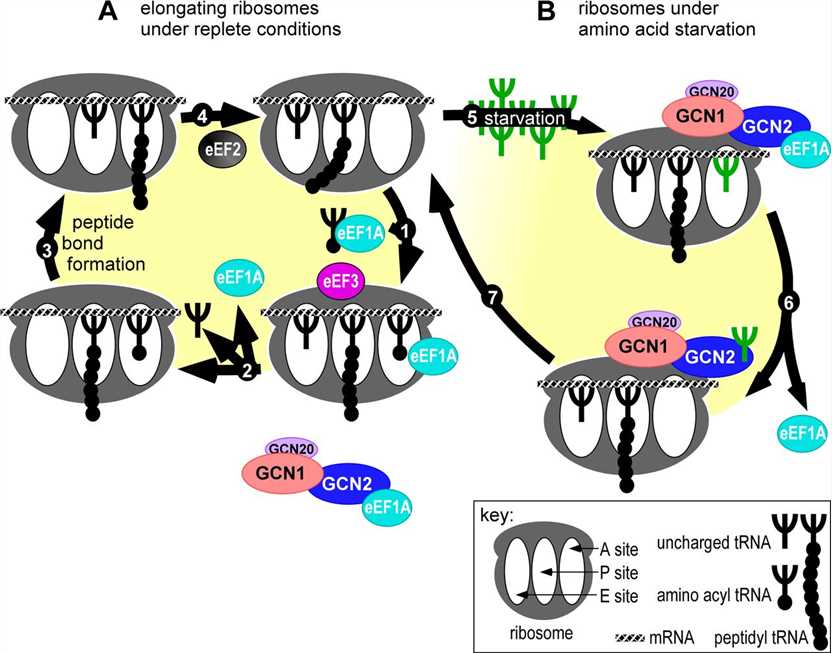 Fig. 1 Model for sensing amino acid starvation during the translation elongation cycle.1
Fig. 1 Model for sensing amino acid starvation during the translation elongation cycle.1
Protein Elongation Factors as Antifungal Drug Targets
Sordarin belongs to a class of natural products with multiple functional groups readily accessible to chemical modification. EF2 from different sources is able to display different conformations depending on whether it is alone or interacting with GTP, GDP, or a ribosome in either the pre- or the posttranslocational state. This conformational flexibility provides its biological properties and may be the reason that explains how such a conserved protein can be the primary target of such very selective antifungal drugs as sordarins. This fact might also lead to a revision of the idea that the prediction of the apparent selectivity of a new antifungal target can be based solely on its primary structure.
The addition of this class to the small number of known EF2 inhibitors (fusidic acid family, ADP-ribosylators, both universal for eukaryotic translocation) provides a powerful new tool for dissecting the EF2 and ribosomal sites involved in translocation. Furthermore, the ability to inhibit protein synthesis specifically in fungi with sordarin demonstrates the potential for exploiting EF2 as a target for developing novel antifungal agents at a time when resistance to current agents is increasing.
With the help of our well-established technologies and experienced scientists, Creative Biolabs provides various antifungal drug discovery services. We provide very flexible options for each specific case. We are happy to make it accessible to all kinds of research and industrial customers. Please do not hesitate to contact us for more information.
Reference
- Visweswaraiah, J.; et al. Overexpression of eukaryotic translation elongation factor 3 impairs Gcn2 protein activation. J Biol Chem. 2012, 287(45):37757-68. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
