Sulfite Reductase
Due to the increasing prevalence of risk factors such as immunosuppressive therapy, AIDS, and indwelling catheters, the incidence of fungal infection has continued to be increased. To solve the problem, the discovery of novel antifungal drugs with new modes of action has aroused great interests of both researchers and patients. As always focused on the spotlight of drug discovery, Creative Biolabs now provides target identification and validation services, especially for sulfite reductase as a potential target.
Sulfite Reductase
The sulfite reductase, which is also known as assimilatory sulfite reductase, assimilatory-type sulfite reductase, or hydrogen-sulfide:(acceptor) oxidoreductase, is primarily found in archaea, bacteria, fungi, and plants. It belongs to the oxidoreductase family and is grouped as either assimilatory or dissimilatory sulfite reductases according to their function, spectroscopic properties, and catalytic properties. The sulfite reductase plays a role in selenoamino acid metabolism and sulfur assimilation. This enzyme is responsible for catalyzing the reduction of sulfite to hydrogen sulfide and water.
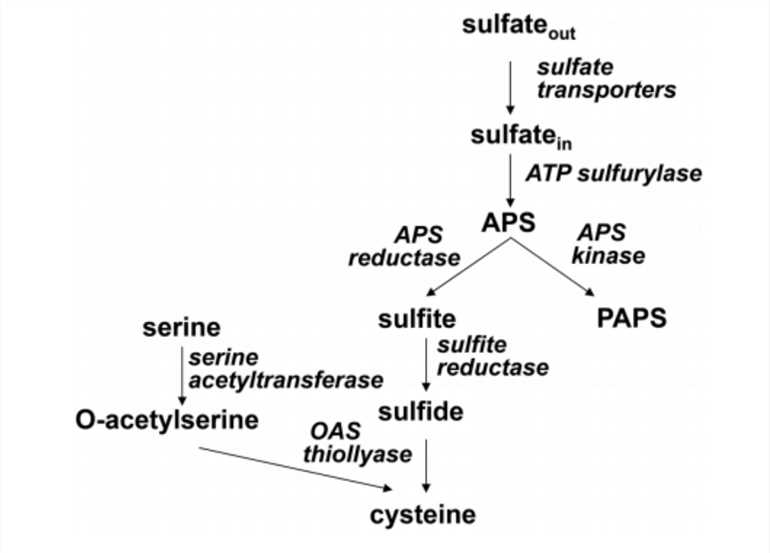 Fig.1 Scheme of sulfate assimilation.1
Fig.1 Scheme of sulfate assimilation.1
Sulfite Reductase as a Target for Antifungal Drug Discovery
Sulfite reductase is involved in the sulfate assimilation pathway, which is not essential for the fungi since fungal organisms can utilize by the availability of methionine from the environment. The process of cysteine synthesis and methionine synthesis in fungi calls for cellular uptake and reduction of sulfate to sulfide which is assimilatory in nature. The sulfate assimilation pathway in fungi is the mechanism that is involved in the cellular regulation of amino acid metabolism and interference of amino acid transport.
One of the antifungal compounds, azoxybacilin, shows a broad spectrum of antifungal activity and was proposed to inhibit the sulfate assimilation (SA) pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Azoxybacilin has also proved to have a unique mode of action in which it exhibited antifungal activity through inhibiting enzyme expression, decreasing the syntheses of both mRNA and enzymes from the genes for SA, especially the induction of sulfite reductase. Obviously, sulfite reductase is a potential target for antifungal drug discovery.
Why Choose Us?
With years of experience, Creative Biolabs is able to provide the state-of-art services for any antifungal projects with target identification services. Our scientists specialized in antifungal studies will work with you to develop the most appropriate strategy to meet your requirements. Now, we provide the best strategy and protocols for the antifungal drug discovery project, especially for Fungal Nucleic Acid and Protein Biosynthesis Targets, including:
In addition to the identification of potential targets for antifungal drug discovery, you might be also interested in other services for Potential Targets for Antifungal Drug Discovery listed below:
If you have any special needs in discovering potential targets for antifungal drugs or be interested in learning more about our antifungal drug discovery services, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. Molecular mechanisms of regulation of sulfate assimilation: first steps on a long road. Frontiers in plant science. 2014, 5, p.589. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
