Ascetic Cell-derived Exosomes (AEX)-based Vaccines
Introduction Applications Others Services FAQs
Introduction of Ascetic Cell-derived Exosomes (AEX)
Ascites an abnormal and persistent collection of fluid in peritoneal cavity develops as a result association between a plethora of physical and biological causes from the main disease condition. These are components of: vascular permeability increase; impaired lymphatic drainage and tumor-induced inflammation cascades. Combined, they form a disease-promoting ecology of cellular and acellular entities that synergistically propagate disease through autocrine/paracrine circuits. Multiple lines of communication between the different cellular components (e.g. tumor cells, immune and stromal cells) is in progress within this dynamic fluid. These are mediated by soluble mediators like cytokines, chemokines, growth factors and metabolites as well as active exosome secretion and uptake, mostly coming from the paracrine/autocrine type.
Ascitic cell-derived exosomes (AEX) are exogenous nano-size vesicles derived from ascitic fluid of cancer patients as essential transitory platform for bioactive molecules. Exosomes carry the molecular hallmarks of their parent cells, that is, DNA and RNA species (e.g. mRNAs, miRNAs) as well as a whole spectrum of proteins and other molecules including heat shock proteins [HSPs], adhesion molecules, or oncogenic factors. Because of their structural stability and permeability across biological barriers, AEX are thus disseminated systemically functioning as long-range messengers for intercellular tumor-non-tumor cell communication. Taken up by target cells, exosome cargo may cause phenotypic alterations, gene expression changes and regulate critical signaling pathways, principally the ones involved in the growth, invasion and metastasis enabling processes immune surveillance as well as drug resistance.
Importantly Exosomes also have a major function in modulating the immune system. Evidence exists that AEX sequester a multitude of immunomodulatory molecules among which are MHC proteins, co-stimulatory molecules and immunosuppressive factors such as PD-L1 and TGF-ß. They are frequently encumbered with antigens that are tumor-associated for example carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) which in some circumstances may enable immune recognition while in others lead to immune tolerance. The increasing awareness for their important steps in both cancer progression and immune regulation make AEX prime vectors and immunotheranostics. Profiling their molecular composition and functional mechanisms may help in the further development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for malignant ascites as well as its induced cancers.
Creative Biolabs offers Exosome Isolation Services including techniques like size exclusion chromatography (SEC), ultracentrifugation, and ultrafiltration to obtain high-quality AEX for research and therapeutic purposes. In addition, we offer a variety of exosome extraction kits for customers to perform their own extractions.
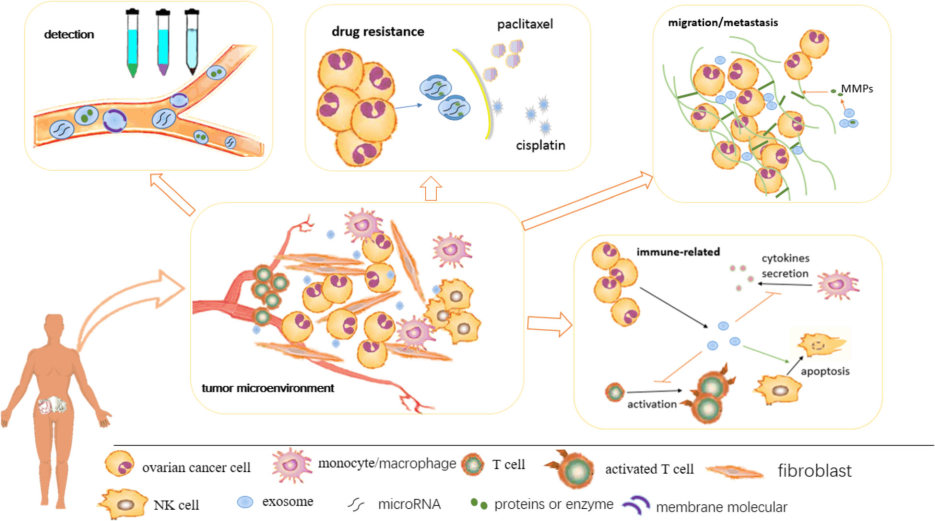 Fig.1 A summary of the roles of exosomes in ovarian cancer.1
Fig.1 A summary of the roles of exosomes in ovarian cancer.1
Application of Ascetic Cell-derived Exosomes (AEX)-based Vaccines
Exosomes carry diverse cellular proteins that vary depending on their origin, some of which differ from typical plasma membrane proteins. These include MHC molecules, transmembrane proteins, adhesion molecules, and metalloproteinases. Emerging research indicates that AEX (ascitic cell-derived exosomes) could serve as a novel nanoscale immunotherapy for cancer, potentially enhancing the immune system's ability to target and destroy tumor cells. Supporting this concept, a phase I clinical trial in colorectal cancer investigated autologous AEX vaccination in 40 advanced-stage patients. Participants received weekly subcutaneous injections for four weeks, either with AEX alone or in combination with recombinant GM-CSF. The findings demonstrate that AEX vaccination is feasible, safe, and well tolerated.
Through our exosome profiling services, related items including exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR analysis, exosomal protein isolation and profiling, and exosomal cytokines profiling, Creative Biolabs provides the tools to analyze and characterize AEX cargo, ensuring high-quality vaccine development.
Other Exosome Vaccine Options at Creative Biolabs
Recent years have seen remarkable progress in cancer immunotherapy. Among emerging approaches, AEX-based vaccines demonstrate significant potential for treating various tumors. Their successful development would add a powerful new weapon against cancer. Beyond AEX vaccines, researchers have also developed immunotherapy vaccines using tumor cell-derived exosomes (TEX) and vaccines using dendritic cell-derived exosomes (DEX).
Exosome Vaccine Development Services from Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs offers exosome cargo loading services and exosome modification services in terms of targeting and phagocytosis evasion to modify exosomes to target specific tumor types or enhance immune responses. we also provide exosome quantification and exosome characterization services through methods like nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), transmission electron microscope (TEM), and western blotting/nano-flow cytometry/ELISA to ensure that AEX meets stringent quality standards.
For more information, please feel free to contact us.
FAQs
Q: What are Ascitic Cell-derived Exosomes (AEX)?
A: Ascitic Cell-derived Exosomes (AEX) are bioactive extracellular vesicles released from ascites cells, loaded with many bioactive molecules including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They are fundamental mediators of intercellular communication and regulators immune responses. AEX have the inborn trait of cargo natural antigen and very good biological properties that could unravel a huge potential in cancer vaccine.
Q: Key advantages of AEX in vaccine development?
A: As AEX naturally contain a large set of tumor-specific antigens that practically activate host-specific immune response and can enhance anti-tumor immunity. They exhibit high biocompatibility, minimal immunogenicity and ideal in vivo distribution, which makes them feasible for the next generation vaccines.
Q: AEX based vaccine development support you can give?
A: From bioengineering system´s efficiency, we provide complete solution (AEX isolation, purification; characterization and omics profiling; engineered modification; functional validation) for AEX-based vaccine research & development of unbiased third-party parties.
Q: The isolated AEX has to be of high purity and activity in physiological condition, how is that done?
A: Depending on the characteristics of the samples, isolation recommendations with respect to the best methods to be used; ultracentrifugation, ultrafiltration, tangential flow filtration or size exclusion chromatography. We ensure that isolated AEX samples will be of high purity, undamaged structure and remarkable biological activity, keeping their native functions with stringent quality control settings in place.
Q: What is available through your services for AEX characterization and analysis?
A: We provide nano tracking number analysis (NTA) on size and concentration, TEM morphology, isolation of exosomal markers Western/bioimmunoassay as well as omic analyses like proteomics, lipid/ metabolite profiling and RNA profiling for high throughput.
Q: Can you perform functional alterations on AEX or not?
A: Yes; AEX we have different types of engineering approach such as genetic modification, surface molecule engineering and carrier ligand engineering to improve the targeting to AEX and deliver therapeutic small molecules also support customized vaccine development therapeutics application
Q: You offer both in vivo functional validation services for AEX-based vaccine, correct?
A: We provide both in vitro and in vivo functional validation services, including uptake studies in recipient cells, assessment of recipient cell viability, proliferation, and migration, in vivo biodistribution studies in small animal models, tumor model establishment, and evaluation of anti-tumor efficacy, comprehensively supporting AEX vaccine development programs.
Reference
-
Li, Xiaoduan, and Xipeng Wang. "The emerging roles and therapeutic potential of exosomes in epithelial ovarian cancer." Molecular cancer 16 (2017): 1-10. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 A summary of the roles of exosomes in ovarian cancer.1
Fig.1 A summary of the roles of exosomes in ovarian cancer.1









