Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Dental Pulp Injury Repair
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
The Dawn of Exosome-Based Regenerative Therapies for Dental Pulp
Dental pulp injury, frequently stemming from deep caries, traumatic incidents, or various restorative dental procedures, presents a significant and persistent challenge within the field of dentistry. Historically, the standard therapeutic approach has often involved root canal therapy, a procedure that, while effective in alleviating pain and addressing infection, necessitates the removal of the vital pulp tissue. This devitalization of the tooth subsequently compromises its natural defense mechanisms, sensory capabilities, and long-term vitality. The prevailing paradigm in contemporary dentistry, however, is increasingly shifting towards the preservation of pulp vitality and the active promotion of its regeneration. This evolving focus aims to restore the tooth's intrinsic function, sensation, and overall long-term health, underscoring a critical and previously unmet need for advanced, biologically-driven regenerative solutions capable of truly restoring damaged pulp tissue.
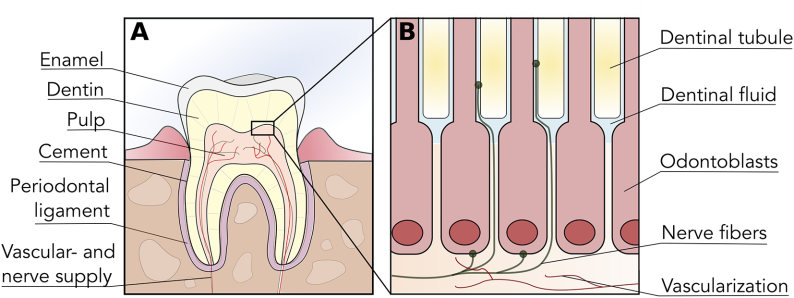 Fig.1 Tooth and dental pulp anatomy.1,3
Fig.1 Tooth and dental pulp anatomy.1,3
In response to this imperative, exosomes have emerged as a revolutionary "cell-free" approach to regenerative medicine, offering a compelling and sophisticated alternative to the inherent complexities and limitations often associated with direct stem cell transplantation. These nanoscale biological messengers are naturally secreted by virtually all eukaryotic cells, including a diverse array of stem cells. Their significance as a transformative therapeutic modality stems from their unique characteristics and profound biological capabilities.
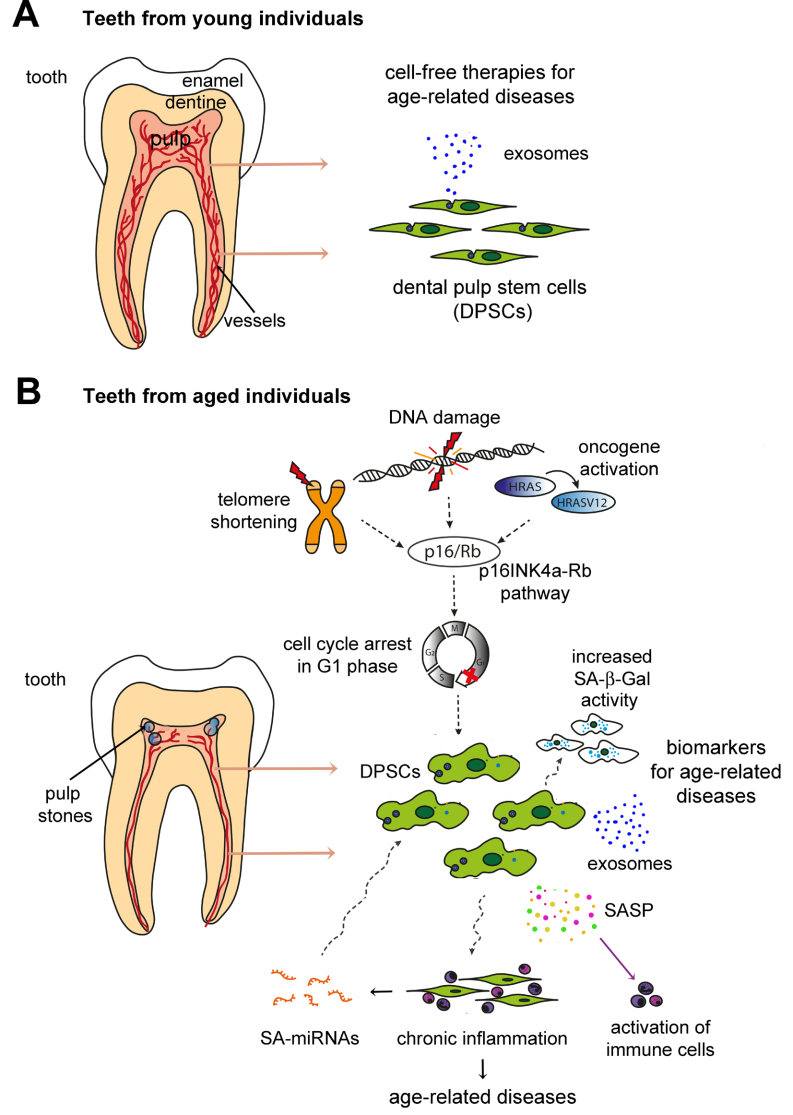 Fig.2 Schematic representation showing the effects of ageing in the dental pulp tissue.2,3
Fig.2 Schematic representation showing the effects of ageing in the dental pulp tissue.2,3
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of exosome research and development, providing comprehensive services that span the entire spectrum from fundamental discovery and meticulous characterization to advanced therapeutic application. The organization's deep expertise in stem cell-derived exosomes positions it as a premier partner for developing innovative and highly effective solutions specifically tailored for dental pulp injury repair.
Properties of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Nature's Nanocarriers for Repair
The inherent therapeutic power of exosomes is fundamentally rooted in their diverse and complex molecular cargo. This cargo is not randomly assembled but rather precisely reflects the specific molecular profile and physiological state of their parent cells. This rich payload includes:
Proteins
A wide array of proteins, encompassing general exosome markers (e.g., CD9, CD63, and CD81, frequently used for identification) and a multitude of functional proteins unique to the originating cell type, which dictate specific biological activities.
Nucleic Acids
A rich assortment of genetic material, critically including microRNAs (miRNAs), messenger RNAs (mRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and even fragments of DNA. These nucleic acids are pivotal in regulating gene expression and influencing the cellular activity and function of recipient cells.
Lipids
Various lipids that contribute not only to the structural integrity and stability of the exosomal membrane but also play significant roles in cellular signaling pathways.
Specific Focus: Dental Pulp Injury Repair
The intrinsic properties and broad regenerative capabilities of stem cell-derived exosomes make them exceptionally well-suited for the complex challenges of dental pulp injury repair.
Exosomes can contribute to dental pulp repair through several key mechanisms:
 Dentinogenesis
Dentinogenesis
Exosomes can deliver specific miRNAs and proteins that promote the differentiation of resident dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) or other pulp progenitor cells into odontoblast-like cells. These newly differentiated cells are crucial for producing new dentin (tertiary dentin or reparative dentin), which is critical for repairing damaged dentin and forming a protective barrier against external stimuli. This is a direct extension of their demonstrated ability to induce osteogenic differentiation, given the similar developmental and regenerative pathways of dentin and bone.
 Pulp Revascularization and Angiogenesis
Pulp Revascularization and Angiogenesis
The potent pro-angiogenic factors carried within exosomes can stimulate the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis) within the injured pulp tissue. Restoring a robust blood supply is absolutely essential for delivering nutrients and oxygen, removing waste products, and supporting the survival and regeneration of pulp cells.
 Inflammation Modulation
Inflammation Modulation
Exosomes possess significant immunomodulatory properties , enabling them to actively reduce the inflammatory response that typically accompanies pulp injury. By dampening excessive inflammation, exosomes help to create a more favorable and less hostile microenvironment for healing, preventing further tissue damage and promoting regenerative processes.
 Cell Survival and Proliferation
Cell Survival and Proliferation
Through the delivery of anti-apoptotic and pro-proliferative signals, exosomes can protect existing pulp cells from death and stimulate the proliferation of resident stem cells and other reparative cells. This dual action contributes significantly to overall tissue repair and the regeneration of a functional pulp.
 Recruitment of Endogenous Stem Cells
Recruitment of Endogenous Stem Cells
Beyond direct cellular effects, exosomes may also act as chemoattractants, guiding and recruiting endogenous stem cells and progenitor cells from surrounding tissues or circulation to the site of injury. This recruitment further amplifies the inherent regenerative capacity of the dental pulp, building on their role in intercellular communication and cell migration.
To further explore these mechanisms, Creative Biolabs provides exosomal RNA isolation and qPCR analysis services, enabling researchers to quantify key regulatory RNAs. Our exosome profiling services, including exosomal protein isolation and profiling service, can help identify bioactive molecules involved in pulp regeneration. These tools are essential for advancing the understanding of DPSC-Exos in dental pulp repair.
Creative Biolabs Capabilities
From the above content, it can be known that exosomes derived from stem cells can promote the regeneration and repair of dental pulp tissue. This suggests that exosomes derived from stem cells have good research significance in the future treatment of dental pulp injury repair. At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to advancing this field through our extensive range of exosome-related services. Our capabilities include:
Isolation
Characterization
Profiling
Validation
Exosome Isolation
Utilizing advanced exosome isolation and purification techniques to obtain high-purity exosomes.
Exosome Characterization
Employing nanoparticle tracking analysis, transmission electron microscopy, and western blotting, which are known as the three gold standard technologies, for detailed characterization analysis.
Exosome Validation
Conducting in vitro and in vivo functional services to validate exosome efficacy and safety in disease models.
If you are interested in developing new exosome-based strategies for dental pulp injury repair or other nerve tissue injuries, contact us today. Leave your contact information and specific intentions, and our professional scientific consultants will reply promptly to assist you.
FAQs
Q: What makes stem cell-derived exosomes superior to direct stem cell transplantation for dental pulp repair?
A: Exosomes offer a "cell-free" advantage, eliminating concerns like immunogenicity, tumorigenicity, and complex handling of live cells. They are stable, can cross biological barriers, and deliver cargo precisely, making them a safer and more scalable option for dental pulp repair.
Q: How do exosomes promote dental pulp regeneration specifically?
A: Exosomes carry bioactive molecules that stimulate pulp cell proliferation, migration, and odontogenic differentiation (for new dentin). They also promote angiogenesis for revascularization and exert anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, creating a favorable environment for healing and functional restoration.
Q: How does Creative Biolabs ensure the quality and consistency of its exosome products?
A: We ensure quality through rigorous, multi-faceted characterization techniques at every stage, including TEM, NTA, ELISA, Western blot, and cargo analysis. Our adherence to robust Quality Control protocols and facilitation of GMP-compliant production pathways ensure reliable, reproducible, and high-quality exosome batches.
References
-
Schuh, Christina M A P et al. "Potential Novel Strategies for the Treatment of Dental Pulp-Derived Pain: Pharmacological Approaches and Beyond." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 10 1068. 18 Sep. 2019, doi:10.3389/fphar.2019.01068.
-
Iezzi, I et al. "The effects of ageing on dental pulp stem cells, the tooth longevity elixir." European cells & materials vol. 37 175-185. 26 Feb. 2019, doi:10.22203/eCM.v037a11.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Tooth and dental pulp anatomy.1,3
Fig.1 Tooth and dental pulp anatomy.1,3
 Fig.2 Schematic representation showing the effects of ageing in the dental pulp tissue.2,3
Fig.2 Schematic representation showing the effects of ageing in the dental pulp tissue.2,3









