Stem Cell-derived Exosome Applications
- Nerve Tissue Injury Repair
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Harnessing Stem Cell-derived Exosomes for Neural Tissue Regeneration
Stem cells (SCs) contribute fundamentally to tissue maintenance and regeneration due to their intrinsic capabilities for long-term proliferation and differentiation into diverse cell types. Yet despite their therapeutic appeal, direct stem cell transplantation faces persistent barriers, including the risk of tumorigenicity, immunogenic reactions, and cellular heterogeneity. Increasing evidence suggests that the regenerative benefits traditionally attributed to stem cell engraftment may, in fact, be largely mediated by paracrine mechanisms—most notably through the release of exosomes.
Stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos) are nanosized extracellular vesicles enriched with bioactive molecules reflective of their parent cells. As a cell-free modality, these nanoscale vesicles enable regenerative treatments with notable benefits, such as improved safety and ease of delivery. Encapsulated within a lipid bilayer, SC-Exos protect labile signaling molecules—including proteins, RNAs, and lipids—from enzymatic degradation. Moreover, exosomes exhibit natural tropism and can traverse biological barriers such as the blood-brain barrier via transcytosis, expanding their potential for use in central nervous system (CNS) disorders. At Creative Biolabs, we recognize the significant promise that stem cell-derived exosomes hold for neural tissue regeneration and have devoted considerable effort to advancing related research and services. To support this research, we offer one-stop exosome services, including exosome isolation, exosome purification, and exosome characterization, to ensure high-quality exosome preparation and analysis for nerve repair studies.
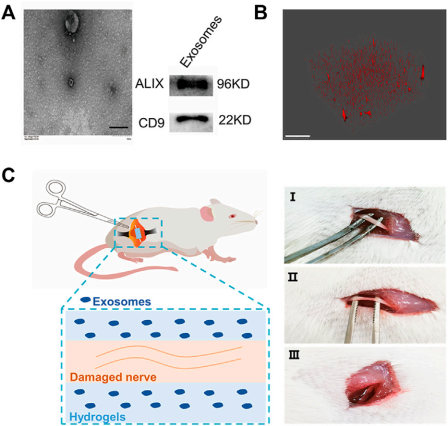 Fig.1 Hydrogel-loaded exosomes for the treatment of sciatic nerve injury.1
Fig.1 Hydrogel-loaded exosomes for the treatment of sciatic nerve injury.1
Properties: How SC-Exos Support Neural Tissue Repair
Emerging data from both preclinical and translational research points to the multifaceted roles SC-Exos play in neural tissue repair:
-
Enhancement of Neuronal Survival and Proliferation
SC-Exos are enriched with neurotrophic factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), which promote survival, proliferation, and differentiation of neural progenitor cells.
-
Promotion of Axonal Regeneration and Synaptogenesis
Axonal regrowth and synaptic remodeling are essential for functional neural recovery. SC-Exos deliver miRNAs and proteins that upregulate regenerative signaling pathways, enhancing axon elongation and promoting synapse formation.
-
Modulation of the Inflammatory Microenvironment
Following CNS injury, activated microglia and infiltrating immune cells amplify inflammation, exacerbating neural damage. SC-Exos can suppress pro-inflammatory responses and promote microglial polarization toward an anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype through the delivery of miR-21, miR-146a, and other immunomodulatory cargoes.
-
Stimulation of Endogenous Cell Migration
Components within SC-Exos, including chemokines and integrin ligands, can direct the migration of neural stem cells or progenitor cells toward sites of injury, facilitating endogenous repair mechanisms.
Together, these synergistic actions have been shown to reverse neuronal damage and accelerate the restoration of neurological functions in diverse preclinical models.
Applications Across Neural Injury Types
The therapeutic potential of SC-Exos has been explored across a wide spectrum of neural injuries, each presenting unique pathological challenges:
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a wide array of technical platforms to support these applications, including exosome profiling (RNA/protein analysis), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), western blotting, and nano flow cytometry analysis. These services ensure that exosomal cargo and surface characteristics are thoroughly characterized, facilitating reliable downstream applications.
From Bench to Application: Creative Biolabs ' Full-Service Support
SC-Exos are increasingly viewed as a transformative platform for neuroregenerative medicine. Their nanoscale size, low immunogenicity, biological cargo, and inherent tissue-homing abilities make them uniquely suited to treating complex neurological injuries. One of the most exciting frontiers in SC-Exo research is the customization of exosomes for targeted delivery. Using advanced bioengineering approaches, Creative Biolabs enables the surface modification of SC-Exos with peptides, antibodies, or aptamers that guide them to specific neural tissue types or injury sites. We also offer cargo-loading services to encapsulate therapeutic miRNAs, proteins, or small molecules into SC-Exos, enhancing their reparative capacity.
To ensure maximum translational utility, we provide solutions for improving exosome uptake and persistence in vivo and engineering for phagocytosis escape. Whether your goal is to optimize delivery to the spinal cord, retina, or peripheral nerves, our team can help design and execute a bespoke strategy. Contact us to help initiate or carry out your exosome-related projects and explore the full potential of SC-Exos in nerve repair.
FAQs
Q: What makes exosomes derived from stem cells a preferable alternative to conventional cell-based therapies?
A: SC-Exos offer many of the therapeutic benefits of stem cells—such as tissue repair, immune modulation, and regeneration—without the risks associated with whole-cell therapies, including tumorigenicity, immune rejection, and differentiation variability. Thanks to their nanoscale dimensions and lipid bilayer composition, exosomes can penetrate challenging physiological barriers—including the blood-brain barrier—facilitating targeted intervention in neurological disorders.
Q: Are SC-Exos capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
A: Yes. One of the unique advantages of exosomes is their ability to traverse the BBB via transcytosis, allowing for the delivery of therapeutic cargo to the central nervous system—something that many conventional drugs cannot achieve.
Q: How does Creative Biolabs support SC-Exos research in neural repair?
A: We offer a full suite of one-stop exosome services, including:
-
High-yield exosome isolation from stem cell cultures
-
Comprehensive characterization services (e.g., NTA, TEM, Western blotting, flow cytometry)
-
Profiling services for RNA, protein, lipid, and metabolite
-
Exosome engineering, including cargo loading and disease-targeted modifications
-
In vitro and in vivo functional studies to validate therapeutic potential
Q: What types of stem cells are available for SC-Exos research at Creative Biolabs?
A: Our expertise spans exosome isolation from a wide array of stem cell sources, such as MSCs, NSCs, iPSCs, among others, tailored to meet the specific requirements of each research context. Each stem cell source has unique properties suited to different neurological repair contexts.
Q: Can SC-Exos be customized for targeted delivery to neural tissues?
A: Absolutely. Our exosome engineering services allow for targeted surface modification, enabling SC-Exos to home in on specific tissues or injury sites. This includes strategies to enhance blood-brain barrier penetration or neural cell targeting.
Q: How can I evaluate the function of my SC-Exos preparation?
A: Creative Biolabs provides in-depth functional evaluation services. These include in vitro assays (e.g., neuroprotection, neurite outgrowth, cytokine inhibition) and in vivo models (e.g., spinal cord injury, optic nerve damage) to assess efficacy in relevant biological systems.
Reference
-
Liu, Zhixiao et al. "Low-Stiffness Hydrogels Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Through the Rapid Release of Exosomes." Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology vol. 10 922570. 23 Jun. 2022, doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.922570. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Hydrogel-loaded exosomes for the treatment of sciatic nerve injury.1
Fig.1 Hydrogel-loaded exosomes for the treatment of sciatic nerve injury.1









