Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Optic Nerve Injury Repair
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Unlocking the Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes for Optic Nerve Injury (ONI)
The optic nerve, formed by the axons of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), serves as the critical communication pathway between the eye and the brain, transmitting visual signals necessary for sight. Damage to the optic nerve (ON), whether from mechanical trauma, elevated intraocular pressure, ischemic events, neoplastic compression, or inflammatory disorders, can disrupt this essential pathway and result in irreversible vision loss. The central nervous system's limited regenerative capacity, coupled with inhibitory molecular signals and glial scarring, poses a formidable challenge to repairing the injured optic nerve. In many cases, patients suffering from ON damage face not only visual impairment but also substantial emotional and functional burdens.
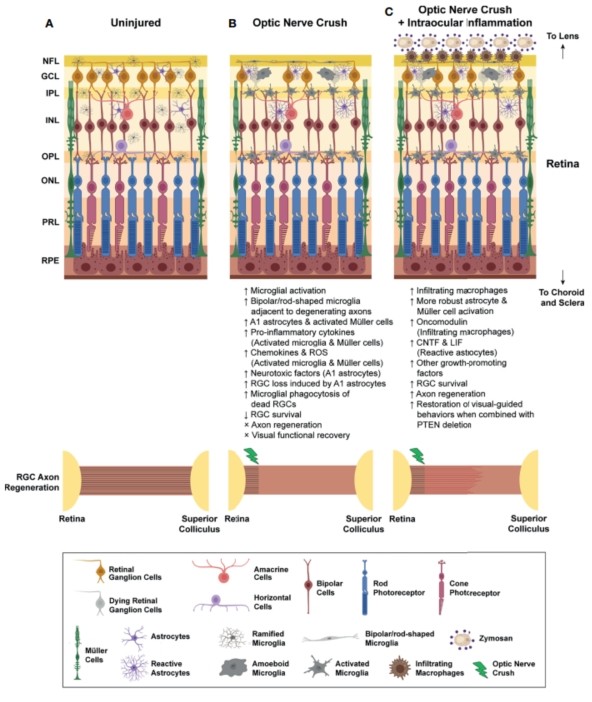 Fig.1 Inflammatory responses after optic nerve crush (ONC) injury.1
Fig.1 Inflammatory responses after optic nerve crush (ONC) injury.1
A key therapeutic objective in this context is to preserve surviving RGCs, promote their regenerative capacity, and modulate the hostile microenvironment at the lesion site. In recent years, researchers have turned their attention to stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos), which offer a promising, cell-free alternative to traditional stem cell therapy. As nanoscale vesicles enriched with proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, SC-Exos inherit the regenerative and immunomodulatory properties of their parent cells. These vesicles can traverse biological barriers, such as the blood-retinal barrier, and deliver functional cargo to target tissues. Creative Biolabs has carefully curated and analyzed recent findings on SC-Exos in ON repair and offers advanced technical services to support this emerging area of research. Our exosome profiling services, exosome proteomic services, exosome RNA sequencing services and exosome lipidomics & metabolomics services can help researchers identify key molecules involved in ONI repair.
SC-Exos in Optic Nerve Injury: Mechanistic Insights
Multiple lines of evidence have demonstrated the ability of SC-Exos to improve outcomes in ONI models via diverse mechanisms:
-
Anti-apoptotic activity: SC-Exos protect RGCs from apoptosis by modulating intrinsic signaling pathways and suppressing pro-apoptotic molecules such as caspase-3.
-
Immunomodulation: Exosomal miRNAs and proteins influence macrophage and microglial polarization, shifting the inflammatory milieu toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype.
-
Neurotrophic support: SC-Exos deliver growth factors and neuroprotective molecules that enhance RGC survival and sustain retinal homeostasis.
Creative Biolabs provides robust platforms for exploring these mechanisms, including proteomic and transcriptomic profiling of exosomal cargo, to uncover the molecular mediators driving therapeutic effects.
Research Results of Exosomes Derived from Different Stem Cells in Repairing ONI
Several types of SC-Exos have been evaluated in ONI animal models:
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes (MSC-Exos): In a rat ON crush model, intravitreal injection of autologous MSC-Exos led to increased RGC survival and reduced expression of apoptosis-related genes. Moreover, there was a noticeable increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines, highlighting the immunoregulatory potential of these vesicles.
-
Umbilical Cord MSC-Exos (UMSC-Exos): In a model of chronic ocular hypertension, UMSC-Exos improved RGC viability and reduced caspase-3 activity. Notably, UMSC-Exos stimulated activation of GFAP+ glial cells, which may support neuroprotection without promoting detrimental gliosis. To validate such findings, Creative Biolabs offers exosomal protein isolation and profiling services, helping researchers pinpoint key proteins associated with neuroprotective functions.
-
Gingiva-Derived MSC-Exos (GMSC-Exos): Following stimulation with TNF-α, GMSCs release exosomes rich in miR-21-5p. This miRNA has been implicated in promoting anti-inflammatory signaling and protecting RGCs from oxidative and apoptotic stress. Creative Biolabs supports these investigations through exosomal miRNA sequencing service and exosomal whole transcriptome sequencing service to decode the regulatory landscape of exosomal RNA.
While current studies predominantly focus on the survival of existing RGCs, challenges remain in promoting axonal regeneration and reconstructing the complete visual pathway. Nonetheless, SC-Exos represent a significant leap forward in developing targeted, minimally invasive therapeutics for ONI. Their biocompatibility, ability to modulate the immune response, and capacity to deliver therapeutic cargo across ocular barriers position them as highly attractive candidates for future clinical translation.
To further accelerate progress, Creative Biolabs offers exosome cargo loading services, enabling researchers to incorporate therapeutic molecules into exosomes before or after isolation. This allows for precise delivery of neuroprotective agents, anti-inflammatory compounds, or gene regulators directly to the ON injury site.
How Creative Biolabs Supports ONI Research
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to advancing exosome-based therapies for optic nerve injury and other neurological conditions. Our comprehensive suite of services includes:
Let 's unlock the full potential of SC-Exos together. Contact us today to discuss your project goals and learn how our exosome services can bring your ONI research to the next level.
FAQs
Q: How do SC-Exos differ from traditional stem cell transplantation in treating optic nerve injury?
A: Unlike live stem cells, SC-Exos are non-replicating, membrane-enclosed vesicles that carry bioactive molecules from their parent cells. They lack nuclei, minimizing the risk of tumorigenesis, immune rejection, and inappropriate differentiation. Moreover, their small size and endogenous membrane markers allow better penetration into tissues like the retina and optic nerve.
Q: Could SC-Exos be combined with other treatments, such as neuroprotective drugs or gene therapy, for better ONI outcomes?
A: Yes, combination strategies are being actively explored. SC-Exos can serve as delivery vehicles for drugs or nucleic acids, or be used alongside established neuroprotective agents to enhance efficacy. We offer customizable exosome engineering services, such as co-loading small molecules or gene regulation components into exosomes for synergistic ON repair.
Q: How are SC-Exos quantified and characterized before functional assays?
A: We use a combination of techniques:
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for concentration and size distribution
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for morphology
-
Western blot or flow cytometry for marker confirmation (CD9, CD63, CD81)
All characterization data is documented in a detailed report to support reproducibility and regulatory compliance.
Q: Which exosome isolation methods are most suitable for preserving the functional integrity of SC-Exos for ONI repair?
A: For functional studies, especially involving neural repair, we typically recommend ultracentrifugation followed by size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) to maintain structural and biochemical integrity.
Q: Do I need to supply my own stem cells, or can Creative Biolabs provide SCs for exosome production?
A: You should send us your proprietary stem cell lines (we will sign a confidentiality agreement). Exosome production will be carried out under standardized, serum-free or exosome-depleted conditions. We also accept the cell culture supernatant collected after your culture cells and provide you with the best exosome extraction technology.
References
-
Au, Ngan Pan Bennett, and Chi Him Eddie Ma. "Neuroinflammation, Microglia and Implications for Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration in Traumatic Optic Neuropathy." Frontiers in immunology vol. 13 860070. 4 Mar. 2022, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.860070. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Inflammatory responses after optic nerve crush (ONC) injury.1
Fig.1 Inflammatory responses after optic nerve crush (ONC) injury.1









