Custom Circular RNA (circRNA) Synthesis Service
Introduction
Linear RNA constructs face challenges in terms of stability and expression levels in preclinical and clinical studies. Our Custom Circular RNAs Synthesis Service addresses these via advanced enzymatic and ribozyme-based circularization, providing highly stable, long-lasting, efficiently translated circular RNAs. Custom-designed, high-purity, and application-optimized, it supports vaccine development, protein expression, and gene therapy, aiding progress from concept to clinic.
Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation
Custom Circular RNAs Synthesis Service
Once considered non-functional byproducts of gene transcription, circular RNAs (circRNAs) are now recognized as a widespread and functionally significant class of RNA molecules. Generated through a process called back-splicing, these covalently closed RNA loops are exceptionally stable, lacking the free 5' and 3' ends that are typically targeted by exonucleases. Their unique structure allows them to persist in cells far longer than their linear counterparts, making them ideal candidates for a wide range of therapeutic applications, from protein expression to vaccine development.
Design of messenger circRNA vectors
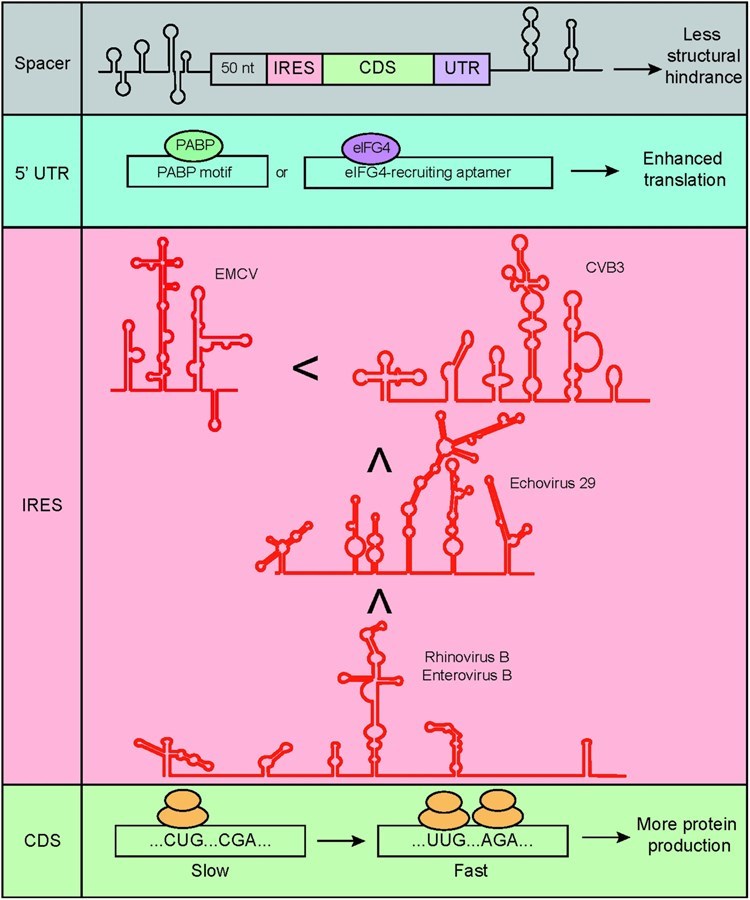 Fig.1 Rational design of circRNA sequences.1
Fig.1 Rational design of circRNA sequences.1
- Translation initiation element selection and optimization: Prioritize elements derived from CVB3, echovirus 29, human rhinovirus B, or enterovirus B for strong activity in pancreatic cancer cells. Enhance efficiency by inserting eIF4G-associated aptamers.
- Spacer design: to reduce structural hindrance, ensuring unimpeded ribosome recruitment.
- Minimizing RNA duplexes: Design sequences to avoid duplex formation, preventing PKR-mediated degradation, and maintaining circRNA stability.
- UTR optimization: Include UTRs with PABP binding sites, poly (A)/poly (AC) sequences, PABP motifs, and eIF4G-recruiting aptamers to boost translation and reduce immunogenicity.
- Codon optimization: Match codons to pancreatic cancer cell tRNA abundance; eliminate adverse base-pairing between the translation initiation element and coding sequences for efficient translation and proper folding.
- RBPs motifs introduction: Incorporate translation-enhancing RBPs motifs to elevate protein expression in pancreatic cancer cells.
Synthesis of Exogenous Circular RNAs (circRNAs)
Exogenous circRNA synthesis primarily involves two approaches: in vivo transcription and in vitro circularization, with specific strategies and characteristics as follows:
- In VivoTranscription
- Utilize introns from endogenously highly expressed circRNAs to mediate circularization via back-splicing. However, this may generate a mixture of circRNAs and linear RNAs, requiring construct optimization to enhance specificity.
- Introduce cis-acting elements or trans-acting factors to mimic natural splicing mechanisms, promoting splice site proximity and improving circularization efficiency.
- Construct vectors using viral promoters (e.g., CMV) and inverted repeats, or combine ribozymes for circularization. Note that some methods may leave residual "scar sequences."
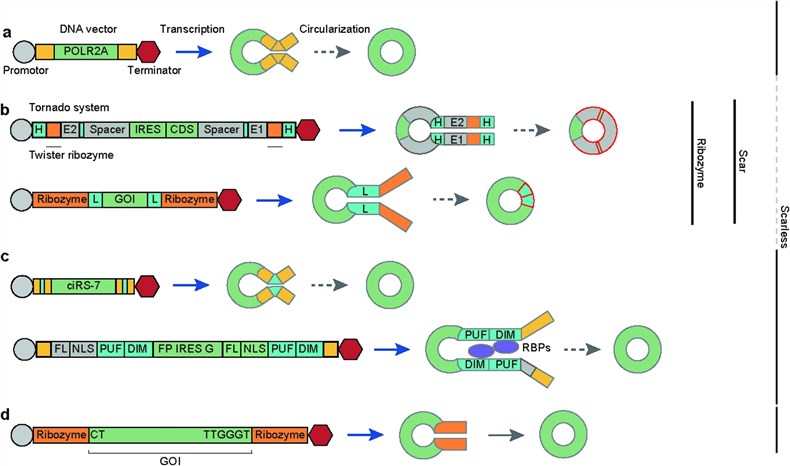 Fig.2 Types of endogenous and synthetic circRNA backbones.2
Fig.2 Types of endogenous and synthetic circRNA backbones.2
-
In Vitro Circularization
- Intron-based systems: Such as the permuted intron-exon (PIE) system, which employs group I self-splicing introns for circularization. Applicable both in vivo and in vitro, but may retain exogenous sequences.
- Scarless strategies: Avoid non-target sequence residues and reduce immunogenicity via rearranging exon sequences of T4 td introns, optimizing the D1 domain of group II introns, or utilizing the trans-splicing activity of Tetrahymena group I introns.
- Chemical/enzyme catalysis: Linear precursors are circularized via T4 DNA ligase, T4 RNA ligases, or chemical reagents. Suitable for short sequences but with low yield.
Workflow
-
Required Starting Materials:
- The target RNA sequence or a plasmid containing the desired gene sequence.
- Details of the intended application (vaccine development, protein expression, etc.).
- Any specific design constraints or optimization preferences (e.g., specific regulatory elements or modified nucleotides).
- Sequence Optimization & Plasmid Design: Expert analysis and optimization of sequences for stability and translation efficiency; design of optimal in vitro transcription plasmids.
- In Vitro Transcription: Linear RNA transcription from designed plasmids using a robust T7 system.
- Circularization: Efficient circularization via enzymatic ligation and ribozyme-mediated self-splicing, with a focus on scarless strategies for purity.
- Purification: Meticulous purification (e.g., HPLC) to remove linear RNA, enzymes, and impurities.
- Quality Control: Rigorous testing: gel electrophoresis, RNase R resistance, UV spectrophotometry, and sequencing to confirm identity and integrity.
-
Final Deliverables: Upon completion, you will receive:
- Purified, high-quality circular RNA molecules.
- A detailed Certificate of Analysis (CoA) outlining purity, concentration, and quality control results.
- A comprehensive Project Report summarizing the synthesis process, optimization strategies used, and a summary of all QC data.
- Estimated Timeframe: The typical timeframe for our synthesis service ranges from 6 to 10 weeks, depending on the complexity of the sequence and the level of optimization required. Rush services are available upon request.
What We Can Offer
Creative Biolabs is a leader in the synthesis of custom circular RNAs, providing a seamless, end-to-end service designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern biological research and therapeutic development.
Customized Design and Optimization
We provide a fully customized service, including sequence optimization to maximize yield and stability, as well as the design of expression systems tailored to your specific project needs.
High-Purity Synthesis
Our advanced enzymatic and ribozyme-based circularization methods, including scarless techniques, guarantee the production of highly pure circRNA, minimizing linear RNA contamination.
Robust Quality Control
We guarantee the stability and integrity of our products through a multi-step quality assurance process, including RNase R resistance testing and identity confirmation via sequencing.
Scalable Production
Our flexible platforms are designed to support your project at any scale, from small-scale R&D batches to large-scale, clinical-grade material.
Expert Technical Support
Our team of experienced scientists provides comprehensive technical consultation throughout the entire project, ensuring that your final product meets all specifications and is perfectly suited for its intended application.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Case Study
| Circularity of the RNAs | Microscopic imaging of the translation product |
|---|---|
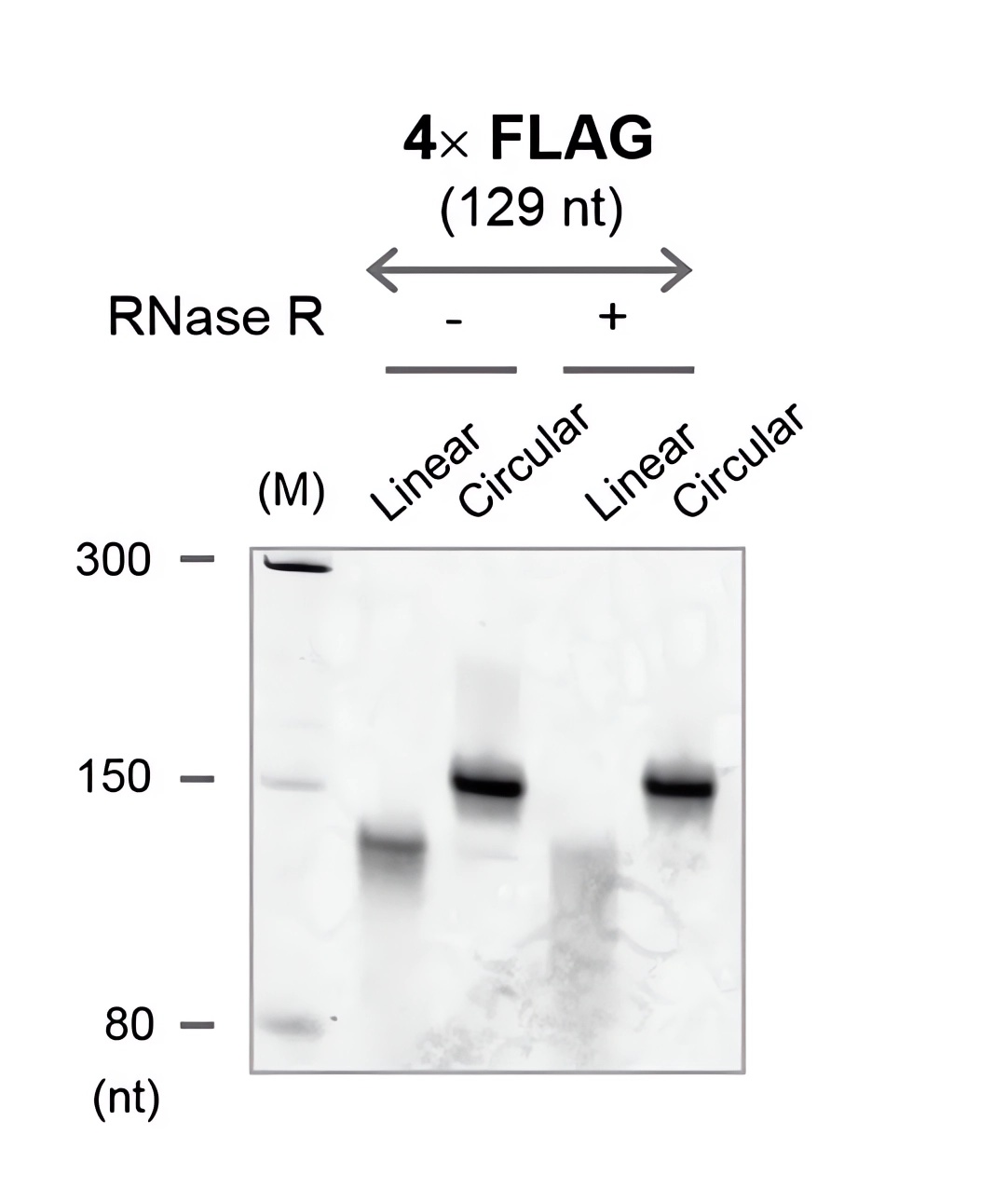
|
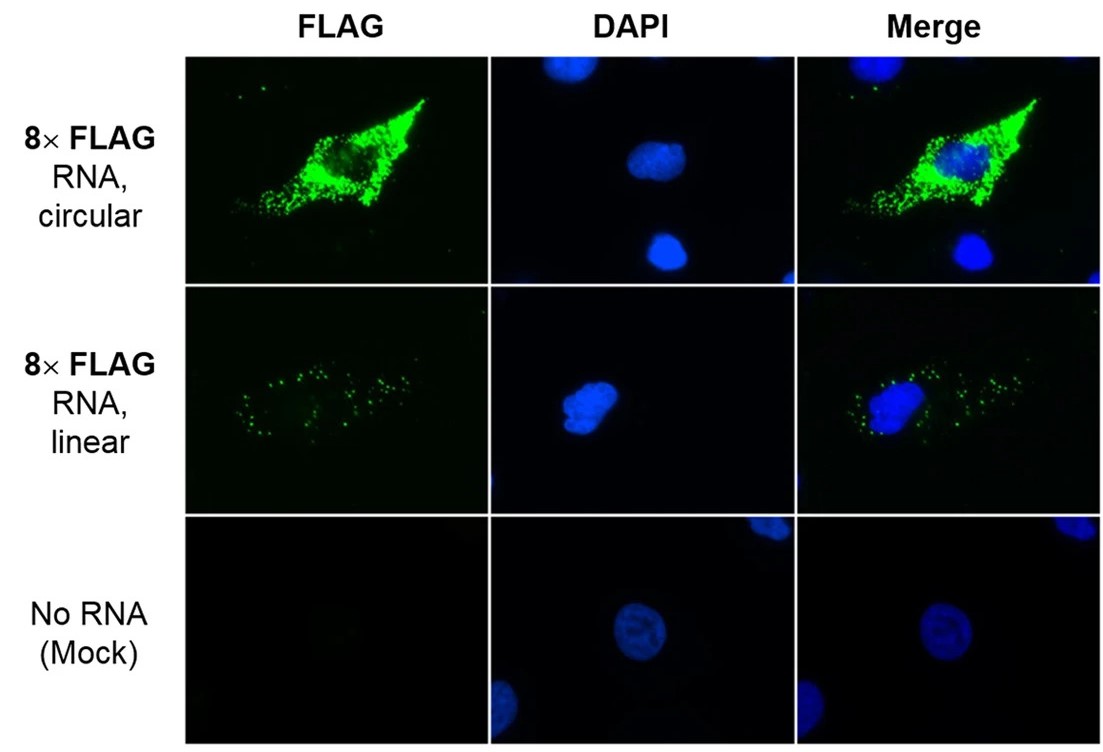
|
| Fig.3 RNA cyclization was verified using denatured PAGE.2 | Fig.4 The translation of circular RNA within cells was observed using an inverted fluorescence microscope.2 |
FAQs
How does circRNA's stability compare to linear mRNA?
Due to its closed-loop structure, circRNA is highly resistant to degradation by exonucleases. This gives it a significantly longer half-life compared to linear mRNA, leading to more durable and sustained protein expression within the cell.
Can circRNA be translated into a protein?
Yes. While circRNA was initially thought to be non-coding, research has shown that it can be efficiently translated into a protein. We can optimize your circRNA with IRES to ensure robust and cap-independent translation.
What is the purity of your synthesized circRNA?
We prioritize product purity through our rigorous purification and quality control protocols. We use advanced techniques like HPLC to ensure our circRNA products have minimal linear RNA contamination, which is critical for reducing off-target effects and maximizing efficacy in your experiments.
What are the key applications for your circRNA?
Our custom circRNA is a versatile platform with a wide range of potential applications, including vaccine development, gene therapy, and sustained protein expression. If you have a specific project in mind, we encourage you to contact us to discuss how our service can be tailored to meet your unique needs.
Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project
References
- Choi, Seo-Won, and Jin-Wu Nam. "Optimal design of synthetic circular RNAs." Experimental & Molecular Medicine 56.6 (2024): 1281-1292. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-024-01251-w. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Abe, Naoko, et al. "Rolling circle translation of circular RNA in living human cells." Scientific Reports 5.1 (2015): 16435. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16435. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, the pictures were cropped.
