Adenovirus Vector Titration Service
Adenovirus vectors have become crucial in the field of adenoviral vector-based vaccine, particularly in inducing strong systemic and mucosal immune responses. Adenovirus vectors titer represents the quantities and infectivity of the virus vector particles. Adenovirus vector characterization by titration assay is helpful for further applications of adenovirus vectors. At Creative Biolabs, cutting-edge gene therapy platforms have been utilized to provide convenient adenovirus vector titration services for basic research and preclinical applications.
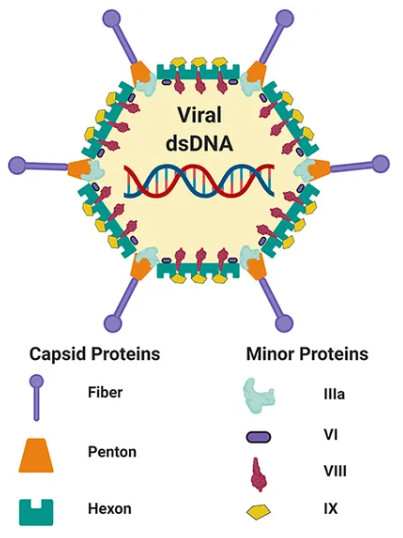 Figure 1 Schematic adenovirus structure.1
Figure 1 Schematic adenovirus structure.1
Adenovirus Vectors Titer
Adenoviruses vectors are a class of widely used gene transfer systems constructed by human adenovirus (especially adenovirus serotype 5) by deleting certain specific gene sequences. Actually, adenovirus has attracted numerous attentions as an excellent gene delivery vector primarily due to its advantages (high-efficiency in infection of dividing or non-dividing cells and ease of large-scale production, purification, and concentration). After the development of first-generation, second-generation, and third-generation, adenoviral vectors are now extensively applied for gene therapy, vaccine delivery, and cancer immunotherapy.
Adenovirus vectors titer is a parameter commonly utilized to represent the concentration or the number of infectious adenovirus vectors particles. Determination of adenovirus vectors titer is of great significance since it is a measure of viral vector effectiveness, which gives guidance to choose the optimum concentration of adenovirus vector transfection.
Types of Adenovirus Vectors
Adenoviral vectors are categorized based on their genetic modifications and serological properties, each with unique characteristics suited for specific applications. Understanding these variations is crucial for selecting the appropriate vector for a specific research or therapeutic purpose.
| Vector Type | Key Features | Applications | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Generation | E1 and/or E3 deleted, capacity up to 8 kb | Gene therapy, vaccine development, basic research | Ad5-CMV-GFP, Ad5-CMV-β-gal |
| Second-Generation | Additional E2 or E4 deletions, reduced immunogenicity, larger capacity | Chronic diseases requiring prolonged expression | Gutless/high-capacity vectors |
| Serotype 5 (Ad5) | Common, well-characterized, broad tropism | Widely used in research and vaccines | Ad5-nCoV COVID-19 vaccine |
| Replication-Competent | Retains replication genes, oncolytic properties | Cancer therapy, oncolytic virotherapy | Conditionally replicative vectors |
| Cell-Type Specific | Tissue-specific promoters, targeted expression | Neurological disorders, specialized applications | AdExL7-NL-LacZ (Purkinje cells) |
Adenovirus Vector Purification
The crude lysate must undergo multiple purification processes to remove cell debris, host cell proteins (HCP), host cell DNA (HCD), empty capsids, and replicable adenovirus (RCA).
- Clarification/nuclease treatment: Remove cell debris and use benzonase to digest residual DNA and RNA.
-
Chromatography: This is the core purification step.
- Anion exchange chromatography (AEX): used for preliminary capture and separation of intact particles from cellular pollutants.
- Hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC): commonly used for fine purification, effectively separating intact (including genomic) capsids from empty capsids, which is a key step in obtaining clinical grade materials.
- Ultrafiltration/dialysis (UF/DF): used for concentration and buffer exchange to form the final formulation buffer.
Adenovirus Vector Titration Technology
Titration quantifies two key parameters: physical titer (total viral particles, VP) and functional titer (infectious units, IU). Accurate titration requires a coordinated approach to ensure reproducibility.
Physical titer determination
UV spectrophotometry: measures absorbance at 260 nm (DNA) and 280 nm (protein).
Advantages: High precision (CV < 5%), suitable for high-throughput analysis.
Functional titer determination
- Plaque assay: Gold standard for IU/mL. Adenovirus infects permissive cells (e.g., HEK293) and plaques (areas of cell lysis) are counted 7–10 days late.
- TCID₅₀ assay: Determines the adenovirus dilution that infects 50% of cells. Calculated using the Reed-Muench method.
- Flow cytometry (FACS): Detects transgene expression (e.g., GFP) in infected cells. IU/mL is calculated based on the percentage of GFP-positive cells.
If there is no precise titration, you will face the following risks:
- Safety and efficacy: Insufficient dosage can lead to treatment failure; Excessive dosage can lead to systemic toxicity and severe immunogenicity.
- Regulatory failure: Inconsistent quality control data may result in batch release failure or IND/BLA application rejection.
- Economic losses: Due to non-reproducible preclinical data and production bottlenecks, expensive material losses, and severe delays.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
As mentioned before, adenovirus vectors titer is an important indicator of viral vector concentration and efficiency. Adenovirus vector titration not only helps to avoid the low success rate of transfection caused by low titer, but also reduces the waste of adenoviral vectors caused by high titer, and even prevents host cells death due to excessive viral vectors infection. Therefore, Creative Biolabs has developed a series of adenovirus vector titration assays to characterize the recombinant adenovirus vectors. Our adenovirus vector titration strategies mainly include but not limited to:
- 50% tissue culture infective dose (TCID50): determining the adenoviral vectors titration by measuring the adenovirus that can cause cytopathic effect in half of the cell culture plates or test tubes.
- Serial dilution method: using serially-diluted adenovirus vectors to infect 293A cells, counting the number of transduced cells via the detection of adenovirus-specific hexon protein based on immunocytochemistry.
- Plaque assay for purified adenovirus vector titration: single-layer HEK293 cells are infected with a series of adenovirus vectors dilutions. The adenovirus multiplied in the infected cells and infected the adjacent cells, producing cytotoxic effects and eventually plaque formation.
- Other determination assays: focus forming assay, bicinchoninic acid assay, etc.
Other Hot Servies
With the first-class expertise of viral vector technology, Creative Biolabs provides a diversity of adenovirus and adenoviral vector titration services for the application of gene therapy and vaccine development. Additionally, based on clients' specific demands, we also offer other various adenovirus vector services, such as:
- Recombinant adenovirus construction
- Adenovirus vector purification
- Adenovirus-based cDNA expression libraries generation
- Upstream bioprocess development for adenovirus vector
- Downstream bioprocess development for adenovirus vector
- Helper-dependent adenoviral vectors
- Adenoviral vector-based vaccine development
- Development of adenoviral vector as immune stimulant
- Adenoviral vector-based suicide gene therapy development
- Adenoviral vector design for RNAi delivery
Our Project Workflow
Creative Biolabs has established a streamlined, transparent workflow to ensure project success from initiation to completion. Our systematic approach ensures clients remain informed at every stage while maintaining the highest standards of quality and timeliness.
-
Phase I
Sample Reception and Preparation
- Sample Logistics: Receive the vector sample, verify the label information against the submission form.
- Cell Preparation: Prepare the sensitive host cells. Ensure they are healthy, in the log phase of growth, and ready to be plated at the required density.
- Vector Dilution: Prepare a serial dilution of the vector sample using appropriate media/buffer to cover the expected titer range.
-
Phase II
Titer Detection Test
- Infection Setup: Add the diluted vector samples (including positive and negative controls) to the plated cells in multiple replicates.
- Incubation: Allow the virus to adsorb to the cells, then incubate until the viral effect is visible.
- Assay Readout (The Core Test).
-
Phase III
Data Analysis and Quality Control
- Titer Calculation: Use the appropriate statistical method to calculate the final vector titer.
- Quality Control (QC): Verify that the results for all controls meet the predetermined acceptance criteria.
- Review: Check raw data, calculations, and reproducibility. If QC fails, initiate an OOS (Out of Specification) investigation and retesting.
-
Phase IV
Certificate and Report Delivery
- Report Generation: Compile the final, QC-approved titer result, the method used, and the QC summary into a formal Vector Titration Report or Certificate of Analysis (CoA).
- Archiving and Delivery: Archive all raw data, records, and the final signed report. Deliver the official report to the client or the relevant manufacturing team.
What Makes Creative Biolabs Your Top Choice
- Technology Platform: Cutting edge titration and purification platform based on rapid ELISA-based purification and density gradient ultracentrifugation systems can improve yield by >200 fold over traditional purification methods.
- Commitment to Quality: Rigorous quality control procedures are incorporated to guarantee specification is met for identity, purity, potency and safety.
- Customization Capabilities: We have staff with experience and expertise in the regulatory requirements for gene therapy products. We can offer advice to the researchers as they progress to the test phase.
- Regulatory Experience: Our team includes experts well-versed in the regulatory requirements for gene therapy products, providing valuable guidance to researchers as they move toward clinical application.
Customer Review

We rely heavily on accurate adenovirus vector titers for our basic molecular biology experiments, and this service has never let us down. Their team delivers consistent, reproducible results—each batch's titer data matches our internal spot checks perfectly—with a quick 3-day turnaround that keeps our projects on track. The reports are straightforward, highlighting key metrics without unnecessary jargon, and their team is always ready to clarify technical details. It's a reliable partner we recommend to every lab in our department.
— Dr. Clara Bennett, Research Associate
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is there often a discrepancy between VP/mL and IU/mL titers?
A: This discrepancy is due to the presence of non-infectious particles. VP/mL (physical titer) counts all particles (full, empty, aggregated, or damaged). IU/mL (infectious titer) counts only particles capable of successful transduction. A high VP/IU ratio (e.g., >50:1) is common and indicates a lower relative efficiency or quality of the batch.
Q: Which titer is more important for clinical dosing: VP or IU?
A: While VP/mL is a key quality control release criterion, IU/mL (infectious unit) titer is generally considered the most relevant parameter for clinical dosing because it reflects the true number of biologically active doses administered to patients.
Q: What are the advantages of using ddPCR over qPCR for physical titers?
A: ddPCR provides absolute quantification by partitioning the sample and counting positive reactions, eliminating the need for external standard curves. This reduces assay variability, improves robustness to inhibitors, and provides more accurate and well-defined VP/mL values, which are preferred for GMP critical reagent testing.
Q: How long does transgene expression from adenoviral vectors typically last?
A: In immunocompetent animals, first-generation adenoviral vectors typically mediate transient expression lasting several weeks due to immune clearance of transduced cells. In immunodeficient models or advanced vector systems with reduced immunogenicity, expression may persist for months.
Drop Us a Line Today!
At Creative Biolabs, we welcome the opportunity to discuss your specific adenovirus vector needs and develop customized solutions to advance your research programs. Contact our technical team today to learn how our expertise can accelerate your path to discovery.
Reference
- Coughlan L. Factors which contribute to the immunogenicity of non-replicating adenoviral vectored vaccines. Frontiers in immunology, 2020, 11: 909. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00909 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
