Custom Polymers Service
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) gene expression silencing is a revolutionary research achievement in the field of biotechnology in the late last century. This phenomenon, called RNA interference (RNAi), provides us with a way to fight many diseases that are difficult to cure with conventional therapies, thereby greatly enriching the technical means of gene therapy. Polymer-mediated siRNA delivery has several advantages, such as easy chemical modification, good biocompatibility, versatility, and fusion with inorganic materials, which can solve various obstacles related to effective siRNA delivery. Creative Biolabs has optimized the siRNA delivery process through the development of different polymer carrier systems to help customers achieve efficient and safe RNAi transfection.
Polymers for RNAi Delivery: The Rationale
RNAi molecules, including small interfering RNA (siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA), are bulky, multi-anionic, and inherently unstable. Their rapid renal clearance, enzymatic degradation by nucleases, and inability to cross cell membranes limit systemic administration. Furthermore, they trigger immune responses, necessitating precise delivery to the cytoplasm of RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISCs).
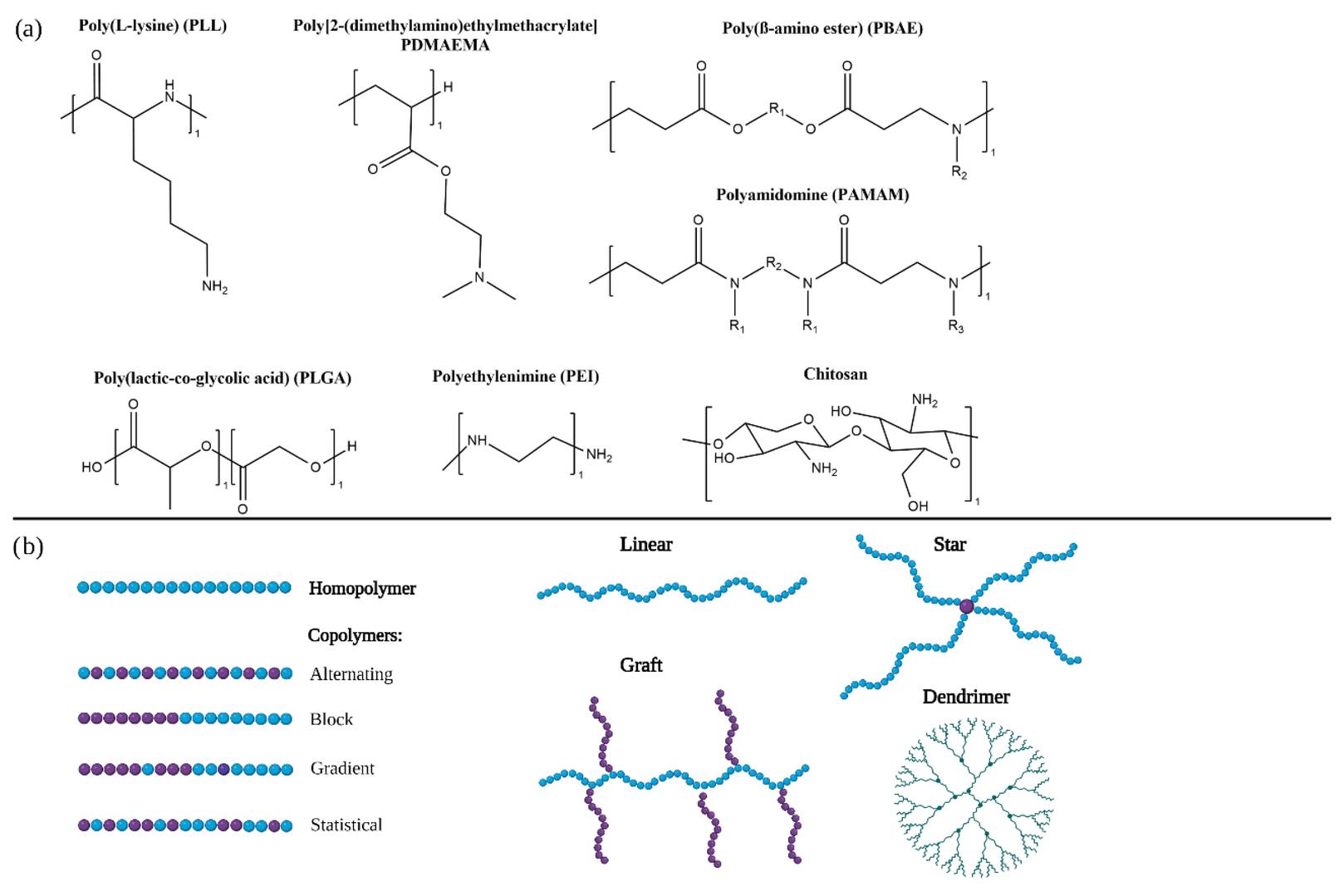 Figure 1. (a) Chemical structures of commonly used polymers in RNA therapeutics. (b) Schematical illustrations of different polymer architectures and topologies.1
Figure 1. (a) Chemical structures of commonly used polymers in RNA therapeutics. (b) Schematical illustrations of different polymer architectures and topologies.1
Custom-synthesized polymers address these challenges through several key mechanisms:
-
Complexation and Aggregation
Cationic polymers electrostatically interact with the negatively charged phosphate backbone of RNA, agglomerating it into a tight, stable polymer complex. -
Targeting and Stealth
Polymers can be functionalized with targeting ligands (e.g., peptides, antibodies, aptamers) to achieve cell-specific uptake.
Types of Polymers for RNA Delivery
RNAi therapy has a wide range of applications, covering fields from oncology to infectious diseases, thus requiring a versatile library of carrier materials. Polymers can be broadly classified according to their origin and chemical structure:
| Polymer Type | Key Characteristics | Advantages for RNAi |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Polymer | Polysaccharides (e.g., Chitosan, Hyaluronic Acid), Polyamino Acids (e.g., Poly-L-lysine) | High biocompatibility, often biodegradable, intrinsic targeting (e.g., HA for CD44 receptors). |
| Synthetic Polymer | Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), Poly (amino ester) (PAE), Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) conjugates | Highly tunable chemical structure, precise control over degradation kinetics, ease of functionalization. |
| Stimuli-Responsive Polymer | Polymers responsive to pH, temperature, or redox potential (e.g., disulfide-linked polymers) | Enhanced on-demand payload release at the disease site (e.g., low pH in tumors or inflamed tissues). |
Polymers vs. Nanoparticles for RNAi Delivery
Compared to LNP systems, polymer nanoparticles (or "polymer complexes") offer superior customizability, particularly for extrahepatic (non-hepatic) applications and for developing carriers with unique degradation properties, making them a preferred choice for drug discovery programs.
| Feature | Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs) | Custom Polymers (Polyplexes) |
|---|---|---|
| Customizability | Moderate; limited by lipid chemistry and fusogenicity requirements. | High; nearly infinite control over monomer type, architecture, molecular weight, and functional groups. |
| Stability | High physical stability, but can be prone to oxidation. | High colloidal and chemical stability; can be lyophilized for long-term storage. |
| Payload | Primarily optimized for siRNA/mRNA. | Highly versatile; can deliver siRNA, miRNA, plasmid DNA, and gene editing ribonucleoproteins. |
| Manufacturing | Complex, often requiring microfluidics. | Relatively simple, scalable, and cost-effective. |
| Safety Profile | Generally well-tolerated, but ionizable lipids can cause inflammatory reactions. | Can be engineered for biodegradability and low toxicity, with a long history of biocompatible materials. |
Our Services
Creative Biolabs offers end-to-end custom polymer services, specifically tailored to clients' unique needs in RNAi molecules.
01 Targeted Ligand Conjugation
Covalently linking tissue- or cell-specific ligands (e.g., N-acetylgalactosamine for hepatocyte targeting, RGD peptides for tumor angiogenesis).
02 Polymer Complex Preparation and Optimization
We utilize dynamic light scattering (DLS) and other techniques to optimize the N/P ratio, particle size, polydispersity, and zeta potential of polymer complexes.
03 In-depth In vitro and In vivo Evaluation
Comprehensive testing, including transfection efficiency, cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, quantification of endosomal escape, and efficacy in disease-related animal models.
04 Custom Polymer Design and Synthesis
Synthesis of proprietary cationic and amphiphilic polymers (e.g., novel PBAEs, PEI derivatives, biodegradable polyphosphates). Precise control over molecular weight (Mw), polydispersity index (PDI), and the introduction of functional groups.
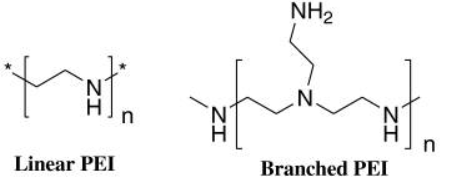
Polyethyleneimine (PEI)
Constructing a cationic carrier with PEI can not only solve the problem of cytotoxicity, but also provide sufficient protection against serum or RNase through effective complexing with siRNA. In addition, PEI can exert a "proton sponge effect" to induce the release of siRNA into the cytoplasm. Incorporating low molecular weight PEI into other polymer structures can also optimize the target specificity of the carrier, circulation cycle, serum stability and other parameters.
Poly(dl-lactide-co-glycolide)
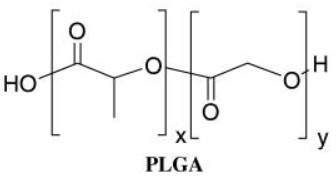
PLGA is a copolymer of glycolic acid (GA) and lactic acid (LA) linked together by ester bonds. We can control the degradation rate of PLGA by adjusting various parameters such as LA / GA ratio, MW and structural polymer matrix. Based on these characteristics, we have developed PLGA nanoparticles (NPs) as carriers of RNAi delivery, which have the advantages of small particle size, high safety and sustained release.
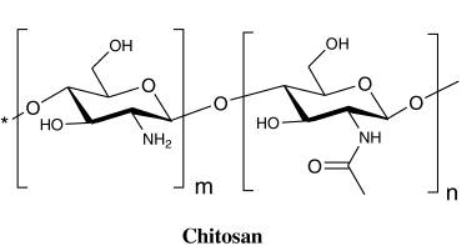
Chitosan
Chitosan is a copolymer of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (GlcNAc) and D-glucosamine (GlcN). We can use positively charged chitosan to combine with siRNA with a negatively charged phosphate backbone to form a multi-stranded body, and its transmission efficiency is mainly affected by the weight ratio.
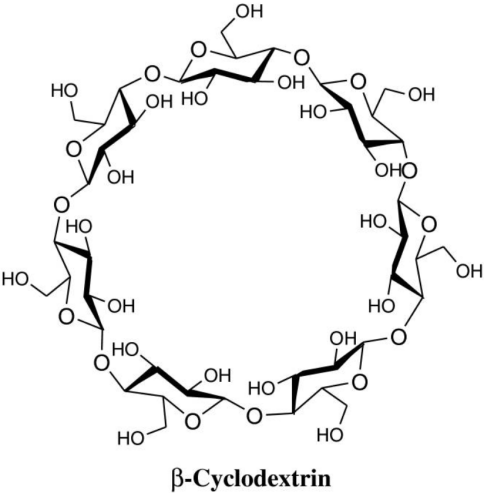
Cyclodextrin
Cyclodextrin (CD) is a naturally occurring cyclic oligosaccharide. Due to its lack of immunogenicity, it has attracted much attention in the field of targeted therapy. CD-based synthetic delivery systems have proven some success in delivering nucleic acid payloads including pDNA, siRNA, and DNAzyme. The main strategy is to form an inclusion complex between the adamantane (AD) -containing molecule and the β-CD molecule. The modular linkage of the AD-PEG conjugate provides steric stability and the targeting ligand (AD-PEG-transferrin) confers cell-specific targeting.
Synthesis of Polymers for RNA Delivery
At Creative Biolabs, we employ a range of advanced polymerization techniques to achieve precise control over polymer properties:
- Controlled radical polymerization: These techniques enable the synthesis of polymers with predetermined molecular weights, low polydispersity, and well-defined structures (block, graft, star).
- Ring-opening polymerization (ROP): Ideal for the synthesis of biodegradable polyesters, polycarbonates, and polyamino acids.
- Combinatorial library synthesis: For projects where the optimal polymer is unknown, we can rapidly synthesize and screen large libraries of PBAEs or other tunable polymers.
Why Choose Our Services?
- Unparalleled Expertise: Our team comprises PhD-level scientists with decades of experience in polymer chemistry and nucleic acid delivery.
- Proprietary Technology Platform: You have access to our proprietary combinatorial libraries and high-throughput screening systems.
- Confidentiality and Intellectual Property Protection: We safeguard your projects with stringent confidentiality agreements and offer flexible intellectual property arrangements.
- Outstanding Success Story: We have successfully collaborated with over 50 biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies to advance their RNAi projects.
Result Delivery
We uphold the principles of transparency and collaboration. You will receive:
01.A complete project report containing all raw and analytical data.
02.Detailed chemical characterization spectra (NMR, gel permeation chromatography).
03.High-resolution electron microscopy images of polymer complexes.
04.Complete reports on in vitro and in vivo studies.
05.Regular project progress updates and channels for direct communication with your project lead scientist.
Customer Reviews
"For years, we have been working on delivering large miRNA constructs to skeletal muscle. The Creative Biolabs team designed a custom, biodegradable PBAE that not only achieved unprecedented delivery efficiency but also demonstrated excellent safety in our toxicology studies. They are truly a partner."
—Director of R&D
"As an academic lab, we lacked the expertise in synthetic chemistry to construct advanced delivery vectors. Creative Biolabs provided a cost-effective custom polymer service that enabled us to validate our hypotheses in vivo. The resulting data was crucial to securing our next R01 research grant. Their scientific rigor and communication skills are outstanding."
—Principal Investigator
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long is your project cycle usually?
A: A standard project takes 8-12 weeks from design to obtaining preliminary in vitro data. The cycle for in vivo studies depends on the specific project.
Q: Can you use my existing RNA sequences?
A: Of course. We can formulate and optimize polymers for any siRNA, miRNA, or other RNAi trigger sequences you provide.
Q: How do you ensure that the polymers are non-toxic?
A: We prioritize biodegradable backbones and employ rigorous in vitro (MTT, LDH) and in vivo toxicity screening methods. Our design principles aim to reduce cationic charge-related toxicity.
Q: What is the minimum quantity of polymer I can order?
A: We offer small-scale exploratory synthesis (approximately 50-100 mg) for preliminary cell culture studies and formulation screening, and can scale up to multi-gram batches as needed for in vivo preclinical trials.
Q: Can you help us design a polymer suitable for a specific organ (e.g., the lung)?
A: Of course. Our design process starts with the target cell/tissue and, using our knowledge base, proposes optimal functionalization options (e.g., targeting ligands, charge, or size) that are known to accumulate in lung endothelial cells or alveolar macrophages.
Connect with Us Anytime!
The future of RNAi therapy lies in precise delivery. Off-the-shelf solutions often fall short of addressing the unique challenges posed by diverse targets, tissues, and vectors. At Creative Biolabs, we offer expert science and technology and platforms to tailor polymer vectors to your specific needs, ensuring they are as innovative as your therapeutic discoveries. If you want to know more details, please contact us by email or send us an inquiry to find a complete solution.
Reference
- Mirón-Barroso S, Correia J S, Frampton A E, et al. Polymeric carriers for delivery of RNA cancer therapeutics. Non-coding RNA, 2022, 8(4): 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040058 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
