Custom Aptamers Development Service
Nucleic acid-based aptamers have emerged as a new class of targeting moieties due to their high specificity and avidity. They possess exceptional folding capabilities, enabling them to form complex three-dimensional (3D) structures, such as hairpin structures, pseudoknot structures, and G-quadruplex structures. This unique structural plasticity allows them to bind with high affinity and extremely high specificity to a wide range of target molecules, including small organic compounds, peptides, proteins, and even entire cells or tissues. Currently, various aptamer-guided RNA delivery systems have been used for RNA therapy. Leveraging its extensive experience in aptamer research, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer our aptamer design service and aptamer short double-stranded RNA conjugation service to all clients interested in RNAi therapy.
Aptamers vs. Antibodies in Drug Screening
In the realm of drug screening and target validation, aptamers present several compelling advantages over traditional monoclonal antibodies.
| Feature | Nucleic Acid-Based Aptamers | Monoclonal Antibodies |
|---|---|---|
| Origin/Selection | In vitro (SELEX) | In vivo (Hybridoma) or in vitro (Phage Display) |
| Stability | High; resistant to thermal denaturation; easily renatured | Low; sensitive to temperature and pH |
| Immunogenicity | Generally low or non-immunogenic | Can be high (HAMA/HACA response) |
| Target Range | Broad: small molecules, ions, proteins, cells, tissues | Primarily proteins and large molecules |
| Synthesis/Modification | Chemical synthesis (low cost, high batch consistency, easy modification) | Biological expression (high cost, batch variation, difficult modification) |
| Size | Small (∼8-15 kDa) | Large (∼150 kDa) |
Aptamer-mediated Small Interfering RNA (siRNA) Delivery System
Aptamer is a big class of RNA or DNA oligonucleotides that have a high selective affinity to the target proteins or receptors. As the nucleic acid versions of antibodies, aptamer possesses unique characteristics, such as easy synthesis, lack of immunogenicity, and small size, which makes it more adaptable for siRNA conjugation and delivery. Compared to antibody or proteins, siRNA conjugation with aptamer is easy to operate. siRNA can be attached to the aptamer by two approaches. One is direct conjugation to the end of the aptamer chain, and the other is its complementary assembly to append with the aptamer. The first aptamer siRNA conjugate was constructed using the latter strategy in which scientists directly in vitro transcribed prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) aptamer and sense strand of siRNA, and then annealed with antisense strand of siRNA to form an aptamer siRNA conjugate-targeting prostate PSMA.
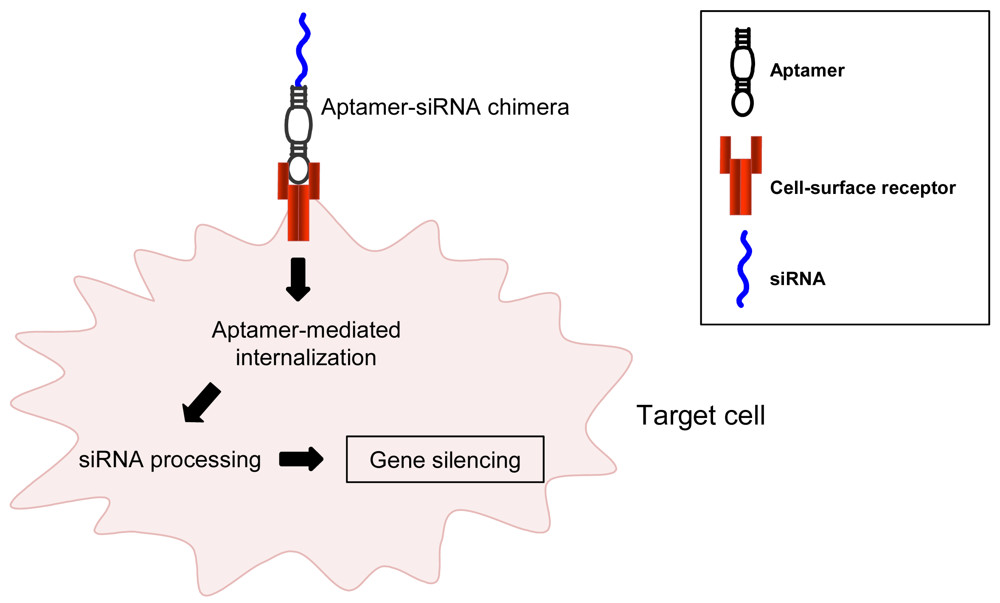 Figure 1. Aptamers as delivery agents. Aptamers that bind to cell surface receptors can be used to deliver siRNA to target cells.1
Figure 1. Aptamers as delivery agents. Aptamers that bind to cell surface receptors can be used to deliver siRNA to target cells.1
Our Strategies for Nucleic Acid-Based Aptamer Development
Customized Variants
We employ advanced methods, including Cell-SELEX for whole-cell targeting and Capture-SELEX for targets that are difficult to purify. We customize screening matrices (e.g., incorporating competing molecules, physiological buffers) to ensure aptamers function optimally under relevant biological conditions.
Rational Library Design
We move beyond purely random libraries, introducing semi-rational or biased libraries enriched with known structural motifs (e.g., G-quadruplex forming sequences) or modified nucleotides (e.g., LNA, 2'-O-methyl, or 2'-amino substitutions) to improve nuclease resistance and binding affinity.
Reverse Screening and Optimization
A key step is rigorous reverse screening of common serum proteins or non-target cells to remove non-specific binders. Post-SELEX optimization includes truncation, mutation analysis, and secondary structure prediction to identify minimum binding motifs and improve synthetic yield and stability.
Dissociable Linker Systems
For therapeutic applications requiring intracellular payload release, we have designed sophisticated dissociable linkers that respond to specific physiological conditions (such as acidic pH, reducing environment, or enzyme activity) to ensure precise delivery of the payload to the site of action.
Site-Specific Modification
We employ advanced synthetic techniques to precisely couple the aptamer sequence at predetermined locations, ensuring consistent drug-aptamer ratios while maintaining structural integrity and binding function.
Electrophilic Group Introduction
We utilize strategically placed electrophilic groups to functionalize the aptamer sequence. These electrophilic groups can form permanent covalent bonds with nucleophilic residues on the target protein. This approach significantly prolongs target binding time and duration of action, potentially overcoming the limitations of traditional non-covalent interactions.
A Flexible Suite of Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs has established several engineering strategies for aptamer design to increased RNA loading efficiency. Our scientists also have accumulated rich experience in constructing aptamer short dsRNA (such as siRNA, miRNA, ssRNA) conjugates to deliver them into tumor cells. When DNA aptamer is used as a targeting ligand, our scientists will optimize a chemical linker to link RNAi and aptamer together. Through direct conjugation to the end of aptamer chain or complementary assembly to append with the aptamer, we have accomplished several aptamer short dsRNA conjugates successfully, which have been turned to be efficient in vivo experiments.
Nucleic Acid-Based Aptamer Development
- Customized aptamer screening: Target-specific SELEX screening for proteins, small molecules, or cell lines.
- Aptamer optimization and truncation: Enhancing affinity, stability, and reducing size.
- Aptamer modification and labeling: Introducing modified nucleotides, fluorescent dyes (e.g., FAM, Cy3, Cy5), biotin, and radiolabeling.
- Aptamer conjugation services: Development of ApDC, aptamer-siRNA conjugates, and functional modifications for biosensors.
Analytical and Validation Services
We provide comprehensive characterization to ensure aptamer quality and functionality:
- Binding affinity measurement (SPR, ITC, BLI)
- Specificity profiling against related targets
- Structural characterization (CD spectroscopy, NMR)
- In vitro and in vivo functional validation
Why Choose Our Services?
Choosing Creative Biolabs as your aptamer development partner can significantly accelerate your R&D process while reducing development risks.
Comprehensive Expertise
Our unique combination of computational design, synthetic chemistry, and biovalidation capabilities provides an unparalleled integrated approach to aptamer development, enabling a seamless transition from computational prediction to functional validation.
Outstanding Success Record
We have successfully developed aptamers for a variety of challenging targets, including membrane proteins, transcription factors, and complex carbohydrate structures, with several candidate aptamers already in preclinical validation.
Accelerated Development
Our computational and machine learning methods significantly reduce development time, with typical project cycles of only 2-3 months, compared to over 6 months using traditional methods.
Application-Driven Design
We design aptamers with an end-application-oriented approach, ensuring optimal performance in your specific application scenario—whether therapeutic, diagnostic, or biotechnological.
Comprehensive Report
- Detailed Technical Documentation: Complete characterization data, including affinity measurements, specificity analysis, and structural analysis.
- Sequence and Modification Specifications: Complete chemical synthesis information for easy customer reproduction and application.
- Recommended Applications: Data-driven guidance to achieve optimal application in specific systems.
- Customized Recommendations: Strategic recommendations for further optimization tailored to specific applications.
Customer Review

"Creative Biolabs has successfully developed a novel cell-targeting aptamer for a highly challenging low-expression tumor antigen. This aptamer exhibits sub-nanomolar affinity and demonstrates excellent batch-to-batch consistency with the ApDC used in our preclinical studies. Their integrated NGS-SELEX technology is truly disruptive."
– Dr. Elena V., VP of R&D.

"Their expertise in site-specific click chemiconjugation is outstanding. We received high-purity, validated aptamer-nanoparticle constructs that significantly improved in vivo targeting specificity in our preclinical models. Comprehensive Kd values and stability data saved us months of validation work."
– Professor Kenji H., Principal Investigator.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can aptamers be made against targets that are not immunogenic?
A: Yes, this is actually one of the major benefits of aptamers. As SELEX is done in vitro and does not have to contend with the biological constraints imposed on antibody development, we are able to develop aptamers against targets that are not immunogenic, including toxic compounds, conserved epitopes and non-immunogenic moieties.
Q: How are aptamers stabilized for in vivo use?
A: We use a variety of different strategies to stabilize aptamers, including:
- Sugar modifications (2'-F, 2'-O-Me) to provide nuclease resistance
- Backbone modifications (phosphorothioate) to provide general biological stability
- Terminal capping to prevent exonuclease cleavage
- Structural constraint to "lock" into functional conformation
These can increase serum half-life from minutes to hours or even days, and can be used to create aptamers appropriate for in vivo therapeutic applications.
Q: What is the regulatory status of aptamer therapeutics?
A: No aptamer-therapeutic conjugates have made it to clinical trials yet, but it is an active area of research. The preclinical characterization of Sgc8c-M and related conjugates in multiple animal species (including non-human primates) has given researchers a regulatory head starts and a clear path toward clinical translation.
Q: How do you control the risk of non-specific binding (off-target effects)?
A: We control this risk during the design process through rigorous reverse selection steps targeting common interfering substances (such as serum components) or non-target cell lines, thereby ensuring that the final aptamer is highly selective.
Connect with Us Anytime!
Aptamer-mediated RNA delivery system is a highly promising approach for targeted delivery for RNAi. With years of experience in aptamer design and conjugation, Creative Biolabs is fully competent and dedicated to serving as your one-stop-shop for the development of aptamer-mediated RNA delivery systems. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly send us an inquiry.
Reference
- Cerchia L, Esposito C L, Camorani S, et al. Coupling aptamers to short interfering RNAs as therapeutics. Pharmaceuticals, 2011, 4(11): 1434-1449. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph4111434 Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
