Development Services of Polyplexes as Gene Delivery System
At Creative Biolabs, we have established ourselves as pioneers in the field of non-viral gene delivery by integrating cutting-edge research with translational expertise to provide clients with innovative polyplex solutions that overcome the limitations of conventional delivery systems. Our multidisciplinary team of scientists brings together expertise in polymer chemistry, nanotechnology, molecular biology, and pharmaceutical sciences to develop customized polyplex platforms that address specific research and therapeutic needs.
Polyplexes Introduction
Gene therapy, the transfer of genetic material into cells to treat disease, is one of the most transformative areas in modern medicine. While the therapeutic potential of nucleic acid vectors, such as plasmid DNA (pDNA), small interfering RNA (siRNA), and messenger RNA (mRNA), is undeniable, a major bottleneck remains the efficient and safe delivery of these large, unstable, and highly anionic molecules across biological barriers. Polyplexes represent a leading solution in non-viral delivery. Polyplexes are self-assembling nanocomplexes that spontaneously form through electrostatic interactions between a cationic polymer (vector) and an anionic nucleic acid carrier.
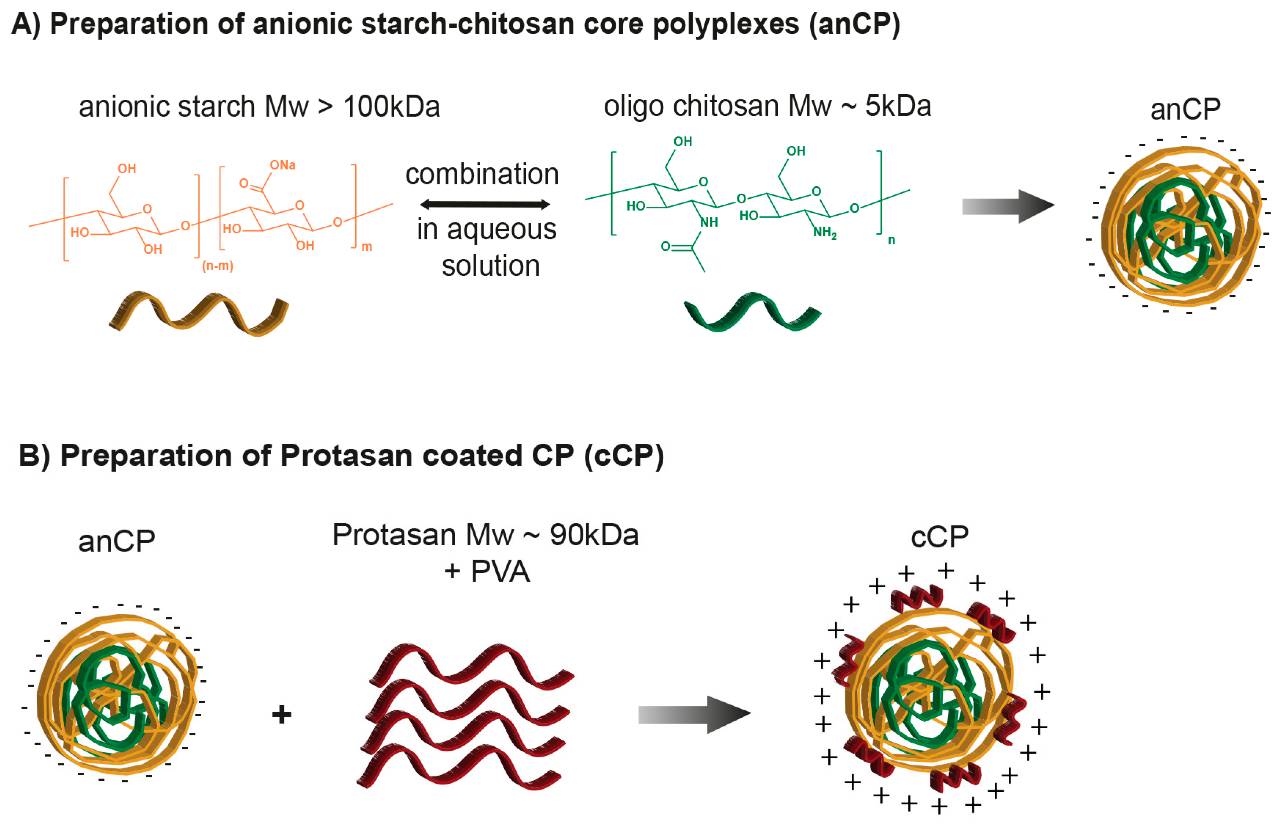 Figure 1. Illustration of drug-free (plain) starch-chitosan polyplex-preparation.1
Figure 1. Illustration of drug-free (plain) starch-chitosan polyplex-preparation.1
Polymeric Material Types
| Polymer Category | Example | Core Advantage/Mechanism | Translational Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Polymer | Polyethyleneimine (PEI) | High transfection via "Proton Sponge" effect; highly functionalizable | Remains the gold standard for in vitro transfection; derivatives show potential in systemic anti-cancer gene delivery models. |
| Natural Polymer | Chitosan | Biocompatibility, biodegradability, low intrinsic toxicity; mucoadhesive properties | Chitosan-DNA polyplexes have been studied for mucosal and oral gene delivery applications, such as treatment for colitis. |
| Biodegradable Polymer | Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) | Controlled release kinetics through bulk hydrolysis; high stability | PLGA-PEI hybrid polyplexes have demonstrated prolonged gene expression in vivo in inflammation models by offering sustained release. |
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
Polyplexes based on polycationic structures have the ability to interact with negatively charged nucleic acids to spontaneously form nanoparticles. Thanks to their high loading capacity and ease of fabrication, several polyplexes have been extensively studied for the development of gene delivery therapeutics. To eliminate the toxicity of polyplexes, Creative Biolabs has been devoted to developing decationized polyplexes that have no detrimental effects on the physicochemical stability or encapsulation ability. Furthermore, the size, shape and surface chemistry of polyplexes vectors are modified to improve the targeting capability.
Chitosan
Chitosan is a biodegradable polysaccharide copolymer with a positive charge. Chitosan as a vector has the properties of biocompatibility, safety and non-toxicity, protects the DNA from nuclease degradation and promotes the uptake. Creative Biolabs provides commercial transfection reagents based on chitosan for therapeutic gene delivery.
Poly (Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) and Poly Lactic Acid
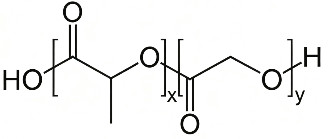
Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) and poly lactic acid (PLA) consist of lactic acid and glycolic acid. Biodegradable PLGA and PLA provide sustained gene delivery by bulk hydrolysis and increase stability.
Structural Design of Decationized Polyplexes
Decationized polyplexes are neutral polymers composed of a PEG corona and a disulfide cross-linked poly (hydroxypropyl methacrylamide) (pHPMA) core to encapsulate and retain the nucleic acids. Decationized polyplexes can function as stable and safe vectors to improve biodistribution for systemic gene therapy.
Advantages:
- No interference with cell viability
- Excellent colloidal stability
- Excellent cytocompatibility
- Excellent safety profile
- Low teratogenicity and mortality profile
Polyplex Characterization Specifications
| Parameter | Specification Range | Characterization Method |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | 80-220 nm (tunable based on application) | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| Zeta Potential | +5 mV to +35 mV (modifiable with PEGylation) | Phase Analysis Light Scattering |
| Nucleic Acid Loading Capacity | 85-99% encapsulation efficiency | Gel Electrophoresis Assay |
| Serum Stability | >80% integrity after 24h in serum | Serum Degradation Assay |
| Cell Viability | Typically >90% (varies by polymer class) | CCK-8/MTT Assay |
| In Vivo Transfection Efficiency | Organ-specific (spleen, liver, lung targeting available) | Bioluminescence/Fluorescence Imaging |
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Polyplex Development?
Creative Biolabs has unique strengths at the intersection of polymer chemistry and translational biomedicine. Our expertise ensures your innovative therapeutic ideas can advance quickly and efficiently from proof-of-concept in the laboratory to preclinical validation.
Precision Engineering of Polymer Scaffolds
Unlike off-the-shelf polymer systems, we specialize in custom polymer synthesis, precisely adjusting molecular weight, structure (linear, branched, dendritic), and degree of substitution to optimize charge density and, crucially, the pKa value required for effective endosomal escape.
Superior Physicochemical Characterization
We provide reliable data demonstrating the quality and stability of your final product. Each complex is thoroughly characterized using advanced technologies to ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
Targeted Delivery and Safety
We specialize in fine-tuning complex modifications (e.g., PEGylation for stealthy delivery, ligand conjugation for active targeting) to maximize the therapeutic index and minimize systemic toxicity.
Applications of Our Polyplex Delivery Services
The versatility of polyplex technology allows for broad application across a wide range of therapeutic areas:
Infectious Disease Vaccines
Development of highly potent and stable mRNA vaccines encapsulated in polyplexes to enhance mucosal and systemic immunity without the cold chain transport of lipid nanoparticles.
Genetic Disease Correction
Systemic delivery of therapeutic genes or siRNA to liver or muscle tissue for long-term protein replacement or gene knockdown.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Delivery of mRNA or pDNA encoding tumor-associated antigens or immune-stimulatory cytokines to enhance anti-tumor immunity.
Regenerative Medicine
Delivery of pro-differentiation factors (e.g., transcription factors) to stem cells in vivo or in vitro to guide tissue repair and regeneration.
Order Process
Creative Biolabs employs a rigorous, efficient three-phase process to accelerate your research timeline:
-
Phase I: Consult & Design
A specialist consults with your team to define the therapeutic target, the preferred nucleic acid cargo (pDNA, siRNA, or mRNA), and the in vivo route of administration. We then propose a custom polymer architecture and initial formulation strategy.
-
Phase II: Synthesis, Formulation & QC
Our chemistry team synthesises, purifies, and characterises the polymer. The formulation team then executes a rational high-throughput screen to identify the optimal N/P ratio and buffer system, followed by comprehensive physicochemical Quality Control (QC).
-
Phase III: Validation & Delivery
The final polyplex product is subjected to cytotoxicity and efficacy validation in relevant cell models. The validated polyplexes, along with a full technical data package, are delivered, ready for preclinical testing.
Trusted by Global Innovators

"We collaborated with Creative Biolabs to develop a targeted mRNA delivery system for our sickle cell disease program. Their diselenide-containing PBAE platform enabled efficient splenic delivery with 90% higher transfection efficiency compared to our previous LNP formulations. The team's expertise in redox-responsive polymers was instrumental in achieving therapeutic protein levels in our preclinical models."
— Dr. Hannah Müller, Lead Scientist

"The mass-ratio-controlled organ-selective platform from Creative Biolabs has transformed our approach to in vivo gene editing. By simply adjusting the polymer: mRNA ratio, we can precisely target spleen, liver, or lung tissues without complex ligand conjugation. This technology has accelerated our research in regenerative medicine applications."
— Prof. James Robertson, Director
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the key advantages of polyplexes for gene delivery compared to lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)?
A: Polyplexes offer several unique advantages over LNPs, including more flexible structures, tunable degradation properties, and reduced cytotoxicity. While LNPs typically require high doses of cationic lipids, which can trigger toxicity and prone to lung accumulation, advanced polyplex systems can be engineered with precise charge densities and biodegradable backbones to minimize these issues.
Q: How can polyplex systems be used to achieve tissue-specific targeting?
A: We employ multiple tissue-specific targeting strategies, including our proprietary mass-ratio controlled organ selectivity platform, which enables precise targeting by simply adjusting the polymer-to-mRNA mass ratio. This mechanism involves generating polyplexes with varying surface charge and pKa properties, which are capable of adsorbing specific plasma protein coronas, forming a "protein fingerprint" that mediates organ selectivity. Furthermore, we incorporate targeting ligands through click chemistry and design stimuli-responsive polymers that activate in specific tissue environments.
Q: What types of nucleic acids are compatible with your polyplex system?
A: Our polyplex platform is compatible with a wide range of nucleic acid payloads, including mRNA for protein replacement therapies and vaccines, pDNA for long-term gene expression, and various RNA therapeutics. We have optimized specific formulations for different nucleic acid types. For example, our degradable polycarbonate carriers demonstrate superior mRNA delivery efficiency comparable to JetPEI, but with a significantly improved safety profile. Our cationic γ-glutamic acid derivatives exhibit excellent DNA binding across a wide range of modification levels (11–95%).
Q: How do you address the inherent cytotoxicity of highly cationic polymers like PEI?
A: We primarily address cytotoxicity through three strategies: 1) Molecular engineering: synthesizing linear or low molecular weight polymers; 2) Biodegradable linkers: incorporating ester or disulfide bonds that degrade within cells; and 3) Surface modification: utilizing PEGylation to shield surface charge and reduce nonspecific electrostatic interactions with cellular components.
Get in Touch Today!
Creative Biolabs has been devoted to improving the stability and efficiency of non-viral vectors by optimizing their structure, charge and formulation. We offer one-stop services about the development of polyplexes as a gene delivery system. Please feel free to contact us and let us know your needs.
Reference
- Yasar H, Ho D K, De Rossi C, et al. Starch-chitosan polyplexes: A versatile carrier system for anti-infectives and gene delivery. Polymers, 2018, 10(3): 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030252 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
