Development of Bacteria as Gene Delivery System
Bacteria become an attractive gene delivery vector because it can transfer therapeutic gene product into the target organism, organ or tissue directly. Creative Biolabs provides the state-of-the-art non-viral vector technology for basic research and preclinical applications.
Introduction
Gene Delivery Systems Overview
The success of gene therapy in treating a broad spectrum of diseases from monogenic to more complex diseases such as cancer has been the major advancement in medicine. One of the most important elements in a therapeutic process is the gene delivery system. Gene delivery systems are non-pharmacological entities that transport foreign DNA/RNA into the host cell to perform certain functions such as expressing a therapeutic gene, silencing a disease-causing gene or correcting the genome through editing processes.
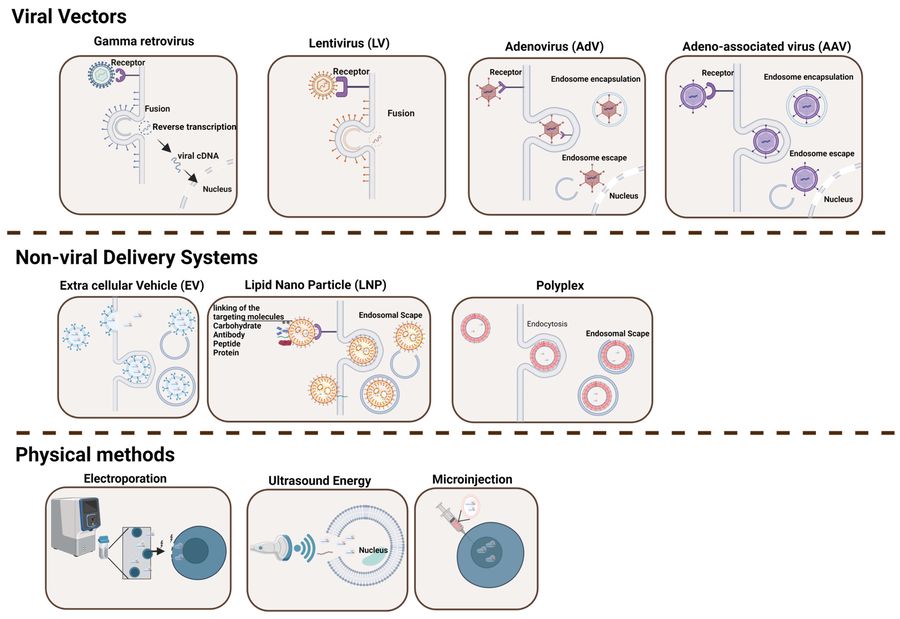 Figure 1 Delivery Systems for Gene Editing Components.1
Figure 1 Delivery Systems for Gene Editing Components.1
Importance of Gene Delivery in Biotechnology and Medicine
Gene delivery systems have been mostly focused on using viruses as the carriers due to their ability to infect a host cell and insert its genome. However, these systems have major drawbacks including immunogenicity, small cargo capacity, and a complicated manufacturing process. This has steered interest into alternative non-viral platforms such as bacteria. Bacteria are an extremely promising and innovative non-viral gene delivery system due to their ease of genetic manipulation and high specificity for target tissues as certain bacteria have the natural ability to target and colonize specific tissues in the body.
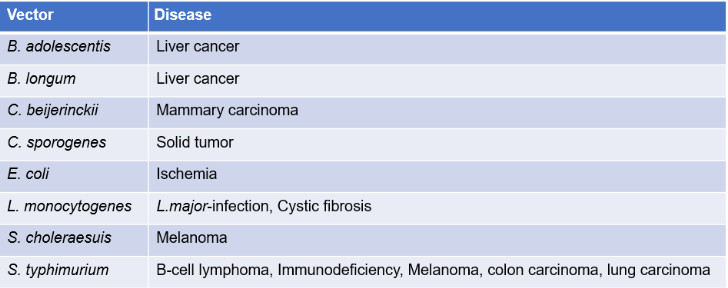 Figure 2 Using bacteria in various disease models.
Figure 2 Using bacteria in various disease models.
Why Choose Bacteria for Gene Delivery?
Natural Tropism
Bacteria can be naturally targeted towards tissues, cells, sub-cellular compartments, etc. This also helps localize the therapeutic genes to the site of disease, thus increasing the local dose and decreasing off-site targeting and activity.
Large-scale Manufacturing
Bacterial systems are also very practical in terms of production, as the fermentation platforms for bacteria are mature and well-understood. Large-scale fermentation production of bacteria is more well-established compared to viral or mammalian vectors.
Ease of Engineering
Bacterial systems are genetically well-characterized and manipulable; this is decades of microbiology research resulting in a mature set of tools to engineer bacterial genomes.
Large Payload Capacity
Bacterial systems also tend to have much higher capacity for therapeutic delivery compared to other platforms.
Safety
Because bacterial systems are so well-characterized and easy to modify, it is possible to implement multiple independent methods of attenuating these bacteria to ensure safe use.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs fully understands the potential of bacteria as a gene delivery system, and as a contract research organization we have the capability to offer end-to-end service for new biomedical discoveries from development and optimization to scalable manufacturing. With services spanning the complete gene therapy process, Creative Biolabs is able to support every step from vector design, preclinical validation and manufacturing.
- Custom Vector Construction and Engineering: We are able to construct and engineer custom bacterial vectors with the desired traits and properties, including insertion of specific promoters, targeting moieties and therapeutic gene cassettes.
- Attenuated Strain Development: Our experts can also develop safe and effective attenuated bacterial strains that maintain tropism with reduced pathogenicity.
- In Vitro and In Vivo Validation: We provide robust assay development and screening to evaluate the efficacy and safety of your bacterial gene delivery system both in cell and animal models.
- Manufacturing and Quality Control: Creative Biolabs can provide scalable manufacturing for bacterial vectors with the highest quality control standards.
Types of Bacterial Vectors
Table 1: Comparison of Major Bacterial Vector Platforms for Gene Delivery.
| Vector Type | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-cell Bacteria | Live, engineered bacteria delivering genetic material | Self-propelled, targetable, scalable production | Potential safety concerns, host immune response |
| Bacterial Minicells | Anucleate daughter cells produced by abnormal cell division | Reduced safety concerns, high payload capacity, surface modifiable | Limited circulation time, rapid clearance |
| Bacterial Ghosts | Empty bacterial envelopes devoid of cytoplasmic content | Preserved surface structures for targeting, improved safety | No genetic replication possible, limited payload |
| Outer Membrane Vesicles (OMVs) | Spherical nanostructures (20-250 nm) released from Gram-negative bacteria | Natural composition, self-adjuvating, membrane fusion capability | Size limitations for genetic payload, immunogenic |
Workflow of Our Adeno-associated Virus Titration
01. Project Consultation & Design - We offer expert consultation and design services to select the most appropriate bacterial strain and genetic construct tailored to your therapeutic target.
02. Vector Construction & Engineering - Our experienced team will engineer the selected bacterial strain to include the therapeutic gene.
03. In Vitro & In Vivo Validation - We perform rigorous validation of the efficacy and safety of the bacteria-mediated gene delivery system both in vitro (in the lab) and in vivo (in animal models).
04. Scalable Manufacturing & Quality Control - Once validated, we scale up the production of the bacterial vector to meet your quantity requirements while adhering to stringent quality control measures.
Why choose Creative Biolabs to meet your research?
At Creative Biolabs, we pride ourselves on providing exceptional value and expertise. Our key advantages include:
- Deep Scientific Expertise
- Comprehensive, End-to-End Solutions
- Unmatched Customization
- Stringent Quality Control
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main advantage of pseudotyping a lentiviral vector?
A: This is application dependent, but bacterial systems have several clear advantages:
- For gut-targeted delivery, nothing even comes close to engineered commensals because of their superior colonization ability and continuous production of the therapeutic molecule.
- For tumor targeting, no synthetic nanoparticles are yet known to be capable of as high of a specific accumulation in the tumor (often >1000:1 tumor:normal tissue).
Q: What advantages do bacterial vectors have over synthetic nanoparticles?
A: Some advantages:
- Self-replication: A single dose can amplify at the target site, which could allow continuous therapy from an initial very small dose.
- Sensing: Bacteria can sense complex disease microenvironments (hypoxia, inflammation, presence of certain metabolites, etc.) in ways that are very challenging for synthetic materials.
- Active motility: Bacteria can actively traverse biological barriers (mucus, tissue matrices) that prevent passive diffusion of synthetic nanoparticles.
- Payload flexibility: Bacteria can deliver nearly any class of molecule, from DNA and RNA to proteins and even synthetic materials that they have been engineered to produce.
Q: How does the efficiency of gene delivery mediated by bacteria compare to viral vectors?
A: Efficiency will depend on the bacterial system, target tissue, and application and may not always be superior. Viral vectors tend to have much higher transduction efficiency in simple gene delivery settings. Bacterial systems on the other hand tend to have advantages in areas such as targeting specificity, payload capacity, and programmability. In some cases, local delivery in specific microenvironments such as tumors and gastrointestinal tract where the overall transduction rate is low, bacterial carriers may lead to more effective therapeutic effect.
Q: How do you ensure the stable maintenance of genetic payloads in bacterial vectors?
A: We adopt various strategies to maintain genetic stability:
- Chromosome integration: For long-term stability, we use transposon systems or site-specific recombinases to integrate payloads into neutral chromosome sites.
- Stable free body system: For larger payloads, we use engineered plasmids with appropriate distribution and addiction systems to ensure plasmid retention during bacterial division.
Don't Hesitate, Contact Us!
With a skilled team of scientists, Creative Biolabs provides cutting-edge bactofection method and various modified bacterial strains for basic research and preclinical applications. Please feel free to contact us for more details and we are pleased to offer you the best services.
Reference
- Taghdiri M, Mussolino C. Viral and non-viral systems to deliver gene therapeutics to clinical targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(13): 7333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25137333 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
