Custom Nanoparticles Service
The mode change of nanoparticles used for RNAi molecule delivery is attributed to the unique advantages provided by nanoparticles compared to other carriers. One of the important advantages is the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, which enables nanocarriers to accumulate in tumors at much higher concentrations than normal tissues. On the basis of our understanding of the development of RNAi and delivery systems, Creative Biolabs is confident in providing you with comprehensive and high-quality services for RNAi.
What Are Nanoparticles?
Nanoparticles are particulate dispersions or solid particles with the particle size in the range of 10-1000 nm. They are the most common choice for the delivery of RNAi. Compared with other carriers, nanocarriers can protect RNAi molecules from enzymatic degradation and immune recognition, have higher transportation efficiency across the cell membrane, and can prevent excretion if the carrier size and surface coating are appropriate. Nanocarriers for RNAi can be divided into organic nanoparticles and inorganic materials. Drugs can be incorporated into organic nanoparticles by chemical bonding or physical embedding. Among inorganic nanocarriers, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are the most commonly used because of their unique properties, such as uniform mesopores, easy functionalization, biocompatibility, high specific surface area, large pore volume and biodegradability.
Nanoparticles for RNAi Delivery
A core challenge in RNAi therapy lies in delivery. Naked RNAi molecules (such as siRNA) are rapidly degraded by nucleases in the bloodstream and struggle to cross cell membranes to reach the cytoplasm, the location of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).
RNAi delivery nanoparticles are engineered to overcome these obstacles.
- Protection: Protecting the RNAi carrier from enzymatic degradation and immune recognition in systemic circulation.
- Stability: Ensuring the carrier remains encapsulated before reaching the target site.
- Targeting: Promoting the accumulation of RNAi at the lesion site (passively targeting tumors through enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects) and/or actively binding to specific cell surface receptors.
- Endosomal Escape: Facilitating the release of the RNAi carrier from endosomes into the cytoplasm (the site of action).
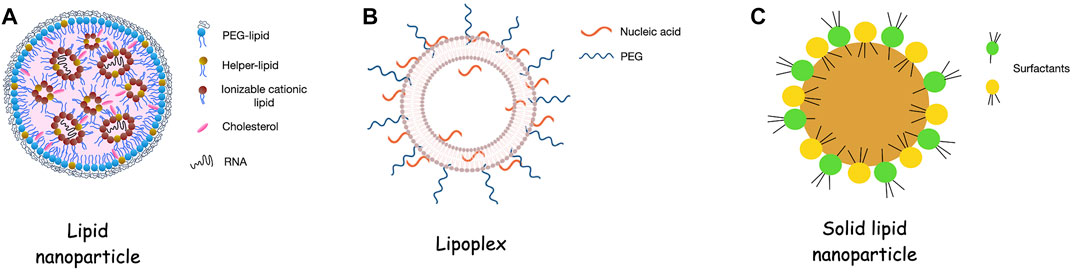 Figure 1 Consistency of lipidic nanoparticles for RNA delivery.1
Figure 1 Consistency of lipidic nanoparticles for RNA delivery.1
Types of Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery
Various nanomaterials have been studied for RNA delivery, each with its unique advantages and limitations.
(1) Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
LNPs are currently the gold standard for systemic RNAi delivery. Their successful application in developing highly effective mRNA vaccines (such as those used to combat infectious diseases) powerfully demonstrates their versatility and effectiveness in nucleic acid delivery systems, marking a significant advancement in biotechnology and therapeutic strategies.
(2) Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
AuNPs provide a highly tunable and biocompatible platform. Their surface can be easily functionalized with thiolized RNA oligonucleotides via strong Au-S bonds. AuNPs are ideal candidates for photothermal therapy and controlled release because their surface plasmon resonances can be used to release RNA payloads under near-infrared (NIR) light irradiation.
(3) Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs)
Silver nanoparticles initially attracted attention for their antibacterial properties, but in recent years they have also begun to be used for gene delivery. Their high surface reactivity allows them to adsorb nucleic acids. However, due to the potential for cytotoxicity from silver ion (Ag⁺) leaching and the risk of long-term accumulation, the application of silver nanoparticles in RNA interference (RNAi) is still in its early stages.
Lipid Nanoparticles for Short Interfering RNA (siRNA) Delivery
Due to its high efficiency and safety, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are currently the most advanced siRNA delivery system in clinical practice.
Delivery Mechanism
- Encapsulation: Ionizable lipid components can efficiently encapsulate anionic siRNA under acidic conditions.
- Systemic Circulation: The polyethylene glycol (PEG) lipid canopy provides concealment, prolonging the circulating half-life.
- Targeting/Uptake: LNPs are passively taken up by hepatocytes via receptor-mediated endocytosis (e.g., ApoE binding to LDL receptors), achieving systemic delivery within the liver.
- Endosomal Escape: After entering the cell via endosomes, the acidic environment of the endosomes protonates the ionizable lipids, leading to charge reversal and endosome membrane instability, ultimately releasing the siRNA into the cytosol.
Our Services
In recent years, the application of nanoparticles as gene carriers in RNAi has attracted extensive attention. Many studies have determined the effective application of RNAi delivered by diverse nanocarriers. In order to systematically regulate the immune system and allow it to cross the physiological barrier, delivery systems must be engineered to provide serum stability, offer high structural and functional tunability, reduce the interaction with non-target cells, enhance cell entry and escape, resist renal clearance, and produce low toxicity and immunogenicity.
Features of Our Custom Nanoparticles
We employ a modular approach to design and customize nanocarriers, ensuring high tunability and scientific rigor.
| Feature | Design Modality | Scientific Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Tailored Scaffold | Custom synthesis of novel ionizable lipids, polymeric materials (e.g., dendrimers, customized PEI), or hybrid systems. | Optimized pKa for superior endosomal escape; enhanced biocompatibility and reduced toxicity compared to off-the-shelf materials. |
| Active Targeting Ligands | Covalent conjugation of peptides, aptamers, or Antibody-siRNA Conjugates (ARCs) to the nanoparticle surface. | High-specificity delivery to non-hepatic or hard-to-reach tissues (e.g., solid tumors, immune cells), maximizing therapeutic index and minimizing off-target effects. |
| Surface Engineering | Customized PEGylation strategies and surface charge modulation (zeta potential). | Extended systemic circulation and improved biodistribution profile for enhanced passive tumor accumulation via the EPR effect. |
| Theranostic Integration | Incorporation of imaging moieties (e.g., fluorophores, magnetic particles) for multimodal applications. | Real-time in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) monitoring of delivery and gene silencing. |
Why Choose Our Services?
Platform Diversity
We are proficient in all major nonviral vector systems, including lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), polymer nanoparticles, exosomes, and inorganic vectors.
Microfluidic Formulation
We utilize advanced microfluidic mixing technology to produce LNPs, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency and precise control of nanoparticle size (crucial for biodistribution).
Comprehensive Characterization
Each custom formulation undergoes rigorous characterization, including dynamic light scattering, zeta potential, and efficient encapsulation and release kinetics analysis.
Success Stories
We have successfully collaborated with numerous biopharmaceutical companies and academic institutions, advancing drug candidates from the discovery stage to preclinical development.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What types of RNAi payloads can your custom nanoparticles deliver?
A: Our services support a variety of nucleic acid therapies, including siRNA, microRNA (miRNA) mimics/inhibitors, antisense oligonucleotides (ASO), and mRNA. The nanoparticle scaffolds are specifically optimized for the physicochemical properties of the payload.
Q: Can you develop nanoparticles targeting non-hepatic sites?
A: Absolutely. While lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are naturally hepatic-oriented, a key advantage of our custom services lies in integrating active targeting ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides) to achieve delivery to extrahepatic tissues such as tumors, lungs, and the central nervous system (CNS).
Q: How does your custom service ensure low immunogenicity?
A: We prioritize the use of biocompatible and biodegradable components, such as ionizable lipids and natural polymers. Furthermore, precise control over PEGylation strategies and particle size is crucial for minimizing nonspecific immune activation. We offer in vitro cytokine release assays.
Q: What is your typical project cycle from project initiation to obtaining initial data?
A: For standard in vitro proof-of-concept projects, we can typically provide initial formulation and gene silencing data within 4-8 weeks.
Q: Can you prepare nanoparticles for delivery to organs other than the liver?
A: Absolutely. While lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are naturally liver-oriented, we employ advanced targeting strategies, utilizing peptides, antibodies, and other ligands to direct particles to the lungs, brain, tumors, and immune cells.
Q: Besides siRNA, do you research other RNA types?
A: Yes, our platform is suitable for miRNA mimics/inhibitors, mRNA, and ribonucleoproteins.
Connect with Us Anytime!
The therapeutic potential of RNAi is directly linked to the efficiency of its delivery system. Creative Biolabs' RNAi delivery custom nanoparticle service boasts cutting-edge technology and a flexible platform for building next-generation nanocarriers. Our expertise in balancing stability, specificity, and cellular accessibility makes us a key partner in achieving highly efficient gene-silencing molecules into targeted drugs, ultimately benefiting the global fields of genomics and personalized medicine. Contact us today for a quotation or any question. Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day!
Reference
- Tsakiri M, Zivko C, Demetzos C, et al. Lipid-based nanoparticles and RNA as innovative neuro-therapeutics. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2022, 13: 900610. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.900610 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
