Development of Stem Cells as Gene Delivery System
The use of stem cells as carriers for therapeutic genes is a novel delivery option for gene therapy. With the comprehensive and advanced stem cell platform, Creative Biolabs provides sundry types of modified stem cells from a variety of sources for delivering therapeutic genes to meet the demands of customers around the world.
Industry Limitations and Solutions
Limitations of Traditional Therapies
❌ Small molecule drugs cannot penetrate the blood-brain barrier (<500 Da penetration rate <1%)
❌ Viral vectors pose immunogenicity risks (30% of patients develop neutralizing antibodies)
❌ Passive targeting results in tumor tissue accumulation rate <0.7%
Breakthrough in Cell Delivery Systems
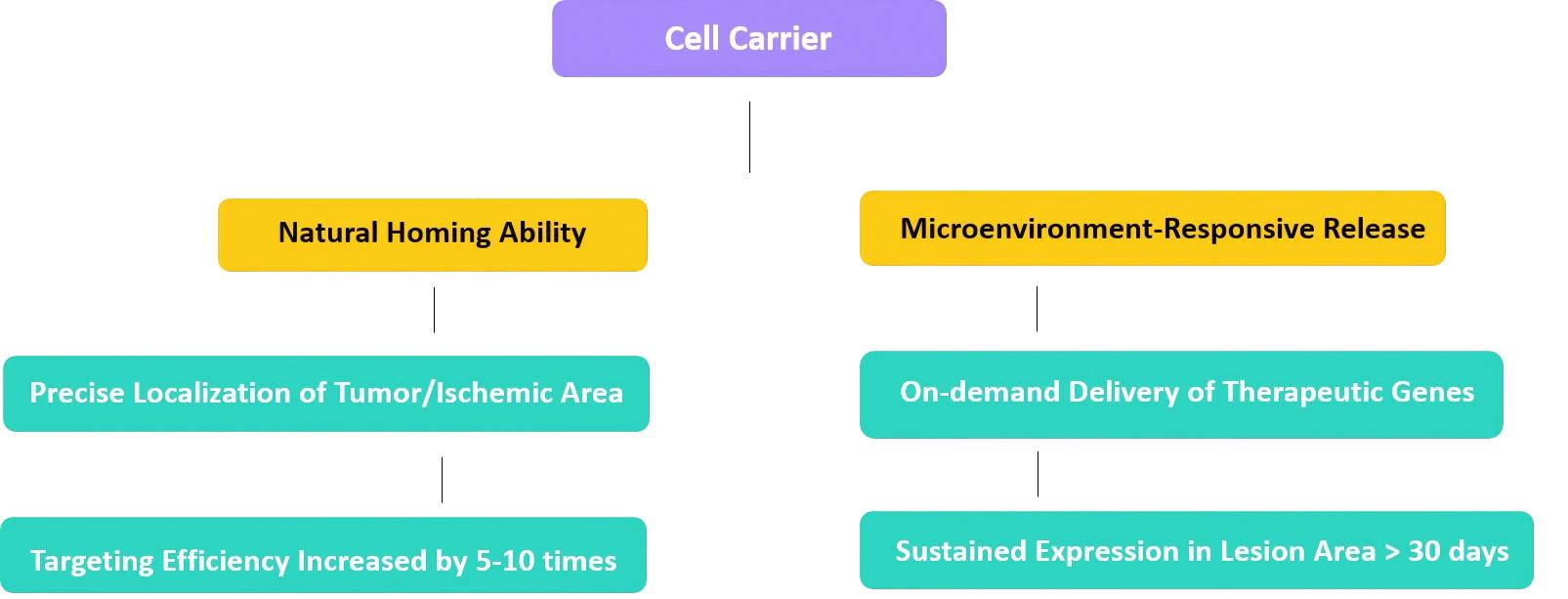
Why Choose Stem Cells for Gene Delivery?
The characteristics of stem cells also make them naturally predisposed to gene delivery. The main advantages are as follows:
Automatic positioning of the target and the act of docking:
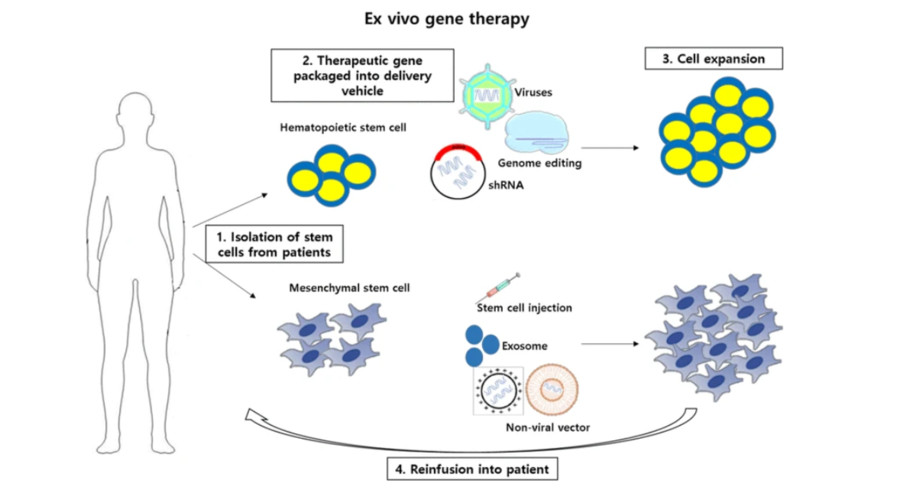 Figure 1 Ex vivo stem cell gene therapy.1
Figure 1 Ex vivo stem cell gene therapy.1
-
Inherent Targeting & Engraftment
Stem cells have the remarkable ability to home in on damaged or diseased areas. For example, neural stem cells can home in on brain tumors, while mesenchymal stem cells have a high affinity for damaged tissues. After homing to the target location, they can be stably implanted and have long survival, so that the long-term sustained therapeutic gene expression can be realized directly in the area where it is needed the most, which can further improve the delivery accuracy and effect. of gene. -
Immune characteristics regulation
In contrast to many viral vectors, stem cells have lower immunogenicity. This minimizes the immune response of the host as much as possible and is safer for therapeutic use. In addition, some types of stem cells have the inherent characteristics of immune regulation. They can actively play a role in the immune response by reducing inflammation and promoting tissue repair in the body. The immune regulation and gene therapy synergistic effect can bring about a significant therapeutic effect. -
Self-updating and differentiation potential
The self-renewal of stem cells can support their massive production to meet the needs of clinical use, and solve the important bottleneck of production capacity. In addition to this, the modified stem cells have the potential for multi-directional differentiation. This means that therapeutic genes can be accurately delivered directly to the affected tissues and cells, and be fully integrated into the body's own repair and regeneration process.
What We Offer?
At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of this exciting field, dedicated to developing complex stem cell-mediated gene delivery platforms that have the potential to open up new therapeutic pathways for various stubborn diseases. This article delves into the scientific foundation, diverse applications, and cutting-edge services provided by Creative Biolabs in this transformative field.
- Custom Gene Delivery System Development
- Stem Cell Sourcing & Expansion
- Gene Editing & Vector Production
- Pre-clinical Research & Development Support
Stem Cells as Vehicles for Gene Therapy
Stem cells contribute to multiple tissues, including bones, cartilages, skeletal muscles, the meniscus, tendons, ligaments, the labrum, neural system, and heart, etc. Combined delivery of stem cells with various therapeutic agents to target specific tissues or organs has the potential to enhance, modulate or initiate repair processes locally or systematically. Creative Biolabs provides various genome editing tools based on recombinant technology such as transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) and the clustered regularly interspersed short tandem repeat (CRISPR)/Cas system.
Stem Cell Types as Gene Delivery System
| Cell Types | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Mesenchymal (MSC) | The mesenchymal (MSC) is an ideal vehicle for cell-based therapies by introducing beneficial genes. MSC has the ability to differentiate into a variety of cell types, including bones, cartilage, adipose (fat) tissues, muscles and marrow stroma. |
| Neural Stem Cells (NSC) | Neural stem cells (NSC) primarily differentiate into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, thus they can serve as vehicles for gene therapy and replace the neurons lost due to injury or diseases. |
| Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) | IPSC is a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be directly generated from adult cells. They have the ability to differentiate into any cell type in the body, providing enormous therapeutic potential |
Partnership Benefits: Why Collaborate with Us?
Choosing Creative Biolabs as a partner means choosing innovation, reliability, and expertise.
- Accelerate R&D: Utilize our profound scientific knowledge and advanced technology to significantly accelerate your treatment plan and bring your discoveries to patients faster.
- Customized solutions: We believe in a customized approach. Our strategy has been carefully customized to meet your unique research and development needs, ensuring a perfect fit with your project.
- Seamless translation: Our comprehensive expertise covers the entire development process from the workbench to the clinic. We provide comprehensive support, considering regulatory factors from the beginning and seamlessly guiding your project to complete each stage.
- Risk mitigation: We are committed to strict quality control and robust, validated methods that help minimize development risks and ensure the maximum success of your valuable projects.
- Professional scientific support: directly contact our top scientists and expert team. We provide unparalleled scientific guidance and collaborative support at every step, promoting genuine partnerships.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What kinds of genetic modification can you perform on stem cells?
A: We offer a range of genetic modification services, including stable delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN, and efficient transduction with optimised viruses (eg lentivirus, AAV) and non-viral vectors for transient or sustained gene expression.
Q: What kind of stem cells have you worked with (MSCs, iPSCs)?
A: We have a lot of experience working with various kinds of stem cells, including MSCs, iPSCs, NSCs for a range of therapeutic applications.
Q: How do you ensure the safety and efficacy of your gene delivery?
A: We have stringent quality control (genetic stability testing, functional testing) as well as GMP compliant manufacturing at multiple levels to ensure that our gene delivery solution is both safe and effective.
Q: Which type of stem cell is most commonly used in gene delivery applications?
A: Although multifunctionality depends on the specific situation, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can be said to be the most universal due to their pluripotency. They can be genetically modified to carry therapeutic genes and then differentiate into almost any cell type required for tissue repair or targeted therapy, providing an autologous source that is not affected by ethical issues related to embryonic stem cells. However, their tumorigenic potential and complex differentiation strategies require careful management.
Get in Touch Today!
At Creative Biolabs, we believe that stem cells are a revolutionary platform that can overcome these challenges. By utilizing their unique biological characteristics - their ability to locate specific tissues, self-renew, and differentiate - we are taking the potential of gene therapy to unprecedented levels. Our commitment to innovation drives us to break through the boundaries of therapeutic development and provide more precise, durable, and safe solutions. If you have any questions or have any difficulties, you can contact us by email or send us an inquiry to find a complete solution.
Reference
- Yong S B, Chung J Y, Song Y, et al. Recent challenges and advances in genetically-engineered cell therapy. Journal of pharmaceutical investigation, 2018, 48(2): 199-208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0381-1. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
