EIF4G2 and Associated Diseases
Founded by outstanding scientists with decades of research experience in science, Creative Biolabs is focused on giving you a deeper understanding of gene therapy and providing end-to-end and custom solutions. Our award-winning team will provide you with the service to address all aspects of your complex problem.
Overview of EIF4G2
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 2 (EIF4G2; also known as p97, NAT1, and DAP-5) is a human protein encoded by the EIF4G2 gene and plays an important role in translation. The translation is initiated by the specific recognition between the cap structure and a cap-binding protein complex which consists of three subunits: eIF4A, eIF4E, and eIF4G. The EIF4G2 gene product shares similar binding sites for eIF4A and eIF3 with the C-terminal region of eIF4G1 which supports translation in cap-dependent and independent pathways. The EIF4G2 gene product functions as a general translation repressor by forming translationally inactive complexes.
EIF4G2 in Disease
EIF4G2 protein plays a critical role in cancer, inflammation, the development of cartilage, and immune infiltration.
- Osteoarthritis
The miR-197/EIF4G2 axis influences chondrocyte migration, proliferation, and inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA). The expression of EIF4G2 mRNA is higher in OA cartilage tissues than in healthy cartilage tissues. High-level EIF4G2 protein is related to the pathogenesis of OA. The expression of miR-197 is significantly down-regulated in the OA cartilage tissues. Overexpression of miR-197 can regulate cell migration, and growth and inhibit inflammation in chondrocytes by directly targeting EIF4G2 mRNA, whereas knockdown of miR-197 induces the expression of inflammatory mediators such as IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. EIF4G2 overexpression can reverse the effects caused by miR-197 mimics. The miR-197/EIF4G2 axis indicates the potential therapeutic targets for OA treatment.
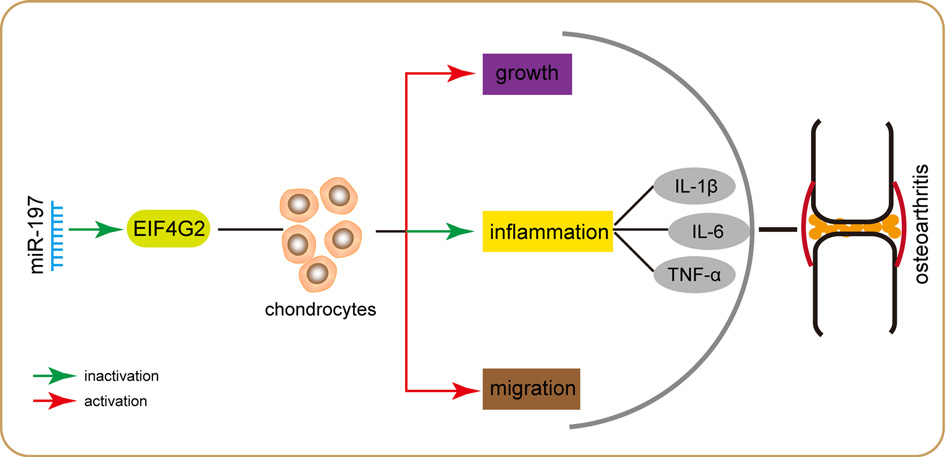 Fig.1 miR-197 promotes cell growth migration and inhibits inflammation in chondrocytes by directly targeting EIF4G2. (Gao, 2020)
Fig.1 miR-197 promotes cell growth migration and inhibits inflammation in chondrocytes by directly targeting EIF4G2. (Gao, 2020)
- Gastric cancer
EIF4G2 is associated with the occurrence and pathogenesis of gastric cancer (GC). The expression of EIF4G2 is upregulated in GC tissues compared to normal tissues. Elevated expression of EIF4G2 modulates tumor immune infiltration and high infiltration of macrophages or tumor-associated macrophage is associated with invasion and metastasis, which indicates an unfavorable and poor prognosis. The hsa-miR-26a-5p is negatively correlated with EIF4G2. TUG1 is positively correlated with EIF4G2 and negatively correlated with hsa-miR-26a-5p. Thus, the TUG1/hsa-miR-26a-5p/EIF4G2 axis is the potential upstream regulatory pathway of EIF4G2 in GC.
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 2 (EIF4G2) is widely distributed and critical for many physiological processes. Creative Biolabs has a team of professionals majoring in gene therapy and is well-equipped to serve our clients. We provide one-stop disease-specific gene therapy development solutions. Please feel free to contact us for more about your EIF4G2 project.
References
- Gao, S.; et al. MicroRNA-197 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, migration, and inflammation in pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by targeting EIF4G2. Bioscience Reports. 2020, 40(9): BSR20192095. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Fu, L.; et al. High Expression of EIF4G2 Mediated by the TUG1/Hsa-miR-26a-5p Axis Is Associated with Poor Prognosis and Immune Infiltration of Gastric Cancer. Journal of Oncology. 2022, 2022: 1–25. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
