Development of Mitochondrial Targeting LNP
Mitochondrial-targeting lipid nanoparticles represent a revolutionary precision medicine platform capable of directly treating diseases caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Strategically integrating advanced lipid formulations with mitochondrial-specific targeting ligands can create nanocarriers capable of overcoming complex biological barriers and reaching intracellular targets. Creative Biolabs is dedicated to leading these advancements, providing robust, scalable, and scientifically rigorous solutions for the most challenging biomedical discoveries.
Mitochondria Overview
Mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell," are crucial hubs for cellular metabolism, apoptosis, and signal transduction. Mitochondrial dysfunction is closely linked to a variety of human diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, effective therapeutic interventions require the precise delivery of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs)—whether small molecules, nucleic acids, or peptides—to the mitochondrial matrix or intermembrane space. The development of mitochondrial-targeting lipid nanoparticles (MT-LNPs) represents a significant advance in nanomedicine, providing a highly biocompatible and scalable platform for this challenging task.
Introduction to Mitochondrial Targeting LNP
The targeted delivery of an engineered gene or gene product to the mitochondrion is a critical first step in the therapeutic restoration of a lost cellular function. Mitochondrial targeting lipid-based nanoparticle (LNP) is a nanoparticle technology that delivers medicament or therapeutic material to the mitochondria of cells. The use of such systems entails extremely targeted delivery to cellular mitochondria, opening up new avenues for improving mitochondrial function and treating mitochondria-related illnesses. Features of mitochondrial targeting LNP include:
- Highly Selective
The Mitochondrial targeting LNP delivers to mitochondria with great selectivity, owing to its unique lipid structure.
- Biocompatibility
The Mitochondrial targeting LNP contains biocompatible lipids, lowering the risk of cytotoxicity and immunological responses.
- Efficient Delivery
The Mitochondrial targeting LNP can provide efficient drug delivery, ensuring that active components reach the mitochondria.
Application of Mitochondrial Targeting LNP
Mitochondrial-targeting lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are primarily used to successfully deliver drugs or therapeutic substances into cellular mitochondria for the treatment of mitochondrial diseases, antioxidant therapy, gene therapy, and cancer treatment. MITO-Porter is a mitochondrial-targeting LNP system with a surface modified with a high concentration of octarginine (R8). Cells absorb R8 through micropinocytosis. R8 can be released from macropinocytosomes into the cytosol, thereby preventing lysosomal degradation. MITO-Porter in the cytosol can connect to mitochondria through electrostatic interactions with R8. The encapsulated substance is transported into the mitochondria via membrane fusion. The following are two applications of MITO-Porter:
1. Coenzyme Q10-MITO-Porter
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a well-known antioxidant and a coenzyme for ATP production in mitochondria. The CoQ10-mitochondrial delivery carrier (CoQ10-MITO-Porter) is a mitochondrial-targeting lipid nanoparticle (LNP) encapsulating coenzyme Q10. Figure 1 illustrates the antioxidant effects of coenzyme Q10 delivery via targeted mitochondrial delivery in vivo.
2. Berberine-Mitochondrial Delivery Carrier (BBR-MITO-Porter)
Berberine (BBR) is a plant molecule that acts on the mitochondrial respiratory chain, triggering mitochondrial stress responses. Its therapeutic effect lies in regulating metabolism. Figure 2 shows a mitochondrial-targeting LNP that efficiently delivers BBR to mitochondria, thereby increasing BBR accumulation in mitochondria. Increased BBR content in mitochondria is crucial for enhancing pharmacological effects.
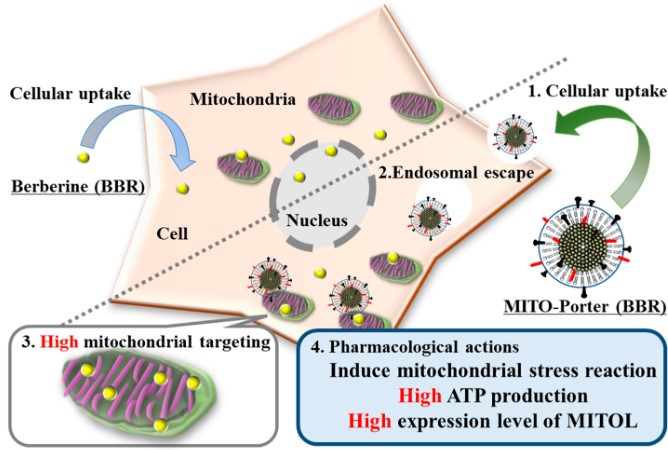 Figure.1 A schematic image depicting the mitochondrial delivery of BBR via the mitochondrial targeting LNP.1
Figure.1 A schematic image depicting the mitochondrial delivery of BBR via the mitochondrial targeting LNP.1
Synthesis of Mitochondrial Targeting LNP
The synthesis of mitochondrial targeting LNPs involves liposome synthesis, surface modification, and nucleic acid packaging.
-
LNP Synthesis
The first step in synthesizing LNPs is selecting the appropriate lipid component. This may include Ionizable lipids, helper lipids, cholesterol, and PEG-lipids to ensure the structure and stability of the LNP. They are mixed in a solvent so that they can self-assemble into nanoparticle structures. -
Surface Modification
For LNP to target mitochondria, specific molecules, often called targeting ligands, need to be introduced on its surface, such as Triphenylphosphonium (TPP), which is a mitochondria-targeting fragment that is coupled to phospholipids and assembled into mitochondria-targeted LNP. These ligands can selectively interact with molecules on the mitochondrial surface to achieve precise mitochondrial targeting. -
Nucleic acid Packaging
If mitochondrial targeting LNPs are utilized to transport oligos (such as siRNA or mRNA), they must be encapsulated within the lipid-based vector.
Types of Mitochondrial Targeting Lipid Nanoparticle
MT-LNPs are classified based on the nature of their constituent components, particularly the mechanisms by which they achieve mitochondrial tropism.
Delocalized Lipophilic Cations (DLC)-coupled LNPs
This is currently the most prevalent type, utilizing the inherent negative membrane potential of mitochondria. DLCs are chemically coupled to lipid components before assembly. This results in a dense distribution of TPP groups on the LNP surface, ensuring efficient passive accumulation into the mitochondria after internalization.
Peptide-mediated Targeting
In addition to simple cations, specific peptides known to interact with mitochondrial surface proteins (e.g., components of OMM translocases/introduction mechanisms) can be coupled to the LNP surface. This approach provides a more active targeting mechanism and may have higher specificity.
pH and Redox-responsive Lipid Nanoparticles
These lipid nanoparticles are designed to release their payload only upon encountering the unique microenvironment of diseased cells.
- pH-sensitive
- Redox-sensitive
Our Services
Creative Biolabs is a leading provider of custom nanomedicine development services, specializing in the precise design of MT-LNPs for partners in academia and industry. We offer end-to-end solutions from initial target identification to in vivo validation.
-
Custom Design and Optimization of Mitochondrial LNPs
We offer comprehensive mitochondrial-targeted LNP design services to meet your specific therapeutic needs. Our approach begins with a detailed consultation to understand your target application, payload characteristics, and delivery requirements. We possess a rich library of ionizable lipids and targeting ligands, enabling systematic screening to determine the optimal combination for your specific mitochondrial delivery application. -
In Vitro and In Vitro Evaluation
Rigorous biological evaluation is crucial for validating mitochondrial targeting efficiency and therapeutic potential. We offer comprehensive in vitro testing services utilizing cell culture models relevant to your disease application. For further validation, we offer in vivo testing services in suitable animal models, including biodistribution studies, efficacy assessments in disease models, and preliminary safety assessments. -
Analytical and Characterization Services
Complete physicochemical characterization is fundamental to the successful development of mitochondrial-targeted lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). We employ state-of-the-art analytical techniques to comprehensively characterize the properties of nanoparticles, including dynamic light scattering for particle size distribution and polydispersity index determination, laser Doppler electrophoresis for zeta potential determination, and the RiboGreen assay for nucleic acid payload encapsulation efficiency determination.
Our Analysis Methods
Creative Biolabs employs a range of advanced analytical and biological methods to ensure the highest quality and scientific rigor in the development of MT-LNP.
Physicochemical Analysis
- Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Electrophoretic Light Scattering (ELS)
- Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Biological Evaluation
- Live-Cell Confocal Microscopy
- Flow Cytometry (FACS)
- Mitochondrial Respiration Assay
- Cytotoxicity Analysis
Why Choose Our Services?
Creative Biolabs possesses unique strengths in mitochondrial nanomedicine, making it your ideal partner and offering the following significant competitive advantages:
- Our team comprises PhD-level nanomedicine experts with decades of collective experience in organelle-targeted delivery systems.
- Our well-established and optimized protocols, along with advanced microfluidic technologies, significantly shorten the discovery and optimization phase, enabling our clients to reach preclinical milestones faster.
- All synthesis and characterization work adheres to stringent quality control standards.
- We possess a large proprietary library of novel ionizable lipids and TPP analogs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the minimum API dosage required for the initial MT-LNP feasibility study?
A: We recommend using at least 50 mg of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) for initial formulation screening and optimization. This is sufficient to provide enough material to explore a range of lipid profiles and complete preliminary physicochemical characterization. For highly efficient or rare molecules, we can design specialized nanoscale screening protocols.
Q: How can we confirm that the LNP has reached the mitochondria and is not just located in the cytoplasm?
A: We employ advanced colocalization research techniques, using live-cell confocal microscopy for analysis. We label the LNP (e.g., using a lipophilic fluorescent tracer) and use a validated fluorescent dye sensitive to mitochondrial potentials to specifically label functional mitochondria. The overlap coefficient (e.g., Pearson correlation coefficient) is then quantitatively calculated to definitively confirm LNP binding to mitochondria and distinguish it from general cytoplasmic accumulation.
Q: Can your MT-LNP be designed for systemic administration (in vivo)?
A: Absolutely. Our formulation is designed with cyclic stability in mind. We optimized the use of polyethylene glycol (PEG) lipids (typically 1.5–2.0 mol%) to form a hydrated shell around the particles, thereby minimizing opsonization and maximizing systemic circulating half-life. Furthermore, we strictly controlled the particle size to less than 150 nm, which facilitates passive accumulation in tumor tissue through enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effects prior to internalization and subsequent mitochondrial targeting.
Q: What is the typical timeframe for developing a lead MT-LNP drug candidate?
A: The timeframe for a typical novel MT-LNP development project, from initial consultation to delivery of a characterized and in vitro validated lead compound, depends on the complexity of the active pharmaceutical ingredient and the scope of required biological testing.
Connect with Us Anytime!
Creative Biolabs is committed to providing high-quality mitochondrial targeting LNP services to customers globally. For more extensive information, please contact us and request a price. We will contact you within 24 hours.
Reference
-
Hori, Ikuma, Hideyoshi Harashima, and Yuma Yamada. "Development of a Mitochondrial Targeting Lipid Nanoparticle Encapsulating Berberine." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.2 (2023): 903. 10.3390/ijms24020903
(Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
