Introduction of KCNS1
KCNS1, the full protein name of which is potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily S member 1, is encoded by the KCNS1 gene in humans. It is a voltage-gated potassium channel subunit and biased expressed in brain, gallbladder, and 3 other tissues. This potassium channel subunit does not form functional channels by itself, but it can form functional heteromeric channels with KCNB1 and KCNB2 to modulate the delayed rectifier voltage-gated potassium channel activation and deactivation rates of KCNB1 and KCNB2.
| Basic Information of KCNS1 | |
| Protein Name | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily S member 1 |
| Gene Name | KCNS1 |
| Aliases | Delayed-rectifier K(+) channel alpha subunit 1, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv9.1 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | Q96KK3 |
| Transmembrane Times | 6 |
| Length (aa) | 526 |
| Sequence | MLMLLVRGTHYENLRSKVVLPTPLGGRSTETFVSEFPGPDTGIRWRRSDEALRVNVGGVRRQLSARALARFPGTRLGRLQAAASEEQARRLCDDYDEAAREFYFDRHPGFFLSLLHFYRTGHLHVLDELCVFAFGQEADYWGLGENALAACCRARYLERRLTQPHAWDEDSDTPSSVDPCPDEISDVQRELARYGAARCGRLRRRLWLTMENPGYSLPSKLFSCVSISVVLASIAAMCIHSLPEYQAREAAAAVAAVAAGRSPEGVRDDPVLRRLEYFCIAWFSFEVSSRLLLAPSTRNFFCHPLNLIDIVSVLPFYLTLLAGVALGDQGGKEFGHLGKVVQVFRLMRIFRVLKLARHSTGLRSLGATLKHSYREVGILLLYLAVGVSVFSGVAYTAEKEEDVGFNTIPACWWWGTVSMTTVGYGDVVPVTVAGKLAASGCILGGILVVALPITIIFNKFSHFYRRQKALEAAVRNSNHQEFEDLLSSIDGVSEASLETSRETSQEGQSADLESQAPSEPPHPQMY |
Function of KCNS1 Membrane Protein
KCNS1, it contributes to M-type current through associating with KCNQ3 to form a potassium channel. This slowly activating and deactivating potassium conductance plays a critical role in determining the subthreshold electrical excitability of neurons. It is important in the regulation of neuronal excitability. In addition, KCNS1 is associated with molecular diversity of a heterogeneous population of M-channels. They are various in kinetic and pharmacological properties, which can induce this physiologically important current. It’s insensitive to tetraethylammonium, but suppressed by barium, linopirdine and XE991. It can be activated by the anticonvulsant retigabine and niflumic acid. As the native M-channel, the potassium channel composed of KCNQ3 and KCNS1 is also suppressed by activation of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor CHRM1. Except for these functions, KCNS1 can act as one of the first prognostic indicators of chronic pain risk. Moreover, KCNS1 in the periphery may play a functional role in ameliorating mechanical and cold pain in chronic states.
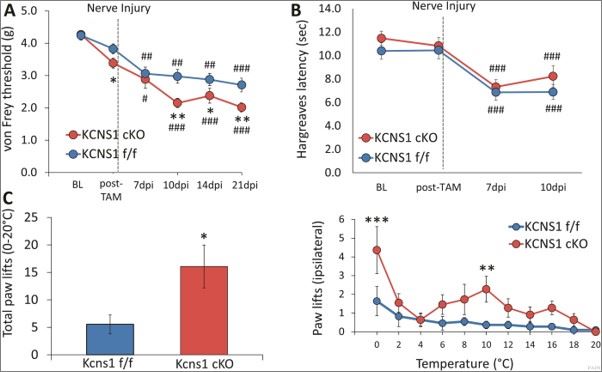 Fig.1 Peripheral Kcns1 deletion triggers exaggerated pain phenotypes after nerve injury. (Tsantoulas, 2018)
Fig.1 Peripheral Kcns1 deletion triggers exaggerated pain phenotypes after nerve injury. (Tsantoulas, 2018)
Application of KCNS1 Membrane Protein in Literature
This article suggests that restoring Kcns1 function in the periphery may be of some use in ameliorating mechanical and cold pain in chronic states.
This article shows that KCNS1 is associated with GCH1 with pain intensity in black Southern Africans with HIV-associated sensory neuropathy.
This study shows the KCNS1 allele rs734784 as one of the first prognostic indicators of chronic pain risk.
This article shows that specific inter-subfamily assembly between rKv3.4 with rKv9.3 or rKv9.1 is controlled by the hydrophobic core but not by the amino-terminal domain.
This article reveals that Kv9.1 and Kv9.2 are colocalized with Kv2.1 and/or Kv2.2 alpha subunits in several regions of the brain. Also, this article shows that neither Kv9.1 nor Kv9.2 have K+ channel activity by themselves, but both can modulate the activity of Kv2.1 and Kv2.2 channels by changing kinetics and levels of expression and by shifting the half-inactivation potential to more polarized values.
KCNS1 Preparation Options
We provide custom membrane protein preparation services for worldwide customers. Leveraging by our advanced Magic™ membrane protein production platform, we are able to present target membrane protein in multiple active formats. Our professional scientists are happy to help you find an ideal method and make your project a success.Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-KCNS1 antibody development services.
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality membrane protein preparation service to facilitate the development of worldwide customer’s research. During the past years, we have successfully established a powerful Magic™ membrane protein platform which enables us to provide a series of membrane protein preparation services. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.