Thrombin binding to its aptamer is the most frequently used model system to demonstrate the proof-of-concept of the aptamer-based affinity assays. The advantages of specific binding affinity, various binding sites, the availability of two aptamers each targeting a specific site, switching of aptamer structures triggered by binding to thrombin, and the catalytic activity of thrombin are the major reasons why thrombin is often selected as a test model. Keeping pace with the market, Creative Biolabs provides one-stop anti-thrombin aptamer development, maturation, and modification services for our honor clients. Aptamer binding assays are also available for you.
Thrombin Introduction
Thrombin is a serine protease that selectively cleaves peptide substrates at Arg residues. With vital roles in physiological and pathological coagulation, thrombin is involved in different diseases. Thrombin is not present in blood under normal conditions. Only after vascular injury, thrombin is rapidly generated from inactive zymogen prothrombin by a series of enzyme cleavages. During coagulation, the concentration of thrombin may vary from pM to μM levels. Therefore, sensitive and specific detection of thrombin assays is important for related disease diagnostics. Immunoassays, clotting-based assays, and enzymatic activity-based assays have been developed for the detection and quantification of thrombin in the blood. Most of the assays for human thrombin deal with the intact α-thrombin which can be proteolyzed to form β-thrombin and γ-thrombin.
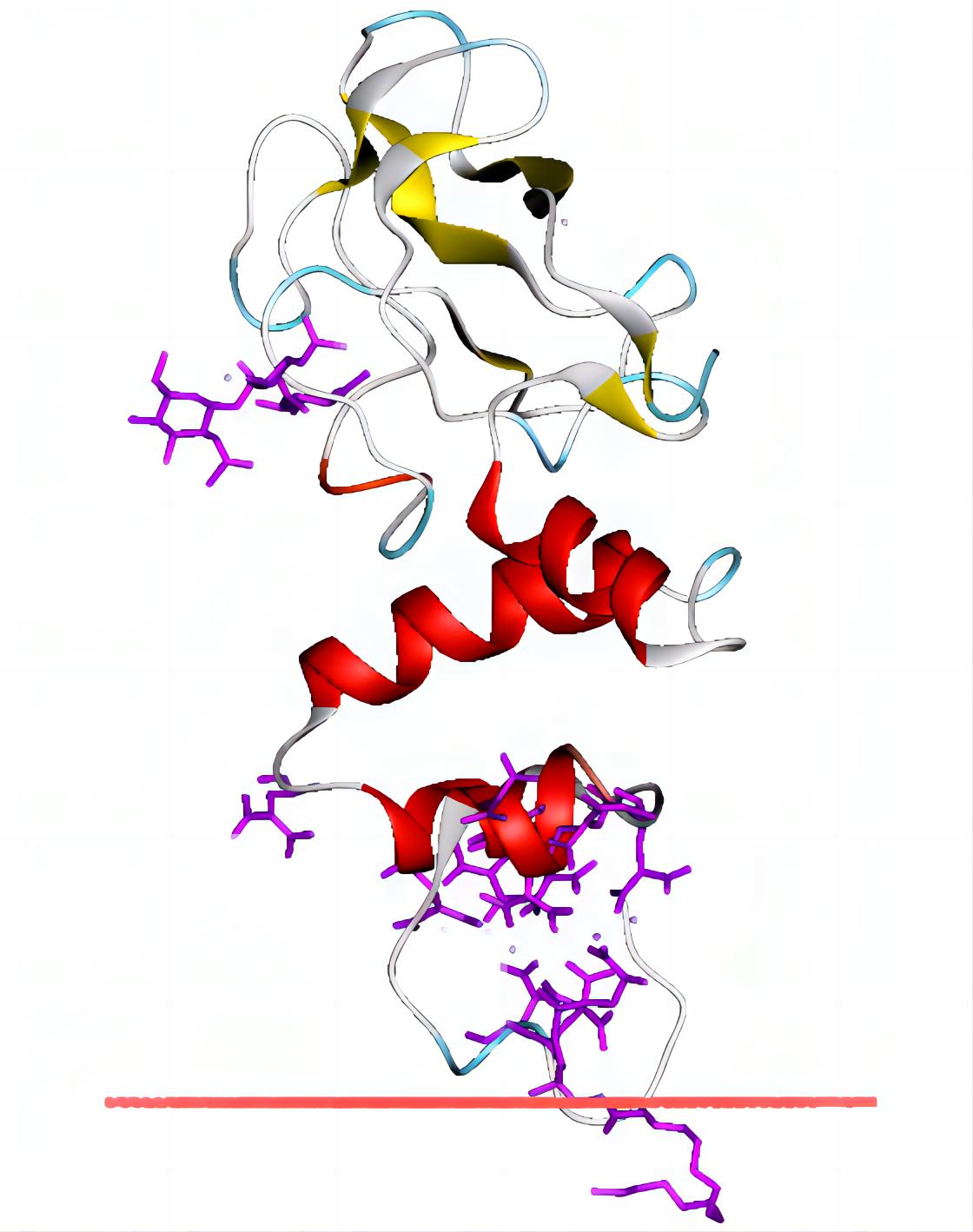 Fig.1 Anchoring bovine prothrombin to the membrane via its Gla domain. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Anchoring bovine prothrombin to the membrane via its Gla domain. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Anti-Thrombin Aptamers
Two DNA aptamers are widely used in aptamer-based assays for thrombin. Apt-15 (5’-GGTTGGTGTGGTTGG-3’) binds with the fibrinogen binding site of thrombin with a Kd around 100 nM, and Apt-29 (5’-AGTCCGTGGTAGGGCAGGTTGGGGTGACT-3’) can bind to the heparin binding site of thrombin with a Kd around 0.5 nM.
 Fig.2 Thrombin and two frequently used aptamers. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.2 Thrombin and two frequently used aptamers. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Detection Approaches
In recent years, different methods have been developed for thrombin detection such as aptamer-based strip biosensor, electrochemical aptasensor, homogeneous assays based on beacons, nanomaterial-assisted assays, and so forth. Besides the traditional strategy using intact aptamer, split aptamer fragments could also be used for thrombin detection. One part is labeled with fluorescein and another part is oligonucleotide sequence. When thrombin was introduced into the system, a target-induced G-quadruplex forms with two split aptamer fragments and thrombin. Moreover, label-free aptasensor system could also be used for thrombin detection.
Platform & Features
- Label-free detection platform
- Aptamer based microsphere biosensor
- Engineered aptamers
- Short oligonucleotides- easy and inexpensive to synthesize and modify.
- Mature DNA aptamer development technology
- Advanced RNA aptamer development approach
The coupling of thrombin aptamer to different transduction principles has demonstrated the wide applicability of aptamers as bioreceptors in bioanalytical assays. If you are interested in aptamers for thrombin detection, please feel free to contact us for more information or a detailed quotation.
Published Data
1. Aptamer-Functionalized Smart Photonic Hydrogels for Thrombin Detection in Human Serum
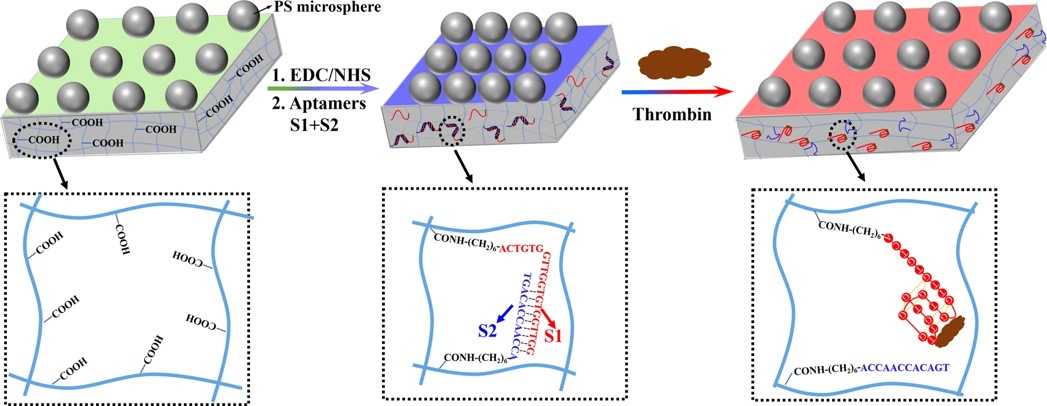 Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the fabrication and detection mechanism of the 2DPCH aptasensors for thrombin.1
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the fabrication and detection mechanism of the 2DPCH aptasensors for thrombin.1
Researchers developed a two-dimensional photonic crystal (2DPC) hydrogel aptasensor for thrombin detection in human serum. The sensor, functionalized with partially complementary aptamers, swelled upon exposure to thrombin, causing an increase in the 2DPC particle spacing. This change was detected by measuring the diameters of the Debye rings diffracted by the 2DPCs, eliminating the need for complex instruments. The swelling was due to decreased hydrogel cross-linking density from specific aptamer-thrombin binding and increased mixing free energy upon thrombin introduction. The optimized aptasensor showed a linear response to thrombin concentrations between 1–500 nM, with a detection limit of 0.64 nM. When applied to human serum, the sensor demonstrated recoveries of 95.74-104.21% and a relative standard deviation of 2.52-6.58%, confirming the sensor's accuracy and practicality. This 2DPC hydrogel aptasensor offers a novel approach for developing sensitive aptasensors and holds potential for use in home diagnostic kits.
2. Development of Sandwich Aptamer Microarray for Human Thrombin Detection
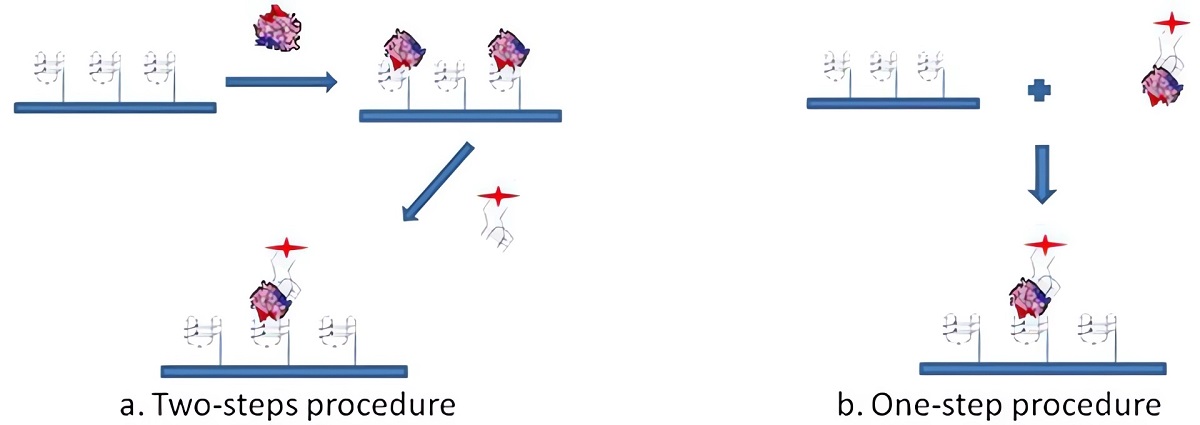 Fig.4 Representation of the SAM for thrombin detection.2
Fig.4 Representation of the SAM for thrombin detection.2
In this study, researchers developed an aptamer-based microarray for detecting human thrombin using two non-overlapping DNA aptamers that target different exosites on the protein. The thrombin-binding aptamer 1, a 15-mer, binds to the fibrinogen-binding site, while aptamer 2, a 29-mer, targets the heparin-binding domain. The Electrophoresis Mobility Shift Assay was used to analyze the binding interaction between thrombin and the modified aptamers, ensuring that chemical modifications did not interfere with aptamer-protein recognition. The validated system was applied to the aptamer microarray, and the results were consistent with solution-phase findings. This validated approach demonstrated the importance of pre-testing aptamer modifications in solution. Finally, the optimal procedure for Sandwich Aptamer Microarray (SAM) was developed, and the specificity of thrombin detection was optimized, highlighting the effectiveness of the aptasensor.
References
- Shen, Peiyan, et al. "Aptamer-functionalized smart photonic hydrogels: application for the detection of thrombin in human serum." NPG Asia Materials 14.1 (2022): 94. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Sosic, Alice, et al. "Human thrombin detection through a sandwich aptamer microarray: interaction analysis in solution and in solid phase." Sensors 11.10 (2011): 9426-9441. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.