With many advantages over other therapeutic agents such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), aptamers have recently emerged as a novel and powerful class of ligands with excellent potential for diagnostic applications. At Creative Biolabs, aptamers could be selected against various molecular targets involved in cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). With continued efforts in the development of aptamer-based diagnostics, Creative Biolabs has found its niches in CVD research. We provide a comprehensive set of aptamer generation as well as modification services against biomarkers involved in CVD for worldwide customers.
Cardiovascular Diseases and Biomarkers
In theory, aptamers can be selected for developing diagnostic tools for various diseases as long as definite targets are available. To date, DNA/RNA aptamers have been explored mainly for the diagnosis of infectious diseases, cancer, and CVDs. In the case of CVD, markers in the blood such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), C-reactive protein (CRP), myoglobin, I-homocysteine, and thrombin have been widely used to select DNA aptamer for the diagnosis of related diseases.
- Myoglobin increases after acute myocardial infarction. It is an important early marker in the urgent diagnosis of CVDs. Scientists selected DNA aptamers against myoglobin using a reported fluidic chip method. The DNA aptamer with the lowest Kd value (4.93 nM) was subjected to the development of different biosensors for the detection of myoglobin.
- CRP is a homopentameric oligoprotein. Many DNA aptamers targeting CRP have been screened and some are used to develop sensors based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology.
- DNA aptamers targeting l-homocysteine have been developed as an aptamer-AuNP sensor, in which the DNA aptamers first coil around the surface of the gold particles and release the particles after binding to the homocysteine.
- von Willebrand factor (vWF)
- Thrombin
- Factor IX
- …….
Services at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs proposes a novel methodology to synthesize high-density DNA/RNA aptamers arrays. Identified aptamers for the cardiac biomarkers will be tested for their limit of detection in human serum. To expand the universality of the assay beyond the limitations of antibodies currently used in different assays, a fluorescent protein dye could be optionally used to correlate array fluorescence intensity to biomarker concentration. A panel of aptamers has been also developed to detect specific glycosylated forms of cardiac biomarkers. Direct binding-based mode, target-induced structural switching mode, sandwich-like mode, and target-induced dissociation mode are available for sensor development. Constructs could be further evaluated in in vivo study. Detailed services include but not limited to the following:
- Anti-CVD biomarker DNA/RNA aptamers development
- Aptamer or its derivatives in vivo evaluation services
- Aptamer-based therapeutic applications assessment
- Aptamer conjugation services
Features
- Aptamer-based proteomic profiling
- Different diagnostic models
- Various CVD biomarker candidates
If you are interested in aptamer development for CVD detection, please feel free to contact us for more information or a detailed quotation.
Published Data
1. A Novel Nanostructured Black Phosphorus Aptasensor for Label-Free Myoglobin Detection
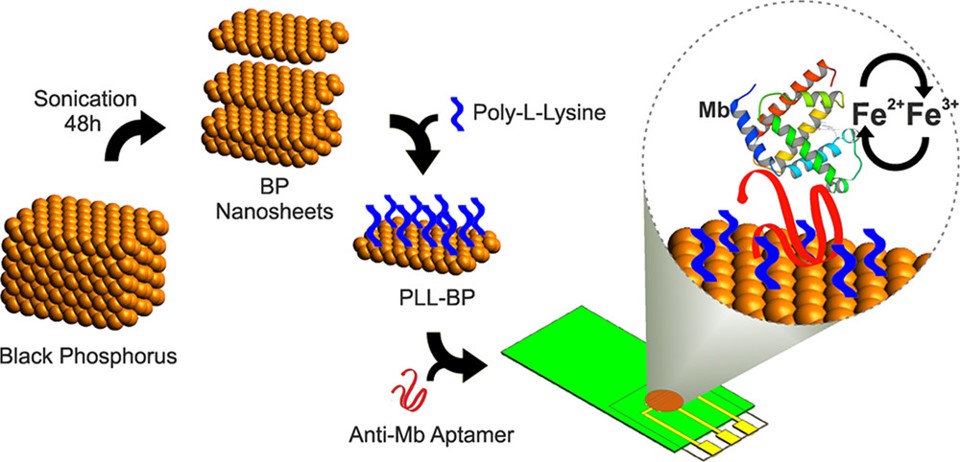 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the sensing platform based on nanostructured black phosphorus functionalized with aptamers for the detection of Mb.1,3
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the sensing platform based on nanostructured black phosphorus functionalized with aptamers for the detection of Mb.1,3
In this study, the electrochemical detection of myoglobin (Mb), a redox-active cardiac biomarker, was achieved using aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus (BP) nanostructured electrodes for direct electron transfer measurement. BP nanosheets were exfoliated in aqueous media using surfactant-assisted liquid-phase exfoliation, and poly-l-lysine (PLL) was employed to functionalize the nanosheets via noncovalent interactions, forming PLL-BP. A modified SELEX method was used to enrich DNA aptamers that specifically bind to Mb, and these aptamers were attached to the PLL-BP via Coulombic interactions. The resulting PLL-BP-based aptasensor served as a label-free electrochemical platform for Mb detection. Direct electron transfer from Mb was observed on the PLL-BP-Apt electrodes. The sensor demonstrated high specificity and sensitivity due to the combined effects of high-affinity aptamers and enhanced electrochemical properties of the nanomaterial. The platform achieved an extremely low detection limit (∼0.524 pg mL–1) with a wide dynamic range. This strategy offers potential for multiplexed CVD diagnosis in complex human samples.
2. Aptamer-Based LDL Particle Quantification
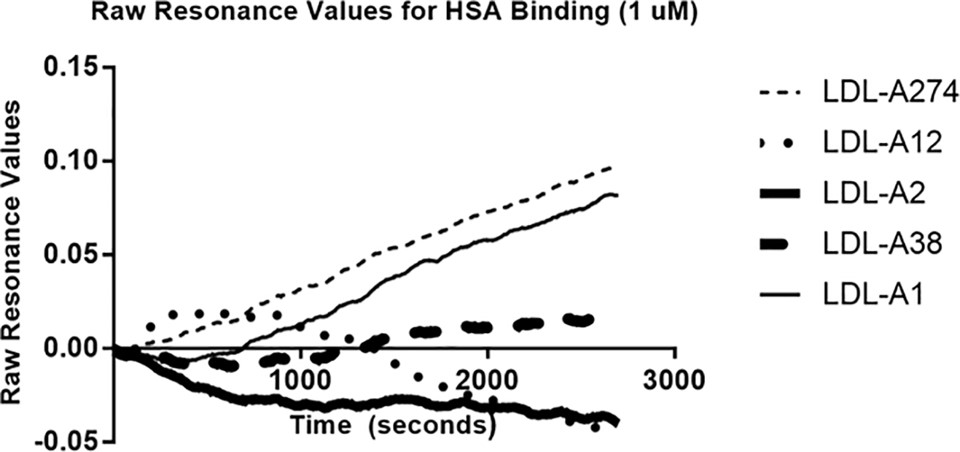 Fig.2 High affinity and specificity of aptamers binding to LDL-P in human serum.2.3
Fig.2 High affinity and specificity of aptamers binding to LDL-P in human serum.2.3
Research has shown that the LDL particle (LDL-P) number is a more sensitive indicator of CVD risk than LDL-C or HDL-C. This study described the selection of ssDNA aptamers against LDL particles using the FRELEX process and identified five ssDNA aptamers with dissociation constants in the low picomolar range, specifically targeting LDL-P and its subfractions. Additionally, a set of antisense sequences had been developed and characterized, which bound to the most effective aptamers and could be displaced by LDL-P. These aptamers and antisense sequences provide the basis for a simple, affordable diagnostic assay for CVD risk assessment.
References
- Kumar, Vinod, et al. "Nanostructured aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus sensing platform for label-free detection of myoglobin, a cardiovascular disease biomarker." ACS applied materials & interfaces 8.35 (2016): 22860-22868.
- Klapak, Daniel, et al. "Development of novel aptamers for low-density lipoprotein particle quantification." PloS one 13.10 (2018): e0205460.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.