Unremitting efforts at Creative Biolabs have been paid to validate macrophages and myeloid dendritic cells (mDCs) markers (M&DC markers) as targets to image the inflammatory process in the living organism. Creative Biolabs now provides customized single domain antibody (sdAb)-based tracer (Nanotracer) tool development services for in vivo imaging. We can also provide further validation, imaging as well as analysis services for worldwide customers.
Imaging Myeloid Cells
In a previously reported study, sdAbs were generated to recognize particular M&DC subsets. 99mTc-labeled sdAbs were used in SPECT/CT imaging studies to visualize targeted cells in naive mice, hence revealing their natural distribution in various organs. Fig.1 shows the specificity of targeting by sdAbs.
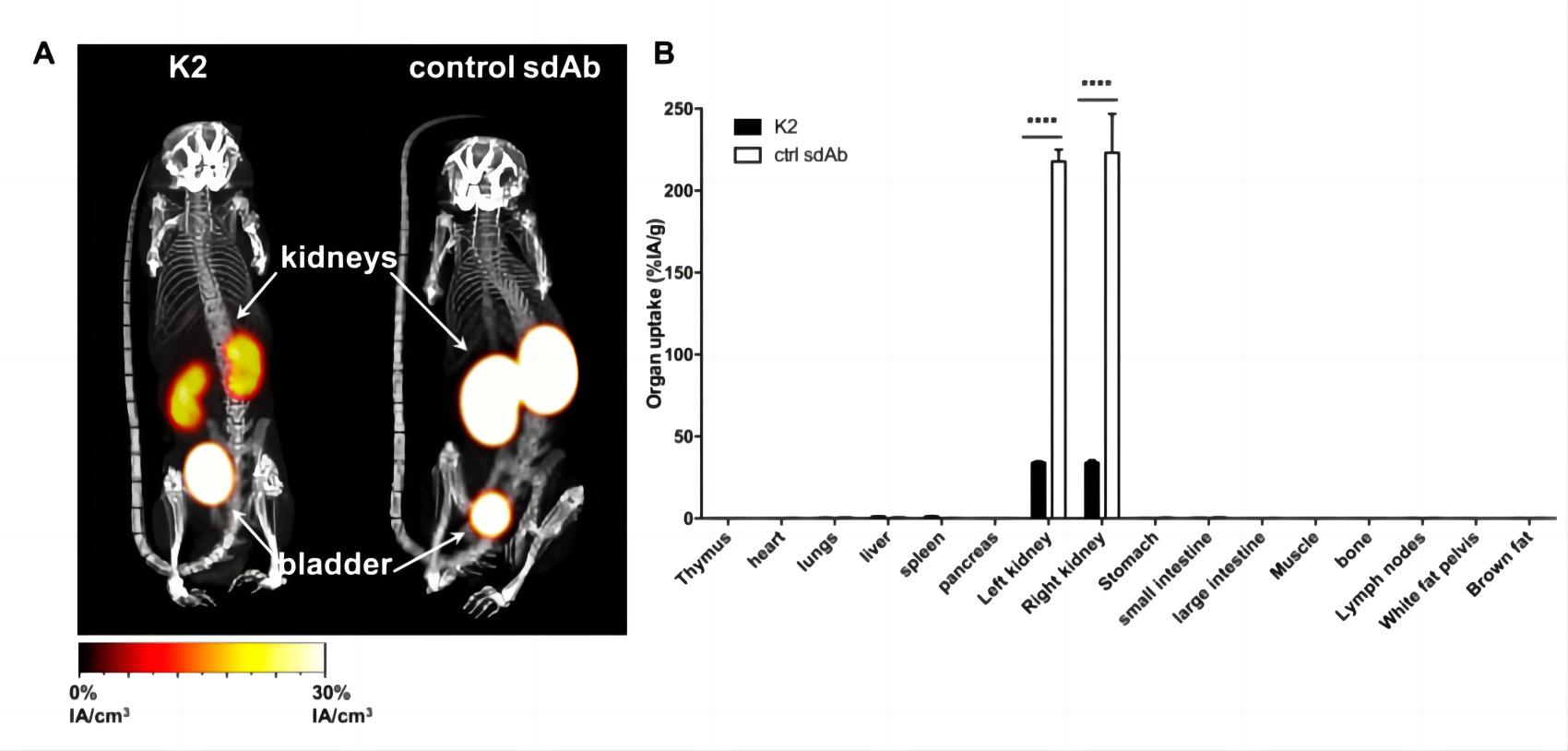 Fig.1 Radiolabeled sdAb shows the signal in mice.1,4
Fig.1 Radiolabeled sdAb shows the signal in mice.1,4
Imaging Alternatively-activated Macrophages
Alternatively-activated macrophages are of the anti-inflammatory, 'healing' type. Under pathological conditions, they counterbalance inflammatory responses and stimulate tissue regeneration in an attempt to return to homeostasis. A particular subset of such alternatively activated macrophages expresses a cell-surface protein, macrophage mannose receptor (MMR). Hence, anti-MMR sdAb is extremely useful to visualize these cells in imaging studies. In comparative biodistribution studies in naive wild-type and MMR-deficient mice, the scientist showed that radiolabeled anti-MMR-sdAbs specifically target resident macrophages in the liver, spleen, lymph nodes and bone marrow.
| Imaging Field | Target | SdAb | Radiolabel | Related Disease | Notes |
| Inflammation Imaging | MMR | MMRCl1 | 99mTc | Tumor immunology; Rheumatoid arthritis | Ready to Use Nano-Imaging Tracer Products |
| MMR3.49 | 99mTc, 18F, 68Ga | Tumor immunology, Atherosclerosis | |||
| DCs | Nb-DC2.1 | 99mTc | A wide range of myeloid cells | ||
| Nb-DC1.8 | 99mTc | Immature bone marrow-derived DCs |
Development Mission
One line of our research aims to validate M&DC markers as targets to image the inflammatory process and its spontaneous evolution and evolution in response to treatment in the living organism based on visualization of (anti-) inflammatory myeloid cells, by using labeled sdAbs targeting M&DC markers.
Customized Services
- Generation and in vitro characterization of sdAbs
- Nanotracers construction services
- In vitro assessment services
- In vivo imaging services
- Statistical analysis
If you are interested in our Nanotracer tool development and imaging services, please directly contact us and consult our technical supports online.
Published Data
1. 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR Nanobody for Macrophage Imaging in Atherosclerotic Plaques
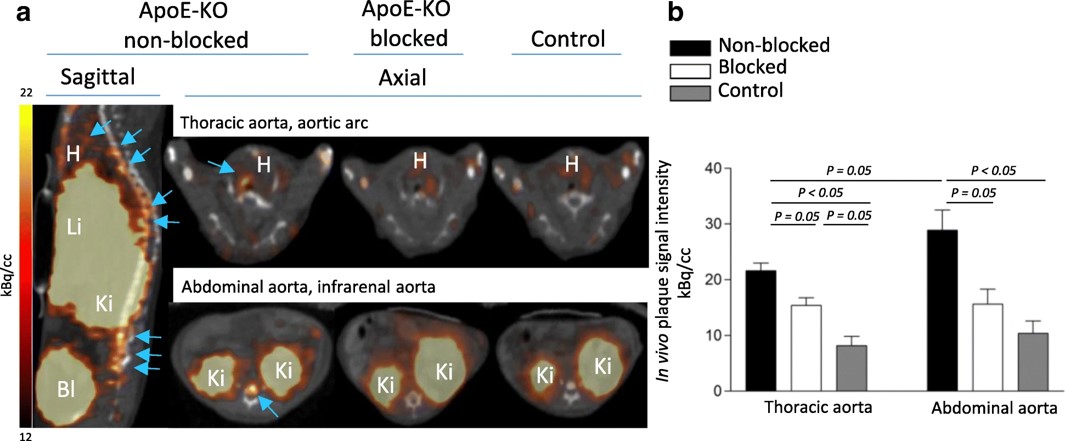 Fig.2 In vivo imaging and specific uptake of 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR Nb in the atherosclerotic lesion.2,4
Fig.2 In vivo imaging and specific uptake of 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR Nb in the atherosclerotic lesion.2,4
This study assessed the potential of 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR antibody for targeting MR-positive (MR+) macrophages and enabling non-invasive imaging of atherosclerotic plaques. The tracer was labeled with 68Ga, achieving >95% radiochemical purity. In vitro studies showed selective binding to M2a macrophages. For in vivo imaging, 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR Nb was injected into ApoE-KO and control mice, and PET/CT scans were performed one hour after injection. Focal signals were observed in the aortic tissue of ApoE-KO mice, but not in controls. Autoradiography revealed tracer uptake in atherosclerotic plaques, which correlated with Sudan-IV staining. The plaque-to-normal tissue autoradiographic signal ratio in ApoE-KO mice was 7.7 ± 2.6. These findings demonstrate that 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR Nb can efficiently target and visualize small-dimension atherosclerotic plaques. This tracer enables non-invasive PET/CT imaging of MR expression in atherosclerotic lesions, offering a potential diagnostic tool for clinical plaque imaging and stability evaluation.
2. [68Ga]Ga-Anti-CD206-sdAb for PET/CT Imaging of Protumorigenic Macrophages in Solid Tumors
![PET/CT images representative of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-anti-CD206-sdAb biodistribution.](images/14-4-7-3-2-Imaging-Inflammation-with-sdAbs-3.jpg) Fig.3 Normal biodistribution of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-anti-CD206-sdAb.3,4
Fig.3 Normal biodistribution of [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-anti-CD206-sdAb.3,4
This first-in-human study evaluated the safety, biodistribution, and dosimetry of the [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-anti-CD206 sdAb PET tracer targeting CD206, a macrophage mannose receptor. Seven patients received an average injection of 191 MBq of the tracer. Safety was assessed through clinical examination and blood sampling before and after injection, with only one mild transient adverse event, unlikely related to the drug, confirming its safety. Biodistribution and dosimetry were evaluated using PET/CT scans at 11, 90, and 150 minutes post-injection, showing uptake in CD206-positive organs like the spleen, confirming the tracer's specificity. The effective dose was 4.2 mSv for males and 5.2 mSv for females on average. No metabolites were observed. Blood-pool activity rapidly diminished over time, allowing for high contrast-to-noise imaging at 90 minutes post-injection. Preliminary tumor uptake data suggest potential for further phase II clinical trials of this tracer.
References
- Broos, Katrijn, et al. "Evaluating a single domain antibody targeting human PD-L1 as a nuclear imaging and therapeutic agent." Cancers 11.6 (2019): 872.
- Varasteh, Zohreh et al. “Targeting mannose receptor expression on macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques of apolipoprotein E-knockout mice using 68Ga-NOTA-anti-MMR nanobody: non-invasive imaging of atherosclerotic plaques.” EJNMMI research vol. 9,1 5. 21 Jan. 2019, doi:10.1186/s13550-019-0474-0IF: 3.1 Q1
- Gondry, Odrade, et al. "Phase I study of [68Ga] Ga-Anti-CD206-sdAb for PET/CT assessment of protumorigenic macrophage presence in solid tumors (MMR phase I)." Journal of Nuclear Medicine 64.9 (2023): 1378-1384.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.