As a leading service provider in the in vitro diagnostics (IVD) industry, Creative Biolabs has assisted our clients with the development of several important IVD assays in recent years. We have accumulated a lot of experience in the development of IVD. We can offer the best one-stop IVD development services by harnessing our extensive expertise and advanced IVD development technologies such as PCR, NGS, WB, immunohistochemistry analysis, and so on.
Introduction of PCR Technology
PCR, also known as polymerase chain reaction, is a revolutionary method that allows the detection of any short sequence of DNA (or RNA) even in samples containing only minute quantities of DNA or RNA. It was developed by Kary Mullis in the 1980s. This technology is based on using the ability of DNA polymerase to amplify a new strand of DNA complementary to the offered template strand. Leveraging the technology, a specific region of a target gene can be amplified by billions of copies in vitro. PCR technologies include reverse transcriptase-PCR (RT-PCR), real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR), and digital PCR (dPCR). RT-PCR is used to convert the RNA strand into a DNA strand, which is used for the detection and quantitation of mRNA. qPCR is applied for the quantification of target DNA throughout the process by monitoring the amplification of DNA in real-time. dPCR is a new, more refined technology that breaks the PCR process up into many smaller steps. It provides higher precision, more reliable measurements, and absolute quantification from very small or mixed samples. Given the advantages of PCR in DNA/RNA detection, it has been applied in IVD diagnosis fields. It can be used to detect a marker gene associated with genetic diseases to accelerate the diagnosis of a genetic disease. It is also applied to detect low levels of viral nucleic acid to identify if you are infected.
 Fig. 1 Summary of a single PCR cycle.
Fig. 1 Summary of a single PCR cycle.
Application of PCR in IVD for SARS-CoV-2
SARS-CoV-2 is a new strain of coronavirus that causes respiratory illness COVID-19 disease. It has killed approximately 2.2% of those worldwide who are known to have contracted it. Currently, many commercial IVD kits have been developed for the clinical diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Among these, several kits are developed based on a qPCR method. SARS-CoV-2 rRT-PCR kits employ oligonucleotide primers and probes labeled with fluorescent reporter dyes and quenchers to qualitatively detect nucleic acid from SARS-CoV-2 in the human nasopharyngeal swab, anterior nasal swab, and mid-turbinate nasal swab specimens. SARS-CoV-2 RNA is first extracted from patient samples and then is converted to cDNA. Next, the probes anneal to specific target sequences on the cDNA. During the extension step of the PCR cycle, the 5' nuclease activity of the DNA polymerase degrades the probes, leading to the reporter dye to isolated from the quencher dye and generate a fluorescent signal. Fluorescence intensity is monitored at each PCR cycle by a Real-Time PCR instrument.
Our Capabilities
Creative Biolabs has assembled a team of world-class leaders who are skilled in the development of IVD assays. Supporting by the experienced leadership team and a powerful PCR technical platform, we provide one-stop PCR-based IVD assay development services for global clients, including design and synthesis of specific primers, probe synthesis, and DNA polymerase synthesis, as well as design and test the assay scheme. If you are interested in our services, please don't hesitate to contact us for more details. We are thrilled to become your reliable partner to develop novel specific IVD assays for disease diagnosis research.
Published Data
1. High-Throughput SARS-CoV-2 Detection Using RT-qPCR Analysis in Pooled Saliva Samples for Epidemiological Monitoring
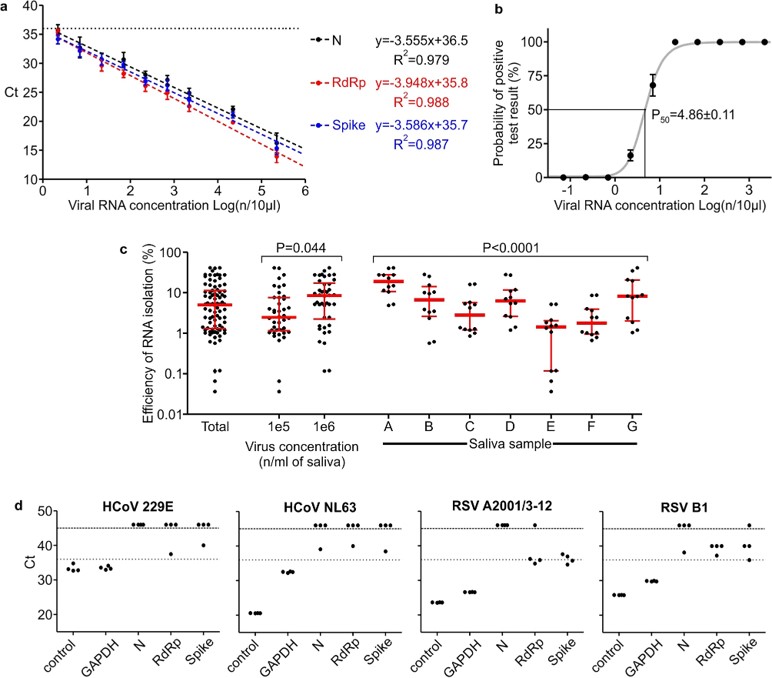 Fig.2 Quantitative performance of screening test.1
Fig.2 Quantitative performance of screening test.1
This study developed a 3-gene, seminested RT-qPCR test for high-throughput SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics, using a fluorescent green dye for detection. The method utilized a two-tier approach with decentralized saliva sample collection and pooling. The first tier involved a highly sensitive screening test, followed by second-tier testing of individual samples from positive pools using an IVD-certified test. The screening test detected viral genome copies with 50% probability at five copies per 10 µl RNA and 95% probability at 18.8 copies, showing a strong linear relationship between Ct values and RNA concentration. In comparison with a commercially available IVD-certified RT-qPCR test, the screening test showed slightly better results (100% specificity, 89.8% sensitivity vs. 100% and 73.5%, respectively). Testing 1,475 clinical samples in 374 pools revealed 0.8% false positives and no false negatives. In weekly testing of 113 individuals over 6 months, the approach detected 18 infected individuals at a lower cost than individual RT-PCR tests.
References
- Różański, Michał, et al. "RT-qPCR-based tests for SARS-CoV-2 detection in pooled saliva samples for massive population screening to monitor epidemics." Scientific Reports 12.1 (2022): 8082. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.