Mechanisms of Immunotherapy in Cancer
As one of the most important immune cells in the body, T cells can differentiate into cytotoxic T cells to kill harmful cells. However, tumor cells can express a protein named PD-L1 which can bind to the PD-1 protein expressed by T cells, and this specific binding, in turn, inactivates T cells, leading to the failure of abnormally proliferating tumor cells killing. Classical PD-1 immunotherapy uses antibodies to neutralize PD-1 or PD-L1 proteins so that the two proteins cannot be recognized and combined, thus ensuring the normal tumor cell killing function of T cells. However, the antibody used is expensive, hence this therapy is not available for a significant number of patients.
Novel Small Molecule-based Immunotherapy for Cancer Treatment
To overcome the shortcomings of classical immunotherapy, scientists have recently found a small molecule inhibitor for the treatment of cancers by utilizing bioinformatic and data analysis tools. Based on the existing inhibitor data, they first used computer-aided drug design (CADD) models and database analysis to screen thousands of molecular structures and find the best ones. They then demonstrated that those small molecules could effectively prevent the formation of PD-1/PD-L1 by preferentially binding to PD1. Consequently, the immune system can perform its normal physiological function and eliminate cancer cells.
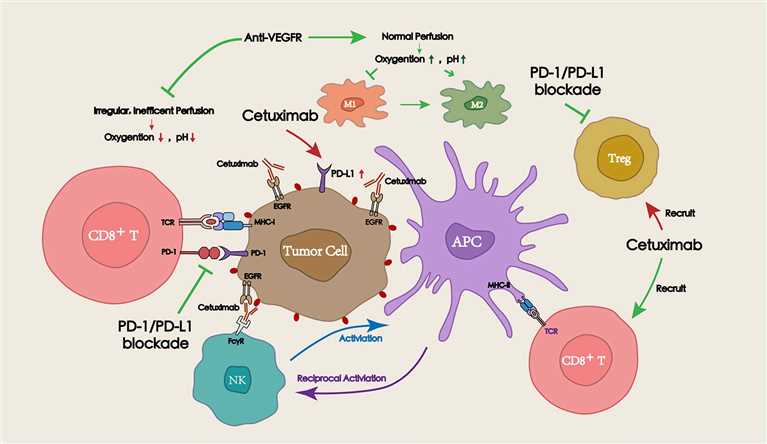 Fig.1 Synergies between radiochemotherapy and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in the tumor microenvironment.1
Fig.1 Synergies between radiochemotherapy and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in the tumor microenvironment.1
Evaluation of Inhibitory Effect of Small Molecules on PD-1/PD-L1 Complex
After the small molecule screening, two different kinds of human cancer cell lines (breast cancer and melanoma) were chosen to perform the in vitro research looking at the impact of those molecules on the PD-L1/PD-1 interaction. The results showed that these small molecules can significantly reduce PD-L1 levels in both cancer cells. In addition, they also demonstrated that these small molecules can activate T cells and facilitate T-cell infiltration.
Advantages of These New Small Molecule Blockers
Compared to classical antibody therapies, small molecule inhibitors have the following advantages:
- Lower prices
- More readily available
- Easier to administer
- Better treatment for some tumor
Reference
- Lin, Weimin, et al. "Crosstalk between PD-1/PD-L1 blockade and its combinatorial therapies in tumor immune microenvironment: a focus on HNSCC." Frontiers in oncology 8 (2018): 532. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.