Basic Information of Protein Biomarkers in Blood
During the metabolic process of tumor tissue, its metabolites and specific biomolecules are secreted into body fluids, which can be used in the screening, diagnosis, prognosis, efficacy evaluation and follow-up of the tumor. Among these biomolecules, proteins, as the main functional units of life activities, are the most widely used biomarkers of disease. To date, miscellaneous protein molecules have been used in the early diagnosis of cancers. For the early diagnosis of lung cancer, currently common blood protein markers mainly include three categories: tumor-associated antigens (TAAs), tumor-associated autoantibodies (TAAbs) and exosomal proteins.
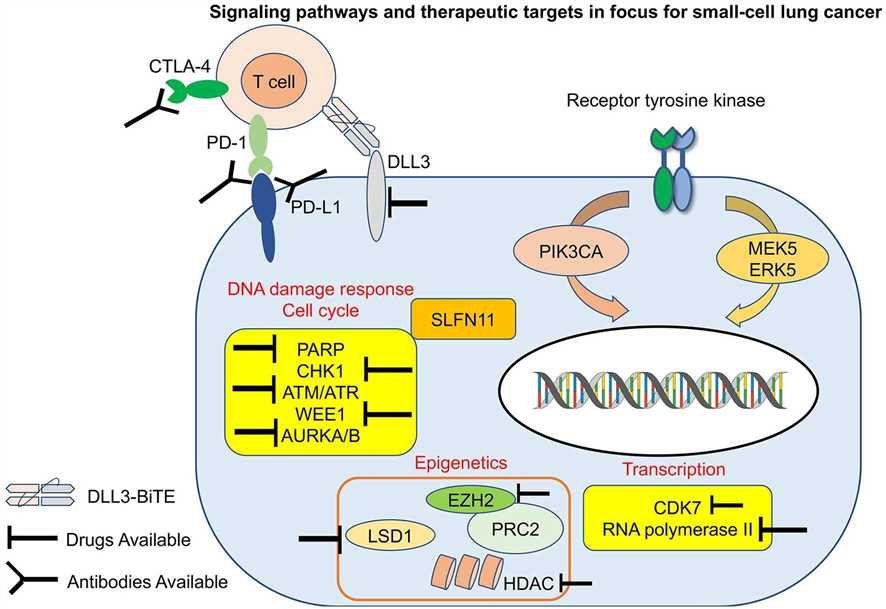 Fig.1 Focused signaling pathways and therapeutic targets in small-cell lung cancer.1
Fig.1 Focused signaling pathways and therapeutic targets in small-cell lung cancer.1
Protein Biomarkers for Lung Cancer
- Tumor-associated Antigens (TAAs)
TAAs are derived from the core molecules of the signaling pathway during tumorigenesis. Unlike tumor-specific antigens, TAA exists not only in tumor tissues but also in normal cells and tissues. Studies have shown that TAA may participate in tumorigenesis through many biological processes. Based on the important role of TAA in tumor metabolism, it plays an important role in the early diagnosis of lung cancer, the monitoring of the treatment process and the assessment of the prognosis of patients. In addition, some specific TAA can be used for the evaluation of tumor grade and recurrence rate.
Unfortunately, there are no specific TAA biomarkers available for the detection of lung cancer. Some TAA, such as neuron-specific enolase (NSE), progastrin-releasing peptide (ProGRP) and CEA can provide certain reference values in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
- Tumor-associated Autoantibodies (TAAbs)
TAAbs can be early reporters of abnormal cellular mechanisms during tumorigenesis. The level of lung cancer-related autoantibodies in healthy people is very low, but even in patients with early lung cancer, the level of autoantibodies in the body has been significantly increased. Therefore, autoantibodies play an important role in the early diagnosis of lung cancer. Many autoantibodies against antigens such as SOX2, CKAP4 and p53 have been widely used in the diagnosis of lung cancer.
- Exosomal Proteins
Exosomes are a group of nanoscale membrane vesicles released extracellular multivehicle in the process of fusion of multivesicular bodies and plasma membrane. As carriers of many intracellular biomolecules, such as DNA, RNA and lipids, exosomes can directly reflect the physiological state of cells. To be more specific, lung cancer cells can secrete exosomes to realize the metastasis and spread of cancer cells, the generation of blood vessels in tumor tissues, and other processes, and exosomes can also help tumors realize immune escape. Therefore, the analysis of exosomes extracted from body fluids can achieve an early diagnosis of lung cancer.
Reference
- Taniguchi, Hirokazu, Triparna Sen, and Charles M. Rudin. "Targeted therapies and biomarkers in small cell lung cancer." Frontiers in oncology 10 (2020): 741. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.