Background
The link between breathing and PD was first discovered in 1817 by the famous British surgeon James Parkinson. Since then, many studies have further confirmed that the respiratory centers in the brain stem of PD patients deteriorate as the disease progresses. What's more, breathing problems often appear earlier than other symptoms. Therefore, the monitoring of breathing is expected to be a new effective biomarker for Parkinson's disease.
Novel AI-based Nocturnal Breathing Signals Monitor for the Detection of PD
Based on the relationship between breathing and PD, Yang and coworkers established an AI-based research model to monitor the nocturnal breathing signals and further predict disease severity and track the progression of the disease over time. In this study, they monitored 11,964 nights of nocturnal breathing signals from 757 PD patients (mean age 69.1) and breathing signals from 6914 healthy individuals (mean age 66.2) as a control group. The model firstly learned the auxiliary role of predicting the quantitative electroencephalogram (qEEG) of each person from nocturnal breathing, which effectively avoids the overfitting of this model and guarantees a comprehensible output of the model. The whole study was divided into two groups. One group uses a breathing belt on the body to trace the breathing signals while another group collects breathing data using a radio device that transmitted a low-power radio signal in the bedroom and analyzes its reflections from the environment.
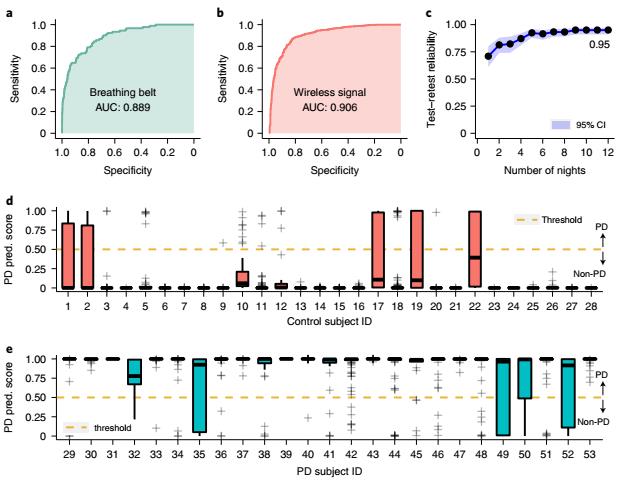 Fig.1 Analysis of nocturnal respiratory patterns for PD diagnosis.1
Fig.1 Analysis of nocturnal respiratory patterns for PD diagnosis.1
Effectiveness of Nocturnal Respiratory Signal Monitoring in Detecting PD
The team use this AI model to detect PD by one night of nocturnal breathing monitor and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves shown in Figure 1 demonstrated the accuracy of the model. Furthermore, they also tested whether combining breath signals of several nights from one individual would improve detection accuracy. The final result shown in Figure 1d,e suggested that the sensitivity and specificity of this AI model-based PD diagnosis would further increase.
Conclusion
Yang and coworkers used advanced AI technology to build an intelligent night-time breathing signal capture and analysis model, and applied it to the precise diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. This method can realize the non-invasive, early and at home diagnosis of PD, which provides a greater possibility to cure the disease.
Reference
- Yang, Yuzhe, et al. "Artificial intelligence-enabled detection and assessment of Parkinson's disease using nocturnal breathing signals." Nature medicine 28.10 (2022): 2207-2215. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.