What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a common form of cardiovascular disease which is caused by the accumulation of cholesterol plaques in the artery walls over time. The accumulated cholesterol would gradually harden and narrow arteries, which in turn causes poor blood circulation, high blood pressure, and even a destructive stroke.
What is the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis?
The inflammatory reaction has been proved to be the dominant cause of the disease. Typically, the progression of the disease can be divided into three major stages, namely fatty streaks formation, atheroma formation, and atherosclerotic plaque formation. Meanwhile, many cells and protein factors, such as endothelial cells (EC), macrophages, plasma low-density lipoproteins (LDL), TG-rich lipoproteins, and cholesterol, would participate in the progress of the above three stages at different stages.
What is New about Atherosclerosis?
Recent findings on atherosclerosis include previously unknown heterogeneity of inflammation, links between the disease and gut microbes, and effects of cellular senescence. The discovery of these new mechanisms is of great significance for the clinical diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis. Detailed research information is as follows:
- Heterogeneity of Inflammatory
For the past few years, lots of compelling evidence showed that increased hematopoiesis for the replenishing of blood cells is positively associated with the incidence of atherosclerosis. Meanwhile, arterial wall cell phenotypes are found to be highly plastic and can transform into different phenotypes along with the progression of atherosclerosis based on recent single-cell RNA-seq studies.
- The Role of Gut Microbes in Atherosclerosis
Previous cross-sectional studies revealed that there is a huge difference in the gut microbes species between healthy individuals and patients with atherosclerosis. More importantly, trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), a metabolite of gut microbes, is of vital importance in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. TMAO can increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decrease anti-inflammatory cytokines. Besides, TMAO can also induce platelet hyperreactivity and finally lead to the formation of atherosclerotic thrombotic.
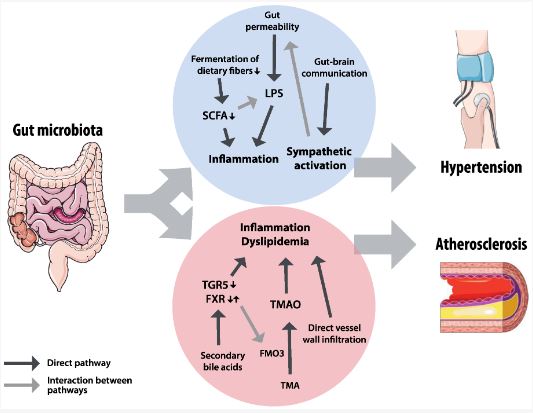 Fig.1 Summary of the effects of gut microbiota on atherosclerosis.1
Fig.1 Summary of the effects of gut microbiota on atherosclerosis.1
- Cellular Senescence
The cellular senescence triggered by oxidative stress, DNA damage, or replicative exhaustion of atherosclerosis-involved cells such as EC, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells, may be closely related to the lesion growth of atherosclerosis and can prevent the rupture of plaque formed before. The detailed mechanism of aging on atherosclerosis is shown in Figure 2.
Reference
- Verhaar, Barbara JH, et al. "Gut microbiota in hypertension and atherosclerosis: a review." Nutrients 12.10 (2020): 2982. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.