These are the most common antibody format, similar to naturally occurring antibodies. They are suitable for a variety of applications, like ELISA, Western blotting, and immunohistochemistry.
Creative Biolabs is one of the well-recognized experts who are professional in in vitro diagnostics (IVD) antibody development. We offer comprehensive recombinant antibody development services, with customized solutions to fit your individual research and development requirements. We use advanced technology and considerable expertise to offer high-quality, dependable recombinant antibodies, accelerating your projects and driving innovation.
Introduction
Recombinant antibodies are generated in vitro through the expression of a defined antibody sequence, offering significant advantages over traditional methods. Unlike traditional monoclonal antibody production, which relies on hybridoma cell lines, recombinant technology ensures batch-to-batch consistency, eliminates cell-line drift, and provides a stable, long-term supply. These antibodies exhibit high specificity, sensitivity, and versatility, making them essential tools in various applications, including proteomics research, human health studies, and drug discovery. Recombinant antibodies are available in diverse formats and can be engineered to improve their properties.
Formats of Recombinant Antibodies
Full-Length IgG
Fab
These fragments consist of the Fab of an antibody, containing the variable regions (Fv) and the heavy and light chains' initial constant domains (C1). Fab fragments are smaller than full-length antibodies, allowing for better tissue penetration and reduced non-specific binding.
scFv
scFvs consist of the variable heavy and variable light domains of an antibody linked by a short peptide linker. scFvs are even smaller than Fab fragments, offering advantages in applications such as gene therapy and bispecific antibody development.
VHH (Nanobodies)
These are small, single-domain antibody fragments produced from camelids (camels, alpacas, and llamas). VHH antibodies are exceptionally small, stable, and have unique binding properties, making them valuable for applications such as targeted drug delivery and imaging.
sdAb
Single-domain antibodies (sdAbs), similar to VHHs, are small, single-variable-domain antibodies. They offer advantages similar to VHHs, including small size, stability, and simplicity of engineering.
BsAb
These engineered antibodies have binding sites for two different antigens, enabling them to target multiple molecules or cell types simultaneously. Bispecific antibodies have shown considerable potential in cancer immunotherapy and other therapeutic applications.
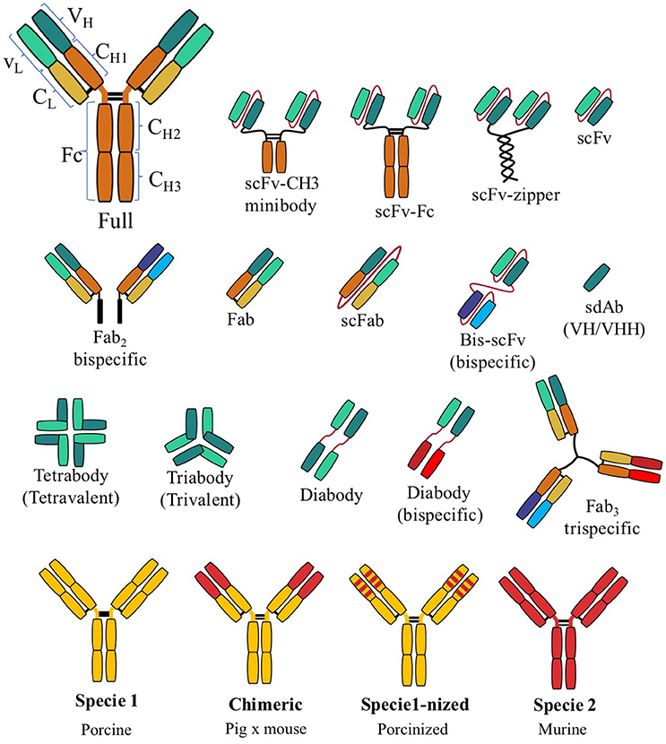 Fig.1 Common types of recombinant antibodies.1,5
Fig.1 Common types of recombinant antibodies.1,5
Service Workflow
We provide a comprehensive suite of recombinant antibody development services, covering every stage from antigen design to antibody function verification. Our expertise and advanced technologies ensure the successful generation of high-quality antibodies tailored to your specific needs.
To initiate the antibody development process, meticulous antigen design is paramount. We deliver expert consultation on antigen design, carefully considering factors such as target accessibility, immunogenicity, and stability. Our services encompass peptide synthesis, recombinant protein expression and purification, and the preparation of other antigen formats. To maximize the success of antibody generation, we employ advanced techniques that ensure the purity and quality of your antigen.
We utilize advanced library generation techniques and possess extensive experience in generating libraries from various species.
Phage display: This technique leverages bacteriophages to display antibodies on their surface, enabling the selection of antibodies with high affinity for a target antigen.
Ribosome display: An in vitro method, ribosome display presents antibodies on ribosomes, facilitating the selection of antibodies based on their binding affinity and translation efficiency.
Yeast display: Antibodies are displayed on the surface of yeast cells in this technique, and flow cytometry is employed for the selection of antibodies with desired characteristics.
Identifying antibodies with the desired binding characteristics is a critical step. To do this, we utilize a range of screening techniques. Our capabilities include ELISA, flow cytometry, SPR, and other high-throughput screening techniques. We use stringent selection criteria to isolate antibodies with high specificity, affinity, and functionality.
The successful production of recombinant antibodies relies on choosing an adequate expression system. We offer expertise in a range of expression systems, including mammalian cells (CHO, HEK), bacteria (E. coli), and yeast. Our optimization of expression conditions, such as codon optimization, vector design, and cell culture parameters, is crucial for maximizing antibody yield and quality. Our flexibility in expression systems allows us to tailor the production process to the specific requirements of your antibody.
We employ a variety of purification strategies, including affinity chromatography (Protein A/G), size exclusion chromatography, and ion exchange chromatography, to achieve this goal. In addition, our modification services include antibody labeling with fluorescent dyes, enzymes, or other tags, as well as fragmentation and conjugation. We ensure the quality and integrity of your antibodies through rigorous quality control testing.
We offer a comprehensive range of functional assays to accomplish this, including western blotting, ELISA, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, and cell-based assays. To support your research and development efforts, we provide extensive reports and data analysis.
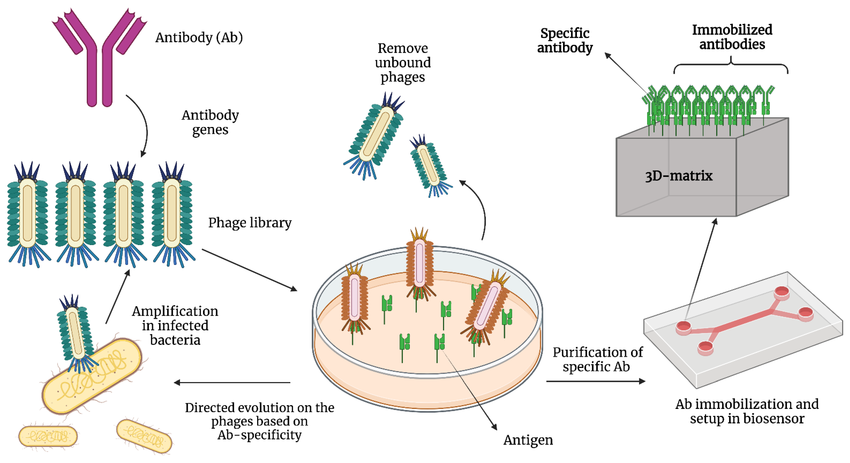 Fig.2 Production of the recombinant antibody.2,5
Fig.2 Production of the recombinant antibody.2,5
Antibody Engineering
Antibody Humanization
To minimize immunogenicity, we employ humanization strategies, replacing non-human antibody sequences with human counterparts. This process generates chimeric antibodies that retain their original specificity while reducing potential immune responses. Our expertise ensures safer, more effective therapeutic antibodies.
Antibody Affinity Maturation
To enhance antibody efficacy, we utilize techniques like site-directed mutagenesis and phage display to improve binding affinity. These methods introduce variations into antibody variable regions, enabling the identification of variants with enhanced binding. Through mutation and selection, we significantly increase antibody affinity, improving target engagement and therapeutic outcomes.
Antibody Fragmentation
For certain applications, smaller antibody fragments are advantageous. We generate fragments, including Fab, scFv, engineered to retain the antigen-binding site but lack the Fc region. Their smaller size improves tissue penetration, clearance, and reduces non-specific binding, optimizing them for applications like diagnostic imaging and drug delivery.
Cuse Study
With over a decade of experience in recombinant antibody preparation, we leverage advanced expression platforms and rigorous quality control systems to provide clients with highly specific, high-affinity, and batch-consistent recombinant antibody solutions! From gene design to purification and validation, we optimize every step to deliver full-length antibodies, scFv, nanobodies, and more, meeting the needs of diagnostics, therapeutics, and basic research.
| SDS-PAGE of Purified (Fab')2-tag free antibody | Elisa Analysis of Purified IgG-tag free antibody |
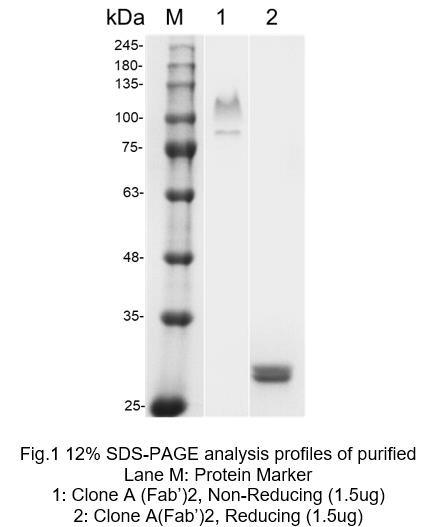

|
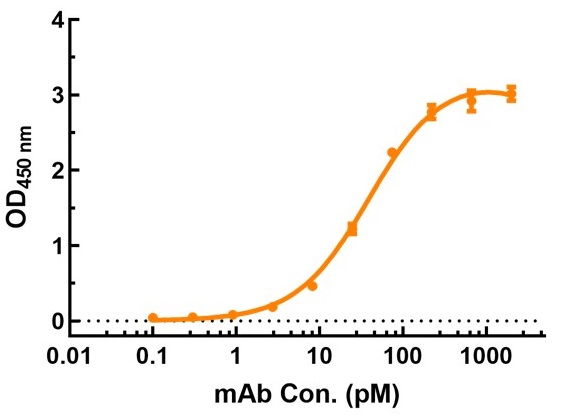
|
Published Data
1. Recombinant scFv Antibody Targeting Platelets Produced in Pichia pastoris
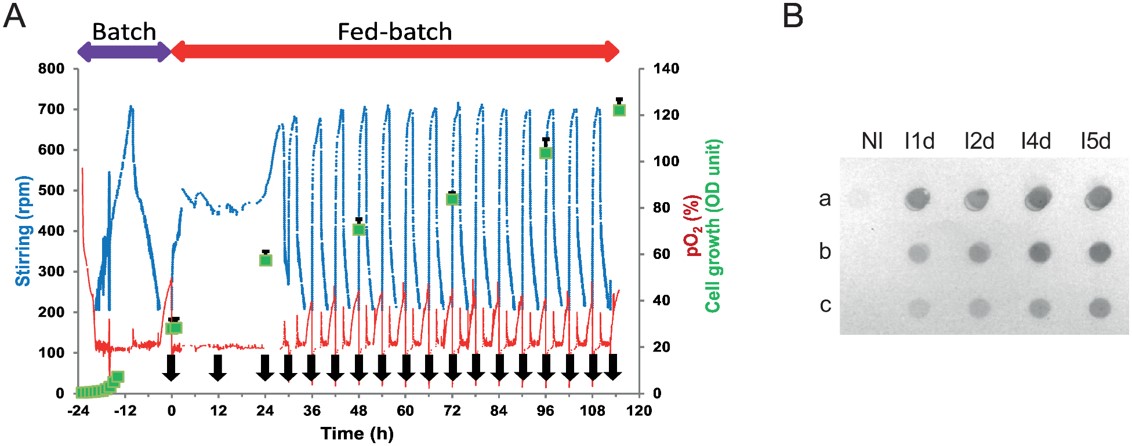 Fig.3 The anti-αIIbβ3 scFv production process.3,5
Fig.3 The anti-αIIbβ3 scFv production process.3,5
In this study, researchers successfully produced highly purified and biologically active scFv fragments in a yeast cell expression modality, obtained from a human anti-αIIbβ3 antibody (HuAb), particularly designed to target atheromatous lesions associated with platelet presence. Various methods, including ELISA, flow cytometry with platelets, affinity binding assays, and immunohistochemistry on atherosclerotic plaques from both animal models and human coronary tissue samples were used to evaluate the immunoreactivity of the anti-αIIbβ3 scFv. Additionally, the optimized expression conditions enabled the recovery of scFv fragments in a form that was not only highly purified but also biologically active, making them suitable for site-specific conjugation to nanoparticles for imaging atherosclerotic plaques, where inflammation and immune responses contribute to plaque instability.
2. Phage Display Single-Domain Antibody Library for Antibody Development
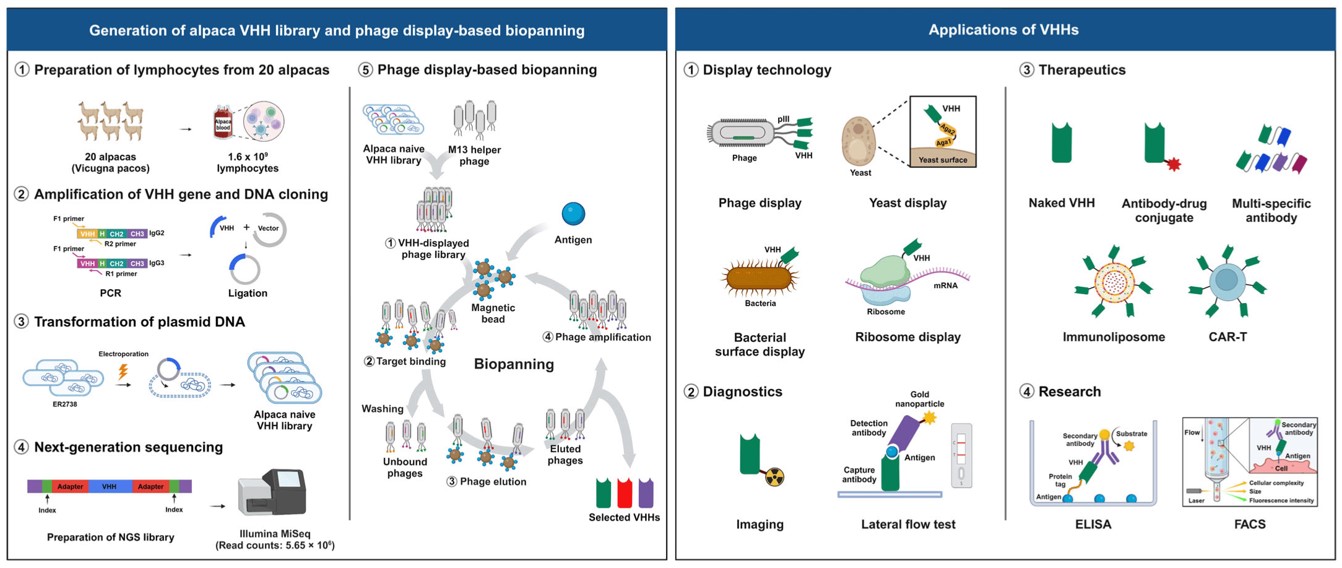 Fig.4 Construction of an alpaca VHH phage display library.4,5
Fig.4 Construction of an alpaca VHH phage display library.4,5
Q&A
-
Q: How do you ensure the specificity and affinity of antibodies?
A: We employ stringent selection and screening processes, including techniques like phage display and affinity maturation, combined with rigorous validation assays such as SPR and ELISA, to ensure high specificity and affinity.
-
Q: How do you ensure that antibodies are consistent between batches?
A: Recombinant antibody production inherently offers high consistency. We use well-defined expression systems, standardized protocols, and thorough quality control testing, including sequence verification and functional assays, to guarantee batch-to-batch reproducibility.
-
Q: How do you define the ownership of intellectual property rights during project cooperation?
A: We establish clear intellectual property agreements with our clients before project commencement. These agreements outline ownership, licensing, and confidentiality terms to protect both parties' interests.
-
Q: How much experience do you have in the field of recombinant antibody development?
A: Our professional team has extensive experience and a proven track record in the field of recombinant antibody development. We have successfully completed numerous projects for global clients.
-
Q: How do you communicate with clients and provide project progress updates during a project?
A: We keep open and transparent contact with our clients throughout the project. We provide regular updates through detailed progress reports, scheduled meetings, and dedicated project managers who serve as the primary point of contact.
References
- Bustamante-Córdova, Lorena, Edgar A. Melgoza-González, and Jesús Hernández. "Recombinant antibodies in veterinary medicine: An update." Frontiers in Veterinary Science 5 (2018): 175. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00175.
- Mayoral-Peña, Kalaumari, et al. "Biorecognition Engineering Technologies for Cancer Diagnosis: A Systematic Literature Review of Non-Conventional and Plausible Sensor Development Methods." Cancers 14.8 (2022): 1867. doi: 10.3390/cancers14081867.
- Vallet-Courbin, Amelie, et al. "A recombinant human anti-platelet SCFV antibody produced in pichia pastoris for atheroma targeting." PLoS One 12.1 (2017): e0170305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170305.
- Lee, Hee Eon, et al. "Development, High-Throughput Profiling, and Biopanning of a Large Phage Display Single-Domain Antibody Library." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 25.9 (2024): 4791. doi: 10.3390/ijms25094791.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.