Stem Cell-derived Exosome Advantage and Application
- Regulating Dendritic Cell
Introduction Applications Services FAQs
Regulatory Potential of SC-Exo on Dendritic Cells (DenCs)
Dendritic cells (DenCs) are among the most powerful antigen-presenting cells in the body and play a pivotal role in initiating immune responses. Whether guiding the immune system toward activation or tolerance, DenCs are central to maintaining immune balance.
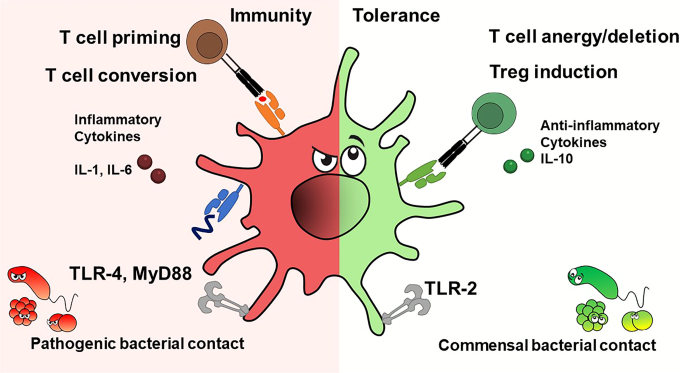 Fig.1 Dendritic cells exhibit immunostimulatory or tolerogenic potential depending on the context.1
Fig.1 Dendritic cells exhibit immunostimulatory or tolerogenic potential depending on the context.1
Stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos) have emerged as promising tools in immune modulation, largely because they inherit many of the functional properties of their parent cells. These nanoscale vesicles can transfer bioactive molecules—such as proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs—directly to DenCs, influencing their maturation, activation state, and downstream immunological behavior. In doing so, SC-Exos help reshape immune responses at a fundamental level.
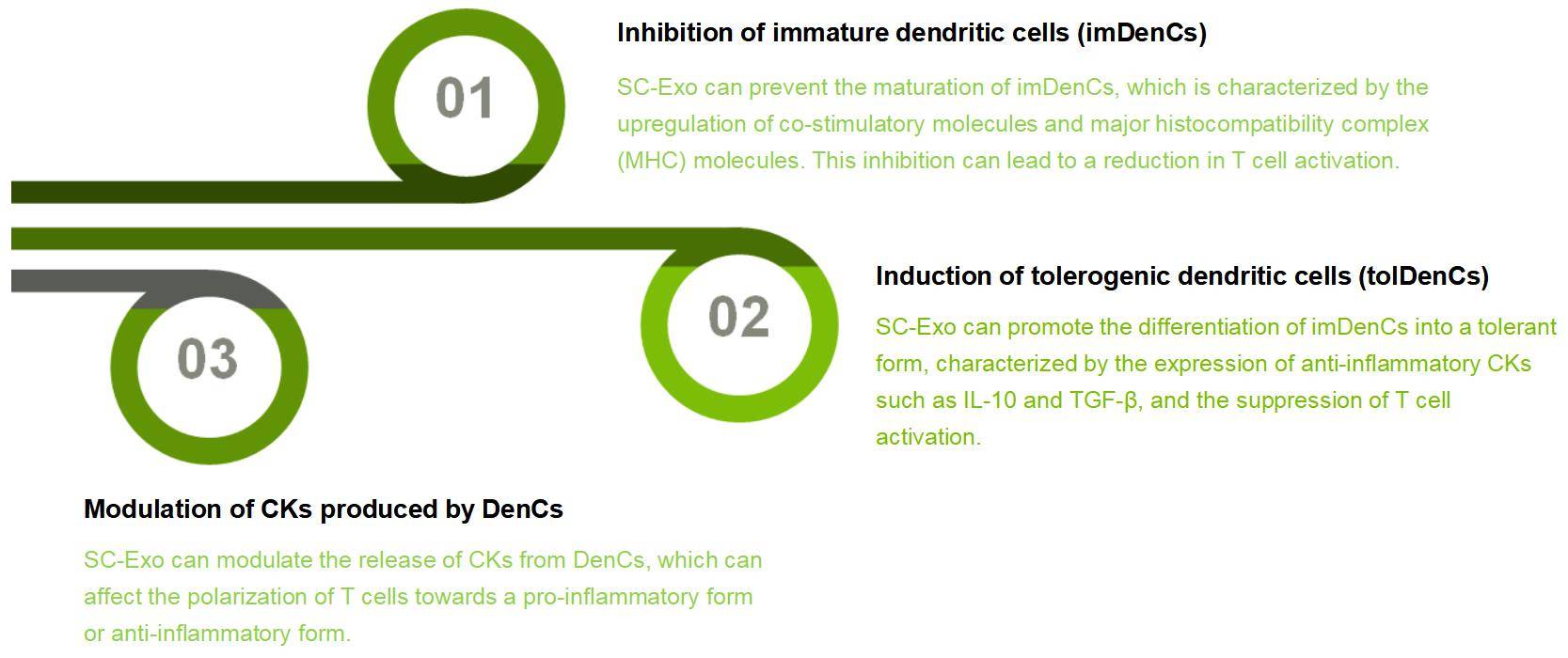
This ability to fine-tune dendritic cell function highlights the potential of SC-Exos as a novel strategy for managing immune-related conditions, including autoimmune diseases and tissue damage. By modulating how DenCs present antigens or trigger immune pathways, SC-Exos may pave the way for more targeted and better-tolerated therapeutic approaches.
At Creative Biolabs, we offer a full suite of exosome-based research services to support your SC-Exo projects. Our capabilities include exosome isolation, profiling, engineering, and cargo loading—all tailored to help you unlock the therapeutic potential of SC-Exos in dendritic cell regulation and immune intervention.
Specific Manifestation of the Ability of SC-Exo to Regulate DenCs
In autoimmune disorders, the immune system mistakenly targets the body's own tissues, often due to dendritic cells (DenCs) mispresenting self-antigens to T cells. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exos) have been shown to interfere with this harmful process. By inhibiting DenC maturation, MSC-Exos help prevent the activation of autoreactive T cells and dampen inappropriate immune responses. For instance, co-culturing DenCs with MSC-derived exosomes in vitro has been found to suppress DenC development and indirectly reduce T cell-mediated immune activation. At Creative Biolabs, we provide tailored exosome engineering services—including MSC-derived exosome modification services,—to support research into autoimmune regulation and therapy in autoimmune disease models.
In conditions marked by chronic inflammation, such as IBD or rheumatoid arthritis, DenCs are key players in driving and sustaining pro-inflammatory immune responses. SC-Exos can curb this process by blocking the transition from immature to mature DenCs and steering the immune system toward an anti-inflammatory profile. One mechanism involves miR-21-5p, a microRNA found in MSC-derived exosomes, which targets CCR7 in DenCs, impairs antigen uptake, and reduces lymphocyte proliferation. Our advanced exosome isolation and characterization services help researchers identify and characterize the active exosomal components in inflammation, enabling precise therapeutic targeting.
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) contribute to treatment resistance and recurrence, but their exosomes (CSC-Exos) may actually offer a unique immunotherapeutic angle. Studies suggest that DenCs that have internalized CSC-Exos become more effective at presenting tumor antigens, thereby enhancing T cell responses. Creative Biolabs supports this line of research with exosomal proteomic detection services and exosomal protein isolation and profiling services, helping to identify immunologically active components in CSC-Exos. Additionally, we provide tumor-targeted exosome modification services designed to improve exosome delivery efficiency and maximize anti-tumor immunity.
In transplant medicine, DenCs play a crucial role in graft rejection by alerting T cells to the presence of foreign antigens. SC-Exos offer a promising strategy to promote immune tolerance by encouraging the differentiation of DenCs into a tolerogenic phenotype (tolDenCs), reducing their ability to trigger rejection. Evidence from animal models, such as mice receiving skin grafts, shows that MSC-derived exosomes can delay DenC maturation and significantly extend graft survival. To further enhance therapeutic outcomes in transplant settings, we offer exosome cargo loading services and targeting exosome construction services, enabling precise delivery of immunosuppressive agents directly to relevant immune cells.
One-Stop SC-Exo Research Services at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we're committed to advancing the potential of SC-Exos, particularly in their role in modulating DenCs and shaping immune responses. With years of hands-on experience in exosome research and development, we offer a comprehensive suite of technical services designed to support every stage of your SC-Exo-based project. Our services include:
-
Exosome Isolation and Purification Services: From exosome isolation to exosome purification, we ensure the highest quality and consistency in SC-Exo preparations.
-
Exosome Characterization and Profiling Services: Through advanced techniques such as western blotting, nanoparticle tracking analysis, transmission electron microscope, exosomal proteomics and exosome RNA sequencing, we help elucidate the molecular profile of SC-Exos.
-
Exosome Engineering Services: We specialize in exosome labeling services and disease-targeted exosome modification services for customized therapeutic applications.
-
Exosome-Based Drug Delivery: Our exosome cargo loading services help optimize SC-Exo as a vehicle for drug delivery, improving therapeutic outcomes in immune-related diseases.
-
In Vivo and In Vitro Functional Research Services: We provide model construction services for diseases such as cancer, inflammatory disease, and autoimmune diseases, supporting the functional research of SC-Exos in various disease contexts.
If you're exploring how SC-Exos can influence dendritic cell biology or aiming to harness their therapeutic potential, we're here to help. Contact us through our website to discuss your project goals and receive tailored technical support.
FAQs
Q: How do stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos) interact with dendritic cells?
A: SC-Exos carry bioactive molecules such as proteins, miRNAs, and lipids that can be taken up by dendritic cells. These exosomes can influence DenC activation, maturation, and antigen-presenting function, thereby modulating immune responses toward either activation or tolerance, depending on the context.
Q: Can SC-Exos be engineered for targeted modulation of DenCs?
A: Yes. At Creative Biolabs, we provide exosome engineering services to modify the surface of SC-Exos or load them with specific molecules, enhancing their ability to selectively interact with dendritic cells and achieve desired immunomodulatory effects.
Q: Are your SC-Exo services customizable based on different stem cell sources?
A: Absolutely. We work with exosomes derived from various stem cells, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), embryonic stem cells (ESCs), and other stem cells can tailor protocols to your specific research needs.
Q: Can you help identify the key molecular cargo responsible for SC-Exo-mediated DenC regulation?
A: Yes, through our high-throughput omics platforms—proteomics and transcriptomics—we help identify and analyze key cargo molecules involved in SC-Exo-induced dendritic cell modulation.
Reference
-
Scheib, Nils, et al. "The dendritic cell dilemma in the skin: between tolerance and immunity." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2022): 929000. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Dendritic cells exhibit immunostimulatory or tolerogenic potential depending on the context.1
Fig.1 Dendritic cells exhibit immunostimulatory or tolerogenic potential depending on the context.1










