PPP1R12A and Associated Diseases
With the help of our excellent and well-trained scientists and advanced platforms, Creative Biolabs is good at strategy design and function assessment of your projects in the field of gene therapy. We can provide detailed and one-stop customer services to meet all your demands.
Overview of PPP1R12A
In humans, protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12A (PPP1R12A, also known as the myosin-binding subunit of myosin phosphatase) is encoded by the PPP1R12A gene and is one of the subunits of myosin phosphatase, which can regulate the interaction between actin and myosin downstream of the guanosine triphosphatase Rho. PPP1R12A is also a critical regulator of protein phosphatase 1C (PPP1C) and mediates binding to myosin. As part of the PPP1C complex, PPP1R12A is related to the dephosphorylation of PLK1. Several transcript variants have been identified for PPP1R12A.
PPP1R12A in Disease
Diseases associated with PPP1R12A include genitourinary and/or brain malformation syndrome, Moebius syndrome, and cancers such as colorectal cancer and cholangiocarcinoma.
- Colorectal cancer
PPP1R12A can be used for the prediction of survival in patients with stage III colorectal cancer (CRC). CRC is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers worldwide and oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy is recommended in advanced CRC patients. PPP1R12A is associated with CRC chemoresistance through increasing Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/AKT pathway by PPP1R12A-induced dephosphorylated Merlin. By analyzing the relative copy number of PPP1R12A, it is found that low PPP1R12A copy number is related to poor overall survival in stage III CRC tissue samples of patients who received chemotherapy treatment. Taken together, the copy number of PPP1R12A can be used to independently predict the overall survival of patients with stage III CRC.
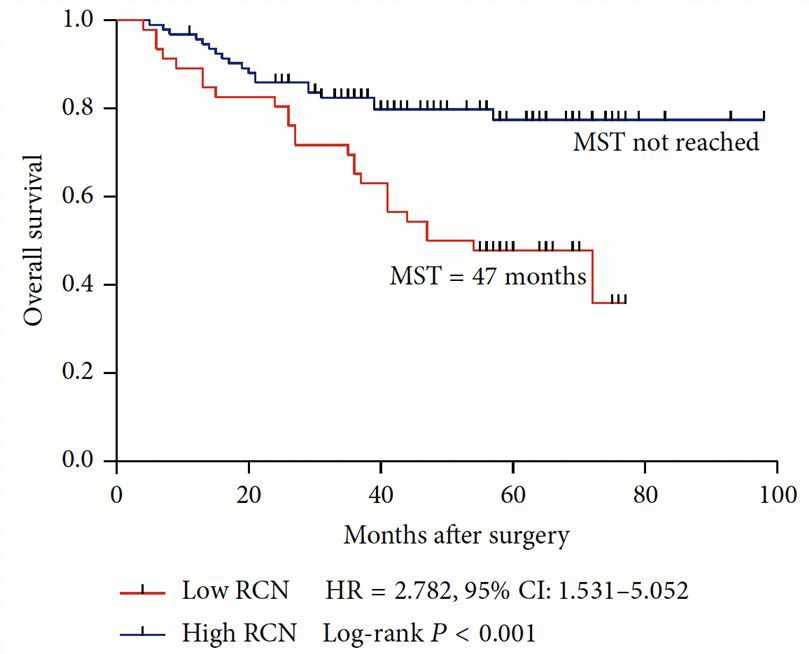 Fig.1 Low gene relative copy number predicts poor overall survival in patients with stage III CRC. (Zhang, 2015)
Fig.1 Low gene relative copy number predicts poor overall survival in patients with stage III CRC. (Zhang, 2015)
- Cholangiocarcinoma
The miR-455-5p/PPP1R12A axis plays important role in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) development. Bile duct epithelial cells-derived CCA is a highly malignant bile duct system tumor and it is reported that miR-455-5p contributes importantly to multiple tumor development. In CCA tissues, miR-455-5p expression is reduced and upregulated expression of PPP1R12A can be observed. In the CCA cell line, overexpression of miR-455-5p inhibits cell proliferation and PPP1R12A expression and promotes apoptosis, migration, and invasion. Whereas inhibition of PPP1R12A expression will reduce the survival of CCA cells and mimics the effects of miR-455-5p on CCA cells. In summary, the miR-455-5p/ PPP1R12A axis controls the survival and metastasis of CCA cells and can be regarded as a potential therapeutic target for CCA treatment.
With the spirit of non-stop exploration, Creative Biolabs is always ready to collaborate with our clients and provide detailed gene therapy development services based on our excellent scientists and advanced platforms. Please feel free to contact us for more details about your PPP1R12A project.
Reference
- Zhang, C.; et al. PPP1R12A Copy Number Is Associated with Clinical Outcomes of Stage III CRC Receiving Oxaliplatin-Based Chemotherapy. Mediators of Inflammation. 2015, 2015: 1–7. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
