PRKDC and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is one of the well-recognized experts who are professional in applying advanced one-stop drug discovery platforms for a broad range of project objectives. Here we describe the PRKDC gene and associated diseases for our clients. We are able to provide technical support services at all stages of your drug development.
Introduction of PRKDC
Encoded by the PRKDC gene, the DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit (DNA-PKcs) is a serine/threonine protein kinase belonging to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family. In fact, the DNA-PKCS itself is unprepared. It can be triggered by using KU at the end of the DNA. In humans, the main function of DNA-PK is to recognize double-strand DNA breaks and catalyze the repair process of non-homologous end joining. In this case, DNA-PKCS plays an important role in DNA to repair the non-homologous end connection (NHEJ) pathway and V(D)J reorganization. Together with ATR and ATM, DNA-PK phosphorylates proteins involved in the DNA damage checkpoint.
PRKDC and Immunodeficiency
Studies have shown that DNA-PKcs knockout mice have serious joint immune defects due to its V(D)J reorganization defects. As part of a multiprotein complex, DNA-PK is also required for the establishment of central tolerance. In one study, mutations in PRKDC can be detected in two patients with typical severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID). In conclusion, PRKDC mutations are strongly associated with autoimmunity and granulomas, and PRKDC hypomorphic mutations prevent AIRE function.
PRKDC and Cancer
The defect of DNA repair genes can cause cumulative DNA damage and become the fundamental cause of cancer. In addition, excessive DNA damage may also increase its genetic changes. Studies have shown that PRKDC mutations were detected in 30% of ovarian cancer and 10% of breast cancer and pancreatic cancer. Interestingly, the mutation and expression levels of PRKDC vary greatly among different tumors. For example, the reduced PRKDC expression can be found in a variety of sporadic cancers, such as breast cancer (57%), prostate cancer (51%), cervical carcinoma (32%), nasopharyngeal carcinoma (30%), epithelial ovarian cancer (29%), and gastric cancer (23%). In most other tumor types, DNA-PKcs expression was significantly higher than in adjacent tissues. The development and treatment of different types of tumors are also affected by DNA-PKcs. It has been used to predict treatment response to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
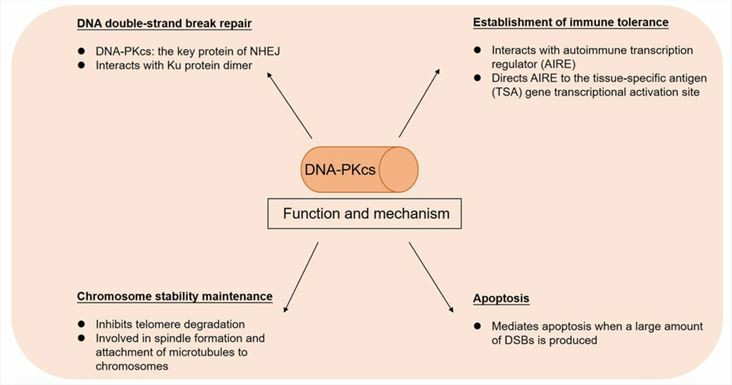 Fig.1 Function and mechanism of DNA-PKcs. (Chen, et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Function and mechanism of DNA-PKcs. (Chen, et al., 2021)
Related Services
- Viral Vector Design and Construction
- mRNA Therapeutics
- siRNA In Vitro Screening Service
- ASO In Vitro Screening Service
Equipped with world-leading technology platforms and professional scientific staff, Creative Biolabs can provide a range of gene therapy related services. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Chen, Y.; et al. Role of PRKDC in cancer initiation, progression, and treatment. Cancer Cell International. 2021 Dec;21(1):1-0. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
