VCAN and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the VCAN gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of VCAN
Encoded by the VCAN gene, versican is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (CSPG) that exists in various human tissues. As a member of the hyalectin family of extracellular matrix (ECM) components, versican simultaneously plays a role in a variety of diseases in a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory manner.
Till now, there are at least five different isoforms of versican have been identified, including V0, V1, V2, V3, and V4. Among them, the V0 and V1 variants are the predominant forms that accumulate in most diseases. The V3 variants are not significantly elevated in disease and may serve as an important means of reducing versican accumulation in tissues to suppress inflammatory responses.
Functions of VCAN
Due to its glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains, versican is negatively charged and attracts water thereby contributing to the viscoelasticity of the microenvironment surrounding cells. Versican can interact with many ECM components near the cell surface, creating a mechanoactive biopolymer around the cell and ultimately affecting cell shape, adhesion, proliferation, and migration. What’s more, versican acts as a depot to regulate the release of cytokines and growth factors at various times, allowing precise control of cellular activity and behavior. Versican is expressed along the neural crest pathway and affects neural cell migration and also directs embryonic cell migration, which is important for heart formation.
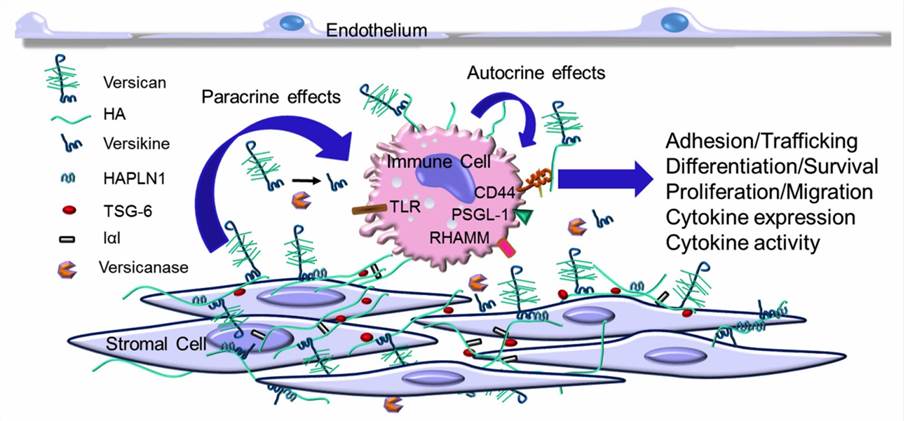 Fig.1 Versican increases in the extracellular matrix (ECM) as part of the early inflammatory response.1
Fig.1 Versican increases in the extracellular matrix (ECM) as part of the early inflammatory response.1
VCAN in Cancer
Expression levels of versican are dramatically increased in disease and low in normal tissues. Compared with control healthy tissue, the expression and accumulation of versican are significantly elevated in leiomyosarcoma (LMS). Studies have shown that versican affects pro-tumor inflammation, and evades immune surveillance and immune regulation to play a central role in cancer development. For example, the over-expression of versican in breast and Lewis lung cancer leads to the accumulation and activation of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) through Toll-like receptor 2 and its co-receptors Toll-like receptor 6 and CD14. In Lewis lung cancer, the stromal cell-derived versican and its fragment versikine are associated with increased angiogenesis, which is an important factor in the inflammatory response of this tumor. Versican plays a central role in a variety of diseases so that has served as a prime candidate for therapeutic intervention in disease treatment.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Wight, T.N.; et al. Versican—a critical extracellular matrix regulator of immunity and inflammation. Frontiers in immunology. 2020, 11: 512. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
