NUMA1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs provides a wide range of services for gene therapy, particularly for strategy design and function assessment in vitro and in vivo, with the assistance of our exceptional and well-trained scientists. We are able to offer any consumer services that satisfy your needs.
Overview of NUMA1
In humans, nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 (NUMA1, also known as nuclear matrix protein-22, NMP22) is a protein encoded by the NUMA1 gene. NUMA1 is a large protein and serves as a structural component of the nuclear matrix. During cell division, NUMA1 can interact with microtubules and is essential in the formation and organization of the mitotic spindle, and the alignment and segregation of chromosomes. Alternative splicing of NUMA1 can lead to multiple transcript variants during translation.
NUMA1 in Disease
NUMA1 mutants are involved in different diseases such as triple-negative breast cancer. It is also related to mitotic lethality in several kinds of cancer cells.
- Triple-negative breast cancer
NUMA1 is related to the progression of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). LINC01194 is served as an oncogene in several cancers containing TNBC and can promote TNBC progression. NUMA1 can be recruited to the 3’ untranslated region of UBE2C by LINC01194 and stabilize UBE2C mRNA, which further enhances the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway via degradation of the inhibitor of the Wnt signal pathway. In TNBC cell lines, loss of NUMA1 can accelerate UBE2C degradation, and overexpression of NUMA1 can restore the expression of UBE2C caused by LINC01194 interference and promote the malignant progression of TNBC. Thus, LINC01194/NUMA1/UBE2C axis can be a promising clinical therapeutic strategy for patients with TNBC.
- Mitotic lethality
NUMA1 is associated with mitotic lethality induced by BMI1 inhibition in cancer cells. BMI1 is an oncogene expressed in several cancer cells. BMI1 overexpression is regarded as a well-established inducer of cancer and the knockdown of BMP1 can result in cell senescence or apoptosis of cancer cells. According to the drug resistance screen of human cancer cells with the treatment of BMI1 inhibitor PTC-318, NUMA1 mutation is identified as the inducer of PTC-318 cell death resistance. BMI1 inhibition causes cell death following mitotic arrest in NUMA1-proficient cells, BMI1 inhibitor-treated cells can tolerate the BMI1-dependent cell death in the NUMA1 knockout condition with a mitotic arrest phenotype. In a word, NUMA1 can be taken into consider when BMI1 related clinical therapies are used.
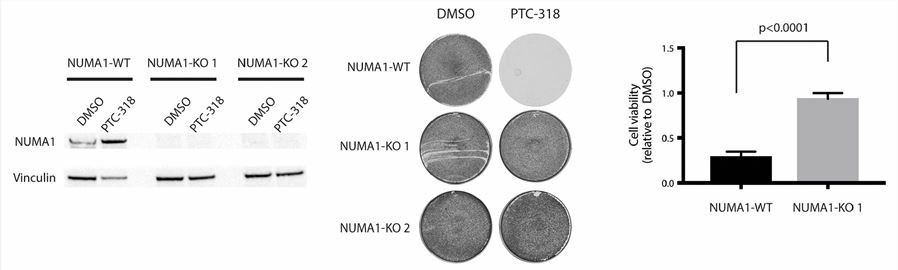 Fig.1 NUMA1 knockout rescues the BMI1 inhibitor-induced mitotic lethality. (Gisler, 2020)
Fig.1 NUMA1 knockout rescues the BMI1 inhibitor-induced mitotic lethality. (Gisler, 2020)
Creative Biolabs is always prepared to work with our clients and offers thorough gene therapy development services in the spirit of never-ending discovery. Please feel free to contact us for more details about your NUMA1 project.
Reference
- Gisler, S.; et al. A genome-wide enrichment screen identifies NUMA1-loss as a resistance mechanism against mitotic cell-death induced by BMI1 inhibition. PLoS ONE. 2020, 15: e0227592. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
