Monoclonal antibody (mAb) is an important class of therapeutic glycoproteins used for the treatment of cancers, inflammation, and infectious diseases. In contrast to other biomacromolecules, the glycan biosynthesis is not directly template-driven but is a complex result of metabolic and enzymatic reactions that are influenced by many different factors.
Nevertheless, mAbs are frequently produced as mixtures of Fc glycoforms and the control of glycosylation to a homogeneous status in various cell expression systems is still a major challenge. As a market leader in the field of therapeutic antibodies, Creative Biolabs has successfully established a wide spectrum of antibody functional assays and offers impeccable chemoenzymatic glycoengineering services for global customers.
Background
IgG antibodies consist of two heavy chains and two light chains that form three distinct protein domains, including two variable Fab domains and one constant Fc domain linked by a flexible hinge region. Many therapeutic antibodies have been developed and IgG antibodies are extensively generated in lots of host expression systems, which contain a conserved N-glycosylation site at the Fc domain.
The Fc domain is a homodimer carrying two N-glycans at the conserved N-glycosylation sites (N297). The attached oligosaccharides are complex, biantennary types with considerable structural heterogeneity, in which the N-linked heptasaccharide core can be decorated differentially with core fucose (Fuc), bisecting N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), terminal sialic acid (Sia), and terminal galactose (Gal). The fine structures of Fc N-glycans can profoundly modulate the effector functions of antibodies, such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
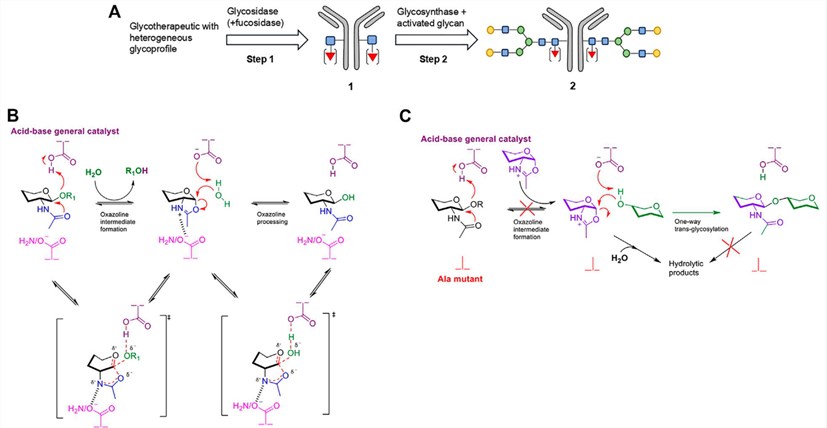 Fig.1 Structures of a typical IgG antibody and the Fc N-glycans. (Huang, 2012)
Fig.1 Structures of a typical IgG antibody and the Fc N-glycans. (Huang, 2012)
Additionally, X-ray crystallographic and NMR structural studies indicate that the Fc N-glycans are located within the CH2/CH3 subdomains of each heavy chain and have multiple non-covalent interactions with the Fc domain to retain its conformational flexibility. Based on compelling studies, the attachment of different Fc glycans can have a distinct impact on Fc domain conformations, and thus glycosylation is a primary concern in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Chemoenzymatic Mechanisms
As we know, the glycans of the protein products can be chemoenzymatically remodeled. The therapeutic mAb with an ability to express defined Fc N-glycans has recently been developed using targeted gene knockdown or knockout methods in different cell lines. An alternative way to regulate the heterogeneity of glycosylation in glycoproteins is to perform glycosylation remodeling by trimming the heterogeneous N-glycans and extending the oligosaccharide moiety via enzymatic glycosylation. A report introduced a chemoenzymatic approach for glycosylation remodeling of intact full-length mAbs (Rituximab) that utilized the transglycosylation activity of EndoS and glycosynthase mutants, employing glycan oxazolines as substrates.
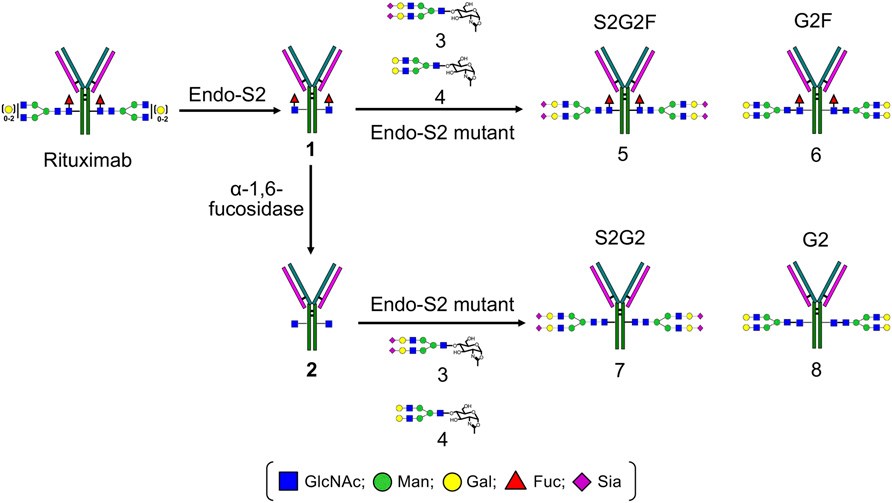 Fig.2 Synthesis of homogeneous antibody glycoforms via chemoenzymatic glycosylation remodeling of the Fc glycans. (Li, 2017)
Fig.2 Synthesis of homogeneous antibody glycoforms via chemoenzymatic glycosylation remodeling of the Fc glycans. (Li, 2017)
EndoS is an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase (ENG’ase) from Streptococcus pyogenes. Itis highly specific for the Fc N-glycans of intact IgG antibodies and capable of hydrolyzing the Fc N-glycans by cleaving the β-1,4-glycosidic bond within the chitobiose core of N-glycans. The glycosynthase mutants (EndoS-D233A and EndoS-D233Q) generated by site-directed mutagenesis have more significant transglycosylation activity than hydrolysis activity, so that glycosynthase mutants can transfer the complicated N-glycans from the corresponding oxazoline onto the GlcNAc or GlcNAcα1-6 Fuc moiety on intact antibodies.
Chemoenzymatic Glycoengineering Services at Creative Biolabs
Controlled alteration of the Fc-attached oligosaccharide to manipulate Fc-mediated antibody functions is becoming a challenging task in antibody engineering. In Creative Biolabs, we have studied a mature chemoenzymatic method for Fc glycosylation remodeling. This approach is composed of two steps:
-
Cleaving all heterogeneous N-glycans by an endoglycosidase to leave only the first GlcNAc at the glycosylation sites.
-
Adding back a well-defined N-glycan block through an endoglycosidase-catalyzed transglycosylation reaction for homogeneous N-glycans.
To control Fc N-glycans, we performed a rearrangement of Fc N-glycans from a heterogeneous N-glycosylation pattern to homogeneous N-glycans by chemoenzymatic processes with three endoglycosidases (Endo-S, Endo-S2, and Endo-F3). Besides, we have also developed a semi-synthesis approach for the sialylated and asialylated biantennary N-glycan oxazolines from sialylglycopeptide (SGP).
Remarkably, our chemoenzymatic glycoengineering technologies display several advantages that cannot be ignored.
-
Multiple highly efficient chemoenzymatic approaches can be chosen for site-selective Fc glycoengineering of an intact mAb.
-
The LC-ESI-MS analysis can be used to confirm the purity of the homogeneous glycoforms of mAb remodeled.
-
Practiced staff and years of experience for many projects, a detailed report and data interpretation for delivery.
If you’re interested in more detailed information about our service, please feel free to contact us or send us an inquiry.
References
-
Huang, W.; et al. Chemoenzymatic glycoengineering of intact IgG antibodies for gain of functions. J Am Chem Soc. 2012, 134(29): 12308-12318.
-
Li, T.; et al. Modulating IgG effector function by Fc glycan engineering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017, 114(13): 3485-3490.
For Research Use Only.
 Fig.1 Structures of a typical IgG antibody and the Fc N-glycans. (Huang, 2012)
Fig.1 Structures of a typical IgG antibody and the Fc N-glycans. (Huang, 2012)
 Fig.2 Synthesis of homogeneous antibody glycoforms via chemoenzymatic glycosylation remodeling of the Fc glycans. (Li, 2017)
Fig.2 Synthesis of homogeneous antibody glycoforms via chemoenzymatic glycosylation remodeling of the Fc glycans. (Li, 2017)