Acinetobacter baumannii-derived Exosome Research & Application
Workflow Insights Infrastructure Our Advantages Client Perspectives FAQs
Among Gram-negative bacteria, Acinetobacter baumannii has emerged as one of the most intensively studied species due to its complex membrane architecture and dynamic extracellular vesicle secretion. Exosomes derived from A. baumannii exhibit remarkable structural stability and biochemical diversity, reflecting the bacterium's capacity to adapt to environmental and host-associated stresses. Recent scientific studies have demonstrated that A. baumannii-derived exosomes can elicit robust immune responses and modulate host–pathogen interactions, providing valuable insight into bacterial communication and intercellular signaling mechanisms.
Creative Biolabs has established a specialized research platform dedicated to bacterial vesicle studies, empowering investigators to isolate, purify, and analyze A. baumannii-derived exosomes with a high degree of precision. Rather than focusing on therapeutic or clinical endpoints, Creative Biolabs' expertise centers on elucidating the biological functions and molecular cargo of bacterial vesicles, enabling researchers to explore novel mechanisms in microbiology, immunology, and molecular biotechnology.
Streamlined Workflow for Exosome Isolation
Our standardized process focuses on the customized development of exosome preparations, designed to ensure purity and reproducibility. Optional downstream analyses - such as proteomic profiling, RNA sequencing, or lipid composition assays - are available upon request, depending on the availability of strain-specific libraries.
1. Bacterial Cultivation
-
A. baumannii strains are cultured in Mueller–Hinton broth under controlled shaking at 37°C overnight.
-
(Optional) For mutant or engineered strains lacking lipopolysaccharide synthesis, colistin is added to maintain selective pressure.
2. Primary Separation
-
Cultures are subjected to high-speed centrifugation to remove intact cells.
-
The resulting supernatant is carefully filtered to ensure a cell-free fraction.
3. Exosome Concentration
-
The filtered supernatant undergoes ultracentrifugation at high g-force to pellet A. baumannii-derived exosomes.
-
Pellets are resuspended in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
4. Quality and Sterility Checks
-
The vesicle preparation is passed through a sterile filter to ensure no viable bacteria remain.
-
(Optional) Agar plate sterility tests and endotoxin quantification (via LAL or horseshoe crab assay) can be performed to validate product quality.
5. Storage and Delivery
Vesicles are stabilized and stored under appropriate temperature conditions for subsequent biochemical or functional research.
To discuss feasibility or request optional analytical modules, reach out to Creative Biolabs' exosome research specialists.
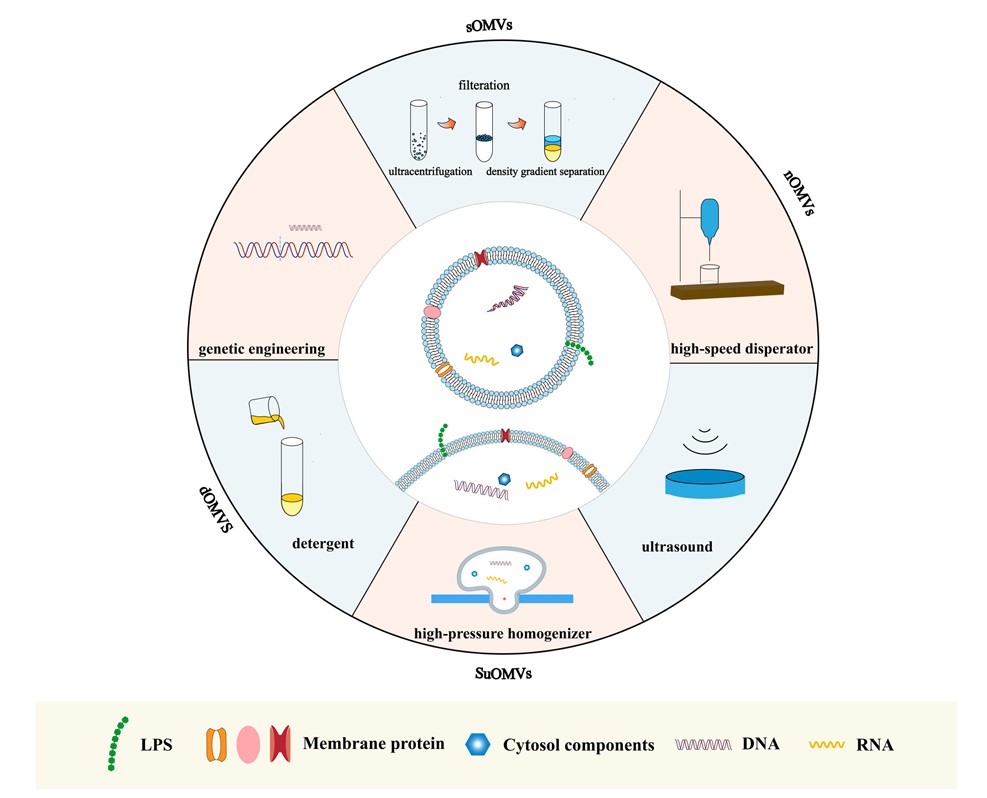 Fig.1 Artificial preparation of A. baumannii exosomes.1
Fig.1 Artificial preparation of A. baumannii exosomes.1
Scientific Insights: Key Findings from Global Research
The field of A. baumannii-derived exosome research continues to expand, with numerous studies uncovering their biological potential. Creative Biolabs follows the latest developments to help clients integrate verified experimental findings into their own projects. Below is a summary of selected academic observations regarding A. baumannii-derived exosomes, highlighting their structural, immunological, and functional attributes.
|
Research Focus
|
Summary of Findings
|
|
Immunogenicity and Antibody Production
|
Studies have demonstrated that A. baumannii-derived exosomes trigger antigen-specific antibody responses when administered in animal models. Antibody titers and total antibody potency increased upon booster immunization, suggesting a stable immunogenic profile that can be leveraged in bacterial immune studies.
|
|
Reduction of Bacterial Load and Inflammation
|
In murine infection models, animals pre-exposed to A. baumannii exosomes exhibited significantly lower bacterial burdens and enhanced survival. Cytokine profiling revealed suppressed levels of proinflammatory mediators, indicating that bacterial exosomes may modulate innate immune signaling.
|
|
Exosomes from Clinical Isolates
|
Research involving exosomes derived from clinical A. baumannii isolates revealed partial immunoprotection against infection. The variable immunogenicity underscores the importance of strain diversity and supports the need for comparative vesicle studies under controlled laboratory conditions.
|
|
Comparison of Administration Routes
|
When comparing subcutaneous versus intramuscular immunization with A. baumannii exosomes, subcutaneous delivery elicited a stronger antibody response and reduced systemic inflammation, suggesting that the delivery route may influence immune activation.
|
|
Nasal Immunization and Mucosal Immunity
|
Nasal delivery of A. baumannii exosomes promoted localized IgA production and enhanced mucosal defense, preventing bacterial spread from respiratory tissues to systemic circulation. These findings highlight the capacity of bacterial exosomes to stimulate site-specific immune barriers.
|
Collectively, these studies underline the biological versatility of A. baumannii-derived exosomes as molecular tools in basic research, particularly for investigating antigen presentation, vesicle-mediated signaling, and host–microbe interactions.
Discuss your research ideas with Creative Biolabs to explore how our platform can enhance your study of bacterial vesicle biology.
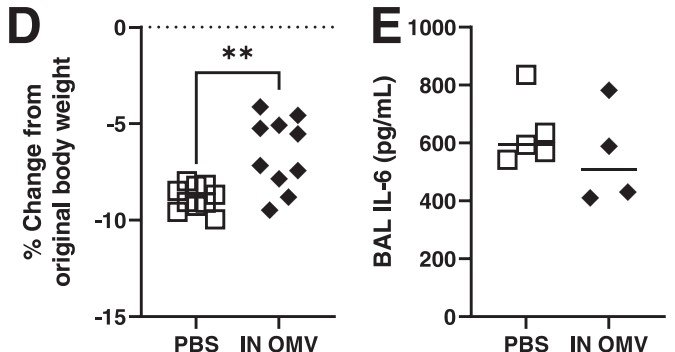 Fig.2 Nasal administration of Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes reduced body weight loss and pro-inflammatory factor levels in mice.2
Fig.2 Nasal administration of Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes reduced body weight loss and pro-inflammatory factor levels in mice.2
Research Support Infrastructure at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs provides an integrated research platform built to empower microbiologists and immunologists investigating Gram-negative bacterial vesicles. Our support ecosystem enables each project - from concept design to validated exosome delivery - to be handled with consistency, transparency, and scientific precision.

Tailored Workflow Development
Optimized protocols customized for A. baumannii and other Gram-negative species.

Cross-Platform Compatibility
Experience with multiple culture media, including both standard and selective formulations.

Optional Characterization Packages:
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) for morphological confirmation.
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for size distribution and concentration.
-
(Optional) Proteomics and lipidomics to analyze exosomal cargo.

Data Transparency and Documentation
Each project includes detailed batch reports and traceable process records.

Flexible Scale Options
From exploratory-scale preparations to large-volume vesicle collection for in vitro studies.
Connect with Creative Biolabs' technical support team to learn how our infrastructure can accelerate your vesicle-based discoveries.
Distinct Advantages of Working with Creative Biolabs
 Expertise in Gram-Negative Vesicles
Expertise in Gram-Negative Vesicles
Deep understanding of bacterial outer membrane vesicle biology, with specialization in A. baumannii.
 Rigorous Quality Standards
Rigorous Quality Standards
Comprehensive sterility and safety validations across all stages of isolation.
 Customizable Project Design
Customizable Project Design
Flexible research options, from basic vesicle isolation to advanced multi-omics integration (optional).
 Dedicated Project Managers
Dedicated Project Managers
Direct communication with assigned scientists to ensure project alignment and timely updates.
Reach out to Creative Biolabs to learn how our tailored project management and technical resources can strengthen your exosome research.
Perspectives from Research Collaborators
Many researchers who have worked with Creative Biolabs describe the collaboration as both productive and reliable. Their experiences highlight the company's commitment to precision and responsiveness throughout the experimental cycle.
Clients frequently note that Creative Biolabs' ability to handle complex bacterial cultures and their derived vesicles significantly streamlines their workflow, enabling them to focus on data interpretation rather than procedural challenges. Others have emphasized the consistency of vesicle yields across independent batches and the professionalism of Creative Biolabs' communication during milestone updates.
To experience the same level of research partnership, reach out to Creative Biolabs' collaboration desk today.
As scientific interest in bacterial extracellular vesicles continues to expand, Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes stand at the forefront of discovery. Creative Biolabs remains committed to refining its methodologies and expanding its strain-specific vesicle libraries, facilitating access for researchers aiming to explore novel biological pathways or design comparative analyses across multiple bacterial species. The company's continued investment in technological innovation ensures that each collaboration contributes to the evolving understanding of microbial communication and vesicle biology. Connect with Creative Biolabs to discuss how your next research initiative can leverage our expertise in bacterial exosome science.
FAQs
Q: What are Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes, and how are they formed?
A: Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes are nano-sized membrane-bound vesicles released from bacterial cells. They are created by the bacterial membrane invaginating and then budding off the vesicle. These exosomes encapsulate various biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, which can influence intercellular communication and environmental interactions.
Q: What are the primary functions of exosomes produced by Acinetobacter baumannii?
A: Exosomes from Acinetobacter baumannii play several crucial roles, including:
-
Horizontal gene transfer: They have the ability to propagate resistance features by passing on antibiotic resistance genes to other bacteria.
-
Modulation of host immune responses: These exosomes may contain immunomodulatory factors that influence host immune pathways, potentially helping the bacteria evade immune detection.
-
Biofilm formation: Exosomes may contain signaling molecules that promote biofilm development, enhancing the survival of bacterial communities.
Q: What are the challenges in studying Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes?
A: Challenges include:
-
Isolation and purification: Obtaining pure populations of A. baumannii exosomes can be complicated due to other membrane vesicles and debris in bacterial cultures.
-
Characterization: Detailed characterization of the exosomal content requires advanced techniques such as mass spectrometry and RNA sequencing, which can be technically demanding.
-
Functional studies: Determining the specific biological functions of the various molecules within exosomes can involve intricate experimental designs and validation processes.
Q: What potential applications do Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes have in research?
A: Research applications of Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes include:
-
Biomarker discovery: Exosomal contents could serve as biomarkers for identifying specific strains or resistance profiles.
-
Vaccine development: Understanding how these exosomes modulate host immune responses might inform vaccine strategies against A. baumannii.
-
Synthetic biology: Exosomes can be engineered for use in targeted drug delivery systems, leveraging their natural ability to carry bioactive molecules.
Q: How can studying Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes contribute to understanding bacterial pathogenesis?
A: Investigating these exosomes provides insight into the mechanisms by which A. baumannii interacts with its environment and hosts. By analyzing the specific molecules within exosomes, researchers can uncover how the bacterium modifies host responses, persists in hostile environments, and develops antibiotic resistance, thereby enriching our understanding of bacterial pathogenesis.
Q: Are any novel methodologies being developed to study Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes?
A: Yes, innovative methodologies such as enhanced imaging techniques (e.g., super-resolution microscopy) and single-vesicle analysis using nanoplasmonics are being explored. Additionally, high-throughput sequencing and advanced bioinformatics tools are facilitating the analysis of exosomal RNA and protein content, allowing for more comprehensive characterizations and functional analyses.
References
-
Weng, Zheqi, et al. "Outer Membrane Vesicles from Acinetobacter baumannii: Biogenesis, Functions, and Vaccine Application." Vaccines 12.1 (2023): 49. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12010049.
-
Higham, Sophie L., et al. "Intranasal immunization with outer membrane vesicles (OMV) protects against airway colonization and systemic infection with Acinetobacter baumannii." Journal of Infection 86.6 (2023): 563-573. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part D & E of the original image and revising the title. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.02.035.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Artificial preparation of A. baumannii exosomes.1
Fig.1 Artificial preparation of A. baumannii exosomes.1
 Fig.2 Nasal administration of Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes reduced body weight loss and pro-inflammatory factor levels in mice.2
Fig.2 Nasal administration of Acinetobacter baumannii-derived exosomes reduced body weight loss and pro-inflammatory factor levels in mice.2













