Neisseria lactamica-derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Workflow Exosome Features Research Edge Client Feedback FAQs
Neisseria lactamica is a non-pathogenic commensal species frequently colonizing the human nasopharynx, particularly in children. Its close genetic relationship to Neisseria meningitidis has made it an intriguing research model for studying immune interactions and bacterial vesicle biology without the pathogenic risks associated with its counterparts.
Recent discoveries have demonstrated that Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes, also known as outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), contain a complex mixture of outer membrane proteins, lipooligosaccharides, and periplasmic components capable of stimulating innate immune responses.
Creative Biolabs provides specialized research services to support Neisseria lactamica exosome isolation, customization, and characterization, helping researchers investigate their molecular composition, immunogenic potential, and biotechnological applications.
Scientific Overview
NEISSERIA LACTAMICA BIOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS
A harmless Gram-negative diplococcus commonly used as a safe comparative model to pathogenic Neisseria species.
Shares numerous outer membrane proteins and structural similarities with N. meningitidis.
Naturally induces mucosal immune responses during colonization.
RESEARCH INSIGHTS ON EXOSOME APPLICATIONS
Exosomes from N. lactamica show immunostimulatory properties through pattern-recognition receptor activation.
These exosomes can serve as model carriers for antigen display and vaccine platform studies.
Engineered N. lactamica-derived exosomes allow for efficient delivery of foreign antigens and targeted immune modulation.
Partner with us to discuss how our Neisseria lactamica exosome expertise can support your bacterial vesicle research.
Workflow
Creative Biolabs follows a well-structured, research-grade workflow for the development and preparation of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes, designed to ensure consistency, purity, and scalability. Our standard workflow focuses on custom exosome generation, while detailed analytical assessments (morphology, proteomics, etc.) are available as optional services depending on the availability of species-specific genomic libraries.
1. Strain Cultivation
-
Culture Neisseria lactamica under aerobic conditions in optimized media to promote outer membrane vesicle formation.
-
Monitor bacterial growth to determine the optimal harvest phase for vesicle enrichment.
-
Ensure strain identity and purity before proceeding to exosome extraction.
2. Primary Vesicle Isolation
-
Centrifuge the culture at low speed to remove intact cells and collect the clarified supernatant.
-
Perform ultracentrifugation to pellet N. lactamica-derived exosomes.
-
Resuspend vesicles in buffer for downstream applications.
3. Endotoxin Reduction and Concentration (optional)
-
Mix 1% sodium deoxycholate with exosome suspension to reduce lipooligosaccharide (LOS) content.
-
Conduct tangential flow filtration to remove detergent residues.
-
Wash the concentrate with sucrose buffer to obtain purified vesicles suitable for further modification.
4. Structural and Morphological Analysis (optional)
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for vesicle imaging and quantification.
-
Validation of vesicle size distribution, uniformity, and bilayer integrity.
5. Molecular Composition Profiling (optional)
-
Proteomic and RNA sequencing to characterize exosome content.
-
Lipidomic profiling for detailed membrane component analysis.
6. Functional Immunoassays (optional)
-
In vitro testing of dendritic cell activation markers and cytokine induction.
-
Quantification of antigen-specific antibody responses in model systems.
Contact Creative Biolabs to design a customized exosome analysis plan aligned with your scientific objectives.
Features of Neisseria lactamica-derived Exosomes
A growing body of research has explored the biological behavior of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes. These vesicles serve as both biological tools and nanoplatforms for antigen presentation and immune response modulation. The following table summarizes major findings from academic studies, highlighting how engineered vesicles can elicit measurable immune responses.
|
RESEARCH FOCUS
|
KEY OBSERVATION OR OUTCOME
|
|
Characterization of exosomes displaying recombinant antigens.
|
Engineered vesicles containing outer membrane proteins and target antigens confirmed through TEM imaging and protein blot analysis.
|
|
Activation of antigen-presenting cells.
|
N. lactamica-derived exosomes induced dendritic cell activation with upregulated CD40 and CD86 co-stimulatory molecules and cytokine production.
|
|
Cytokine modulation in immunized models.
|
Immunization with antigen-modified vesicles elevated IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 cytokine secretion, suggesting balanced pro- and anti-inflammatory responses.
|
|
Induction of adaptive immunity.
|
Enhanced expression of TNF-α, IL-4, IFN-γ, and IL-2 in CD4⁺ and CD8⁺ T lymphocytes indicated strong T-cell activation.
|
|
Antibody production and antigen recognition.
|
Mice immunized with antigen-coupled vesicles produced significantly higher antibody titers compared with free antigen controls or unmodified vesicles.
|
Discuss your next experimental setup with us and explore advanced ways to engineer exosomes for molecular research.
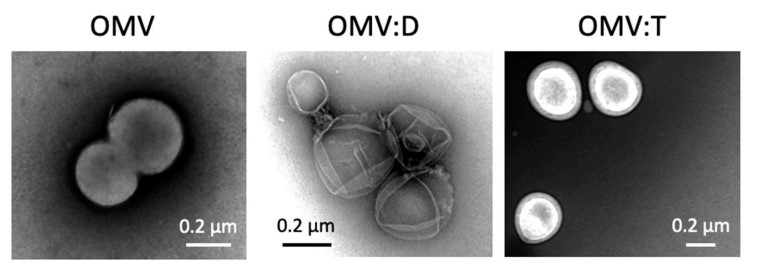 Fig.1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Distinctive Attributes and Research Advantages
Natural Immunogenicity with Safety
-
As a non-pathogenic species, Neisseria lactamica offers a safer model for studying vesicle-mediated immune modulation.
-
Its exosomes can mimic pathogen-associated patterns without associated biosafety risks.
Versatile Engineering Potential
-
Compatible with fusion expression systems and protein display strategies.
-
Supports customizable antigen conjugation and surface modification studies.
Scalable and Reproducible Production
-
Creative Biolabs' streamlined workflow allows scalable exosome production with consistent yield and composition.
-
Quality control ensures reliable batch-to-batch comparability.
Comprehensive Customization Options (optional)
-
From biotinylation-based antigen coupling to proteomic mapping, Creative Biolabs enables flexible project scopes.
-
Optional molecular analysis and data interpretation support are available upon request.
Reach out to us to customize your Neisseria lactamica exosome workflow from isolation to detailed characterization.
Voices from Our Collaborators
"We collaborated with Creative Biolabs for a comparative exosome study using Neisseria lactamica. Their production consistency and documentation were outstanding - it made downstream immunogenicity work much easier."
— Research Fellow
"The optional biotinylation and antigen-display workflow provided by Creative Biolabs allowed us to create customized vesicles for antigen mapping. Their team was proactive in troubleshooting and optimizing yield."
— Senior Scientist
"Creative Biolabs' exosome purification quality was beyond expectation. TEM images were clean and vesicle distribution was uniform. Their technical support helped us publish our findings faster."
— Assistant Professor
Contact Creative Biolabs to discuss your Neisseria lactamica exosome project.
The study of Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes continues to open new avenues in microbial communication, mucosal immunology, and nanoscale antigen display systems. With their safety profile and engineering flexibility, these vesicles represent a valuable resource for basic microbiological and immunological research. Creative Biolabs remains committed to advancing bacterial vesicle research by providing reliable, high-quality materials and technical expertise to laboratories worldwide. Begin your Neisseria lactamica exosome study with Creative Biolabs - your trusted partner in bacterial vesicle research.
FAQs
Q: What unique characteristics do Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes possess compared to exosomes derived from other bacterial species?
A: Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes have unique lipid and protein compositions that may influence immune responses. Their distinct surface markers may facilitate specific interactions with host immune cells, potentially leading to unique immunomodulatory effects.
Q: How do Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes influence the host immune system?
A: Research indicates that these exosomes can induce tolerogenic responses by modulating dendritic cell function and skewing T-cell responses. This can be crucial for understanding their role in maintaining immune homeostasis and potentially preventing overactive immune reactions.
Q: Are there specific pathways through which Neisseria lactamica exosomes promote cellular communication with host cells?
A: Yes, Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes utilize various signaling pathways, including those involving Toll-like receptors and other surface receptors. These pathways can help in delivering regulatory molecules that promote cell-to-cell communication and modulate inflammatory responses.
Q: What potential biotechnological applications exist for Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes in vaccine development?
A: Due to their immunogenic properties, Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes are being explored as carriers for antigen delivery in vaccine formulations. Their ability to trigger specific immune responses could enhance vaccine efficacy, particularly against pathogens colonizing mucosal surfaces.
Q: Can Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes be engineered for enhanced therapeutic delivery?
A: Yes, researchers are investigating methods to modify these exosomes to improve their stability and targeting capabilities. Techniques such as genetic engineering can be employed to load specific therapeutic molecules or to express ligands on their surface for targeted delivery to particular cell types.
Q: What role do Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes play in inter-bacterial communication?
A: These exosomes are believed to play a role in horizontal gene transfer and metabolic cooperation among bacteria. They can carry genetic material and proteins that may influence the behavior of neighboring bacterial populations, potentially altering their virulence or resistance profiles.
Reference
-
Barbosa, Mayra M. Ferrari, et al. "Primary and memory response of human monocytes to vaccines: role of nanoparticulate antigens in inducing innate memory." Nanomaterials 11.4 (2021): 931. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using part of the original image and revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040931.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Transmission electron microscope micrographs of purified and engineered Neisseria lactamica-derived exosomes.1









