Klebsiella pneumonia-derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Workflow Insights Our Advantages Client Perspectives FAQs
Klebsiella pneumoniae, a gram-negative bacterium, has attracted considerable attention due to its ability to release nanosized outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), often referred to as bacterial exosomes. These vesicles encapsulate a variety of biomolecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, making them an emerging platform for studying bacterial communication, immune modulation, and drug delivery.
At Creative Biolabs, our scientific team specializes in developing and analyzing bacterial-derived exosomes from multiple species, including Klebsiella pneumoniae. Leveraging years of experience in vesicle isolation, structural characterization, and compositional profiling, we help researchers advance their investigations into vesicle-mediated interactions and therapeutic material transport in vitro and in vivo.
Overview of Klebsiella pneumoniae-Derived Exosomes

Natural Nano-Transporters
Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosomes have shown remarkable potential as natural nanocarriers capable of encapsulating various drug molecules or genetic materials. Their lipid bilayer structure ensures stability in biological environments while allowing efficient cellular uptake.

Intrinsic Immunogenicity
These exosomes retain the antigenic profile of their parental bacterial membrane, providing a naturally immunogenic surface that can engage immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells. This property has drawn attention to their potential use in immunological modeling, rather than in therapeutic applications.

Dual-Function Platform
Researchers have explored their ability to act simultaneously as carriers and immunostimulants. Their combination of bioactivity and biocompatibility makes them highly attractive for fundamental studies focusing on exosome–host interactions and immune signaling.

Controlled Cargo Encapsulation
Through optimized culture and isolation workflows, Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosomes can be used to encapsulate small molecules or nucleic acids with minimal changes to vesicle morphology and size distribution, maintaining homogeneity across preparations.
Interested in understanding how Creative Biolabs can help optimize your bacterial exosome workflow? Contact our scientific consultants.
Isolation Workflow for Klebsiella pneumoniae-Derived Exosomes
Creative Biolabs follows a reproducible and rigorously validated isolation pipeline for Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosomes. The workflow allows flexibility for optional downstream characterizations based on project requirements and available species-specific data.
Standard Exosome Customization Steps
-
Culture Preparation – Grow Klebsiella pneumoniae in sterile LB medium under controlled conditions with continuous shaking to promote uniform vesicle secretion.
-
Primary Centrifugation – Remove intact bacterial cells through low-speed centrifugation at 4°C to eliminate large debris.
-
Filtration & Concentration – Filter the supernatant through 0.22 μm membranes and concentrate vesicle fractions using ultrafiltration membranes.
-
Ultracentrifugation-Based Purification – Subject the concentrated supernatant to ultracentrifugation and further separate exosomes to ensure vesicle uniformity.
Optional (Based on Library Availability)
-
Comprehensive proteomic and lipidomic profiling
-
RNA cargo identification and miRNA analysis
-
TEM structural imaging for morphology confirmation
-
Surface antigen analysis by flow cytometry or immunoblotting
To request a detailed Klebsiella exosome workflow proposal tailored to your project, reach out to Creative Biolabs' technical support team.
Highlights from Research on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Derived Exosomes
Creative Biolabs continuously reviews and integrates findings from scientific literature to help clients interpret emerging research directions. Below is a concise summary of representative studies on Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosomes conducted by scientists worldwide.
|
RESEARCH
|
KEY FINDINGS AND CONCLUSIONS
|
|
Characterization before and after drug loading
|
Transmission electron microscopy and DLS confirmed that exosome morphology remained consistent before and after drug encapsulation, with only a slight increase in mean particle diameter, confirming structural stability.
|
|
Drug delivery efficiency
|
In vitro and in vivo analyses demonstrated efficient internalization of drug-loaded vesicles by non-small cell lung cancer cells, outperforming the uptake of free drugs.
|
|
Antitumor efficacy of drug-loaded vesicles
|
Drug-loaded exosomes exhibited enhanced cytotoxicity and apoptosis induction in tumor cells, leading to marked necrosis in animal models, validating their potential as delivery vehicles.
|
|
Immune modulation by unloaded vesicles
|
Even empty Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosomes induced macrophage recruitment (increased F4/80 expression) and elevated serum cytokine levels, suggesting their intrinsic ability to stimulate immune responses.
|
|
Pharmacokinetic advantages
|
Encapsulated chemotherapeutic agents showed slower clearance and prolonged systemic circulation, indicating improved stability and pharmacokinetic profiles when delivered via bacterial exosomes.
|
Creative Biolabs' scientists can assist you in reproducing or expanding upon these findings with tailored experimental plans - contact us for collaboration details.
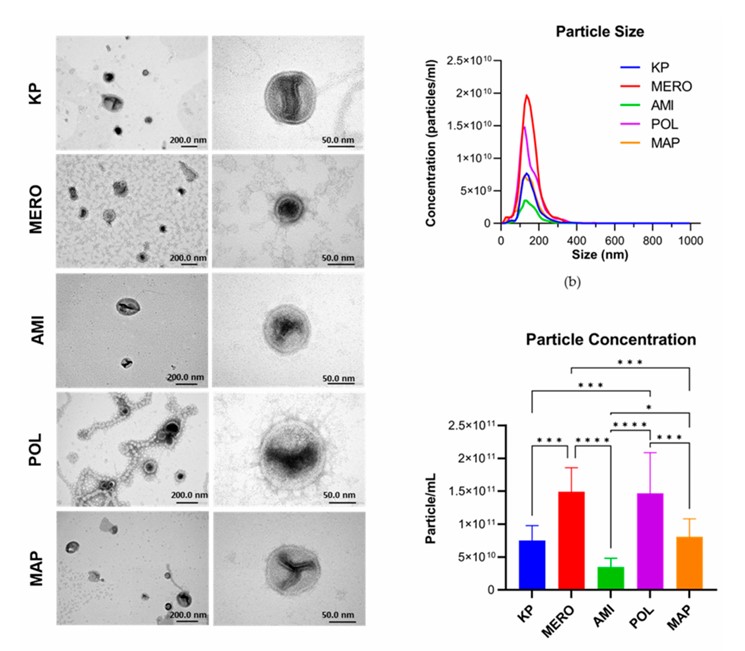 Fig.1 Klebsiella pneumoniae OMVs characterization by TEM and NTA.1
Fig.1 Klebsiella pneumoniae OMVs characterization by TEM and NTA.1
Advantages of Partnering with Creative Biolabs for Klebsiella pneumoniae Exosome Studies
 End-to-End Customization:
End-to-End Customization:
Creative Biolabs provides tailored research services for bacterial exosome projects, from strain cultivation to exosome customization and data interpretation.
 Proven Reliability:
Proven Reliability:
Our workflow integrates strict quality control checkpoints and sterile handling to ensure reproducible vesicle yields and consistent physicochemical characteristics.
 Flexibility in Analytical Scope:
Flexibility in Analytical Scope:
Clients can choose from a range of optional characterization techniques depending on research goals, available budget, and downstream applications.
 Access to Specialized Expertise:
Access to Specialized Expertise:
Creative Biolabs' microbiology and vesicle engineering teams have in-depth experience with gram-negative bacterial systems, enabling project-specific consultation and rapid troubleshooting.
To start designing your customized Klebsiella exosome research package, contact Creative Biolabs' bacterial vesicle specialists.
Insights from Researchers Who Partnered with Creative Biolabs
Our clients' experiences highlight the reliability and scientific rigor that define Creative Biolabs' bacterial exosome services.
"Working with Creative Biolabs transformed our bacterial vesicle study. Their team not only optimized our Klebsiella pneumoniae culture parameters but also provided insightful recommendations on gradient purification and QC checkpoints. The resulting vesicles had exceptional purity and reproducibility."
"Creative Biolabs' support was invaluable in developing our pilot-scale bacterial exosome isolation workflow. The team maintained constant communication, ensuring each step - rom sample preparation to vesicle quantification - was scientifically sound and aligned with our research objectives."
"We appreciated how Creative Biolabs' scientists integrated optional proteomic profiling into our exosome project. Their data interpretation guidance saved us weeks of analysis and helped us validate vesicle composition more accurately."
Collaborate with Creative Biolabs to experience the same level of technical precision in your exosome research.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs
-
Proven track record in Gram-negative exosome engineering
-
Dedicated scientific support from concept to data delivery
-
Modular service design allowing flexible project scaling
-
Integration of optional advanced analytics such as NTA, TEM, and proteomics
Creative Biolabs provides specialized services for Klebsiella pneumoniae-derived exosome research, including customized isolation workflows, structural analysis, and compositional profiling. Explore how Creative Biolabs supports cutting-edge studies on bacterial exosomes and gram-negative vesicle biology. Reach out to Creative Biolabs to begin your Klebsiella pneumoniae exosome project with a trusted research partner.
FAQs
Q: How do Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes contribute to virulence?
A: Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes can encapsulate and transport virulence factors, such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS), adhesins, and enzymes. These exosomes can affect host cell signaling pathways, modulate immune responses, and enhance bacterial survival and persistence in hostile environments, thereby implicating their role in enhancing the virulence of Klebsiella pneumonia.
Q: What methods are commonly used to isolate and characterize Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes?
A: Common methods for isolating Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes include ultrafiltration, ultracentrifugation, and precipitation techniques. Characterization typically involves techniques such as NTA for size assessment, electron microscopy for morphology, and mass spectrometry for protein profiling to confirm the presence of exosomal markers.
Q: What are the potential applications of Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes in research?
A: Potential applications include the use of exosomes as biomarkers for infection diagnosis, tools for studying bacterial-host interactions, and the development of exosome-based therapeutic vectors for drug delivery. Additionally, they can serve as models for understanding the mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and studying the effects of environmental stresses on bacterial survival.
Q: Can exosomes from Klebsiella pneumoniae impact the behavior of host immune cells?
A: Yes, exosomes from Klebsiella pneumoniae can significantly impact host immune cell behavior. They may carry immunomodulatory molecules that can activate or suppress immune responses, potentially leading to altered inflammation or immune evasion strategies. Research in this area helps elucidate how Klebsiella pneumoniae manipulates host defenses.
Q: Are there differences in exosome content among different Klebsiella pneumoniae strains?
A: Yes, the content and functional properties of exosomes may differ among various strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae due to genetic variations, environmental influences, and differing virulence traits. Comparative studies can provide insights into strain-specific mechanisms of pathogenicity and their corresponding exosomal profiles.
Q: How can understanding Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes advance our knowledge of antibiotic resistance?
A: By studying the role of exosomes in the transfer of genetic material and resistance determinants among bacteria, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying antibiotic resistance. This understanding could contribute to the development of strategies to combat the spread of resistance genes and enhance our ability to manage infections caused by resistant strains.
Q: What future research directions are recommended for Klebsiella pneumonia-derived exosomes?
A: Future research could focus on elucidating the molecular mechanisms through which exosomes modulate host responses, exploring the role of exosomes in inter-bacterial communication, and investigating their potential as targets for novel antimicrobial strategies. Additionally, studies aimed at understanding the in vivo dynamics of exosomes in infection models will help translate findings into practical applications.
Reference
-
Lucena, Aline Castro Rodrigues, et al. "Modulation of Klebsiella pneumoniae Outer Membrane Vesicle Protein Cargo under Antibiotic Treatment." Biomedicines 11.6 (2023): 1515. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061515.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:





 Fig.1 Klebsiella pneumoniae OMVs characterization by TEM and NTA.1
Fig.1 Klebsiella pneumoniae OMVs characterization by TEM and NTA.1









