Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Cartilage Injury Repair
Overview Services Features FAQs
The mechanical breakdown of cartilage caused by a variety of reasons is known as cartilage injury, including chemical, biomechanical, bone or joint infections, which eventually lead to loss of chondrocytes and degenerative degeneration. Creative Biolabs explores the function and mechanisms of SC-Exo (stem cell exosomes) and provides related research services.
Overview of Causes and Mechanisms
Mechanical injury
Tearing of cartilage tissue mainly caused by trauma is due to the degeneration of cartilage cells caused by external forces, which leads to fracture and destruction of the cartilage layer.
Chemical injury
Chemical injury refers to various chemical damages to the cartilage layer caused by the release of inflammatory factors, tissue fluid and extracellular matrix components into the joint cavity, especially the detrimental effects of the breakdown of matrix components such as proteoglycans, collagen fibers and hyaluronic acid on the structure of the joint cavity.
Our Services
Our research focuses on the innovative application of stem cell-derived exosomes in the repair of cartilage injuries. We offer comprehensive services that include the isolation and characterization of exosomes from stem cells, in vitro and in vivo testing of exosome efficacy in promoting cartilage regeneration, and the development of tailored exosomes for specific cartilage research.
Features of Various SC-Exo Applications in Cartilage Repair
The intervention value of SC-Exo has been revealed, and the development of relevant bioengineering solutions benefits from a thorough understanding of the functional and mechanistic variations between various types of SC-Exo and its derivatives in cartilage repair.
-
Wharton's jelly mesenchymal SC-Exo: Sequencing of Wharton's jelly mesenchymal SC-Exo screens revealed that miR148a enriched in Wharton's jelly mesenchymal SC-Exo repairs cartilage by inhibiting chondrocyte differentiation to a hypertrophic phenotype.
-
Bone marrow SC-Exo: Bone marrow SC-Exo combined with hydrogels as a tissue engineering material-based intervention to mitigate inflammatory damage to cartilage by promoting polarization of the immune microenvironment toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype in a rat model of knee cartilage injury.
-
Umbilical cord mesenchymal SC-Exo: LncRNA H19 was identified in umbilical cord mesenchymal SC-Exo as a functionally important molecule mediating their regulation of chondrocyte activity, which can adsorb miR-29b-3p to restore TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway operation and promote chondrocyte proliferation and regeneration.
-
Infrapatellar fat pad SC-Exo: Autophagy is involved in the maintenance of cartilage homeostasis and delays the pathological process of arthritis. Infrapatellar fat pad SC-Exo were shown to exert chondroprotective effects through the mTOR autophagic pathway mediated by miR-100-5p.
-
Synovial fluid mesenchymal SC-Exo: The use of synovial fluid mesenchymal SC-Exo as delivery vehicles for induction molecules to chondrocyte differentiation can effectively be homed in synovial mesenchymal SC-Exo to improve cartilage regeneration.
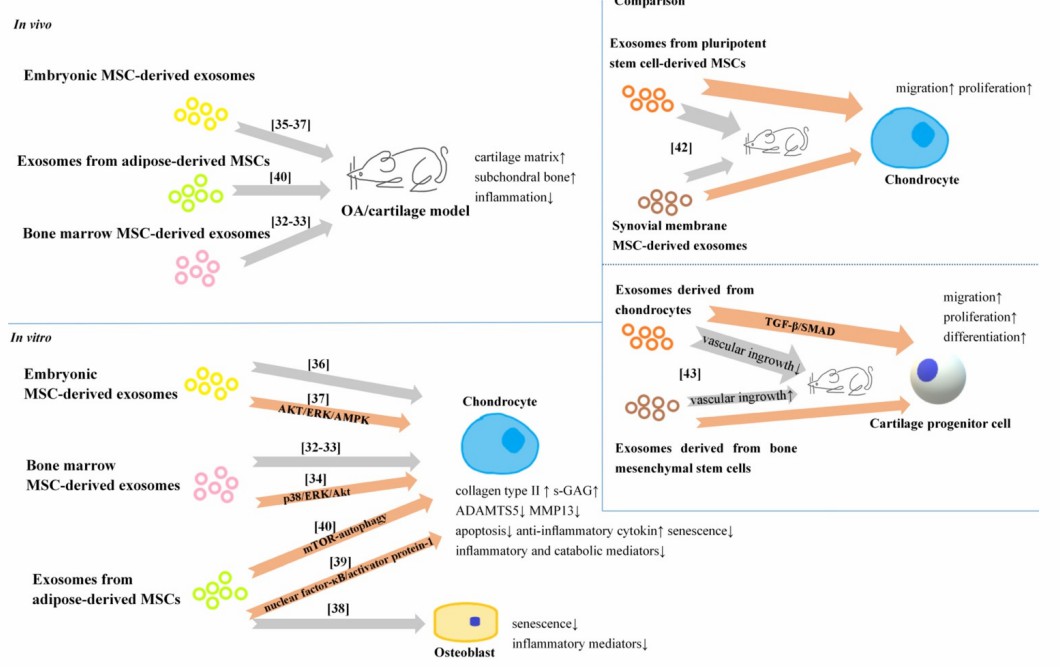 Fig.1 Positive effects of SC-Exo on chondrocytes. (Zhou, 2020)
Fig.1 Positive effects of SC-Exo on chondrocytes. (Zhou, 2020)
The use of SC-Exo in cartilage injury repair can alleviate arthritic pain and structural deformation of joints. Creative Biolabs has a skilled technical system for scaling up SC-Exo constructs and mechanistic studies to help advance client projects. Please contact us with your interest.
FAQs
Q: What specific mechanisms do SC-Exo utilize to promote cartilage repair?
A: SC-Exo promote cartilage repair through several mechanisms, including the delivery of bioactive molecules such as growth factors, cytokines, and microRNAs that modulate inflammation, enhance cell proliferation, and stimulate extracellular matrix production. These exosomes also facilitate communication between cells, promoting a regenerative environment conducive to cartilage healing.
Q: In what ways do the features of exosomes differ depending on the source of stem cells utilized for their isolation?
A: The characteristics of exosomes can differ markedly based on the origin of the stem cells. Each source may yield exosomes with distinct molecular profiles, including variations in protein content, lipid composition, and RNA species, which can influence their therapeutic efficacy and mechanisms of action in cartilage repair.
Q: What role do exosomes play in the communication between stem cells and cartilage cells during the repair process?
A: Exosomes function as essential mediators of intercellular interaction among stem cells and chondrocytes. They facilitate the transfer of signaling molecules, such as proteins and RNAs, which can influence the behavior of recipient cells. This communication helps to modulate cellular responses, promote chondrogenesis, and enhance the overall regenerative capacity of the cartilage microenvironment, thereby supporting the repair process.
Q: What are the safety and immunogenicity profiles of stem cell-derived exosomes in cartilage injury applications?
A: Preliminary studies indicate that stem cell-derived exosomes exhibit low immunogenicity and are generally considered safe for therapeutic use. They do not typically provoke significant immune responses, making them suitable for allogeneic applications. Nonetheless, continuous research is crucial to comprehensively ascertain their long-term safety profiles and any possible harmful consequences.
Reference
-
Zhou, Quanfa, et al. "Exosomes in osteoarthritis and cartilage injury: advanced development and potential therapeutic strategies." International Journal of Biological Sciences 16.11 (2020): 1811. Under open access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Positive effects of SC-Exo on chondrocytes. (Zhou, 2020)
Fig.1 Positive effects of SC-Exo on chondrocytes. (Zhou, 2020)









