Stem Cell-derived Exosome Applications
- Skin Injury Repair
Introduction Properties Applications Services FAQs
Stem Cell-derived Exosomes Have the Potential to Repair Skin Damage
The field of regenerative medicine has witnessed revolutionary advancements, with a growing focus on cell-free therapeutic paradigms that address many limitations of traditional cell-based treatments. A significant area of progress lies in the remarkable potential of exosomes, particularly those derived from stem cells. These nanoscale exosomes are fundamentally changing the approach to tissue repair and regeneration.
Exosomes are naturally occurring biological nanoparticles, typically ranging from 30 to 150 nm in diameter, secreted by nearly all cell types. They serve as crucial mediators of intercellular communication, encapsulating and transporting a diverse array of bioactive molecules—including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids like messenger RNA (mRNA) and microRNA (miRNA)—from donor to recipient cells. This transfer of information profoundly influences cellular behavior and various physiological processes. Stem cell-derived exosomes (SC-Exos) are of particular interest due to their ability to mirror the regenerative capabilities of their parent stem cells, circumventing the inherent complexities associated with direct cell transplantation. Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of harnessing this potential, especially for challenging applications in skin injury repair. We are ready to support your work with our comprehensive exosome manufacturing services and expertise.
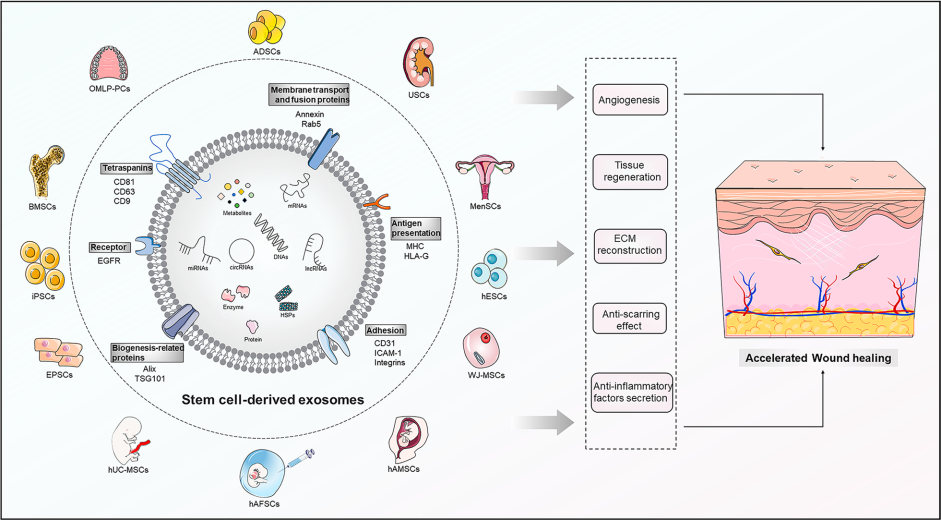 Fig.1 Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.1
Fig.1 Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.1
Properties of Stem Cell-derived Exosomes
SC-Exos present significant advantages over traditional stem cell therapies, positioning them as a promising cell-free therapeutic platform that addresses many of the limitations associated with direct cell transplantation. The shift towards a "cell-free" paradigm represents a fundamental advancement in regenerative medicine. Traditional stem cell therapies often encounter challenges related to cell survival, retention within the target tissue, potential immunogenicity, and the risk of tumorigenicity. Exosomes, by delivering the therapeutic signals of stem cells without the need for the cells themselves, inherently bypass these issues. This not only makes them a safer option but also opens avenues for broader adoption, potentially reduced regulatory hurdles, and the development of more standardized, off-the-shelf treatments, thereby increasing the accessibility of regenerative medicine.
The key advantages include:
 Good Safety Profile
Good Safety Profile
Exosomes do not express major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I or II antigens, which significantly reduces the risk of immune rejection in recipients. Furthermore, they are non-self-replicating, mitigating concerns about tumor formation, vascular obstruction, or unwanted mutations that can be associated with live cell transplantation.
 Enhanced Stability and Transport
Enhanced Stability and Transport
The protective lipid bilayer of exosomes ensures the stability of their contents, allowing for long-term storage at -80℃ while maintaining biological activity. This inherent stability greatly simplifies logistics for application and distribution compared to the challenges of handling live cells.
 High Efficiency
High Efficiency
Their nanoscale size facilitates direct cellular uptake by recipient cells through various mechanisms, including endocytosis and membrane fusion. This leads to efficient transfer of their bioactive cargo and a rapid impact on target cell function, enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
 No Ethical Restrictions
No Ethical Restrictions
As subcellular structures secreted by cells, exosomes bypass many of the ethical considerations and regulatory complexities often associated with the use of live stem cells.
 Wide Range of Sources
Wide Range of Sources
SC-Exos can be readily isolated from the culture supernatant of various types of stem cells (e.g., those derived from umbilical cord tissue, bone marrow, or adipose tissue), as well as from diverse body fluids and blood, ensuring a broad and accessible supply for therapeutic applications.
Applications in Skin Injury Repair
SC-Exos hold immense promise for revolutionizing the treatment of various skin injuries, from sun damage to complex wounds and scars. Their multifaceted mechanisms of action make them exceptionally versatile therapeutic agents.
While specific research on SC-Exos for direct UV injury repair is an evolving area, the general regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties of exosomes are highly relevant. UV radiation induces oxidative stress and inflammation in skin cells, leading to damage. SC-Exos, through their ability to modulate immune responses and reduce inflammation, can mitigate the acute inflammatory phase of UV-induced skin damage. Their capacity to promote cell proliferation and survival can also aid in the recovery of damaged keratinocytes and fibroblasts, supporting the skin's natural repair processes following UV exposure.
Wound healing is a complex, highly orchestrated biological process involving distinct phases: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling. SC-Exos play crucial roles across all these stages, accelerating healing and significantly improving outcomes. The ability of exosomes to influence multiple, distinct phases of wound healing through various mechanisms (e.g., angiogenesis, immune modulation, cell migration, ECM production) suggests that they are not merely performing single functions but are coordinating a complex biological cascade. This "orchestrating" capability makes SC-Exos particularly powerful for complex or chronic wounds where multiple biological processes are dysregulated, implying a more comprehensive and effective therapeutic intervention compared to approaches targeting only single pathways.
Minimizing scar formation and improving the appearance of existing scars remain significant challenges in wound care and aesthetic medicine. SC-Exos offer a promising avenue for regenerative scar management. The data indicates that exosomes do not merely "reduce" scars but actively promote "remodeling" and influence the quality of the newly formed tissue, leading to "near-complete resolution without visible scarring" in some cases. This suggests a move beyond simply minimizing scar size to achieving a more functional and aesthetically pleasing tissue regeneration, offering a significant advantage over traditional scar treatments.
Creative Biolabs' Expertise and Services
Creative Biolabs is not merely an observer of this exciting field; the company is an active pioneer. The team comprises leading experts in exosome biology, dedicated to translating cutting-edge research into tangible therapeutic solutions for skin repair and rejuvenation.
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to advancing the field of exosome-based therapies for skin injury repair through our extensive range of services. Our robust and modular platform is designed to support every stage of research and development:
The services offered span the entire pipeline of exosome-based therapy development, from initial research and discovery to preclinical validation.
Our team is here to support every stage. Contact us today to learn how our comprehensive exosome technology services can help advance your skin injury repair research.
FAQs
Q: How safe are stem cell-derived exosome therapies for skin injuries?
A: Based on extensive research, stem cell-derived exosomes are considered remarkably safe. Unlike live stem cells, they are non-replicating and do not express major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, which significantly reduces the risk of immune rejection or tumor formation. Their subcellular nature also bypasses many ethical concerns associated with cellular therapies, providing a more universally acceptable therapeutic option. Rigorous quality control measures are prioritized to ensure the highest safety standards for exosome preparations.
Q: How effective are exosomes in treating chronic or complex skin wounds?
A: Exosomes have demonstrated significant potential in treating complex and chronic wounds. They actively participate in all phases of wound healing—modulating inflammation, promoting angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation), stimulating cell proliferation and migration, and facilitating healthy extracellular matrix remodeling. Preliminary data and early-phase studies suggest improved healing rates and reduced scarring, particularly in challenging cases like diabetic models, where conventional treatments often prove ineffective.
Q: Can exosomes help with aesthetic concerns like sun damage or scarring?
A: Absolutely. Exosomes are showing great promise in addressing aesthetic concerns. For sun damage (photoaging), they work by reducing oxidative stress, calming inflammation, stimulating collagen and elastin production, and strengthening the skin barrier, leading to overall rejuvenation and repair of damaged skin. In scar management, exosomes promote healthy collagen remodeling, which helps minimize scar formation and significantly improve the overall appearance, texture, and coloration of existing scars, offering a more regenerative outcome than traditional methods.
Q: What is the future outlook for exosome therapy in skin repair?
A: The future for exosome therapy in skin repair is incredibly promising. While much of the current evidence stems from preclinical studies, rapid advancements in exosome engineering, isolation techniques, and sophisticated delivery systems (such as hydrogels) are actively paving the way for broader applications. The field is actively engaged in research to standardize these processes and explore new therapeutic avenues. Despite the current lack of widespread application, the potential for personalized and scalable wound care solutions is immense, with continuous efforts aimed at overcoming existing hurdles for future success.
Reference
-
Zhou, Chuchao et al. "Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing." Stem cell research & therapy vol. 14,1 107. 26 Apr. 2023, doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03345-0. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.1
Fig.1 Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.1