Stem Cell-derived Exosome Application
- Lung Injury Repair
Overview Services Features FAQs
SC-Exo (Stem cell exosomes) have potential applications in mitigating inflammation, cell necrosis and fibrosis in lung tissue injury. Creative Biolabs is committed to accumulating insights into the functions and mechanisms of SC-Exo in the repair of lung tissue injury.
Lung Tissue Injury Causative Factors
Lung tissue injury consists of three main pathological changes: inflammation, necrosis and fibrosis. The inflammatory response is the main factor leading to lung tissue injury, and common inflammatory conditions include bacterial infections, viral infections, fungal infections, allergic reactions and autoimmune diseases. Necrosis and fibrosis are direct damage to the lung tissue, where the cellular structure is destroyed, resulting in decreased lung function.
 Fig.1 Causes of Lung Tissue Damage
Fig.1 Causes of Lung Tissue Damage
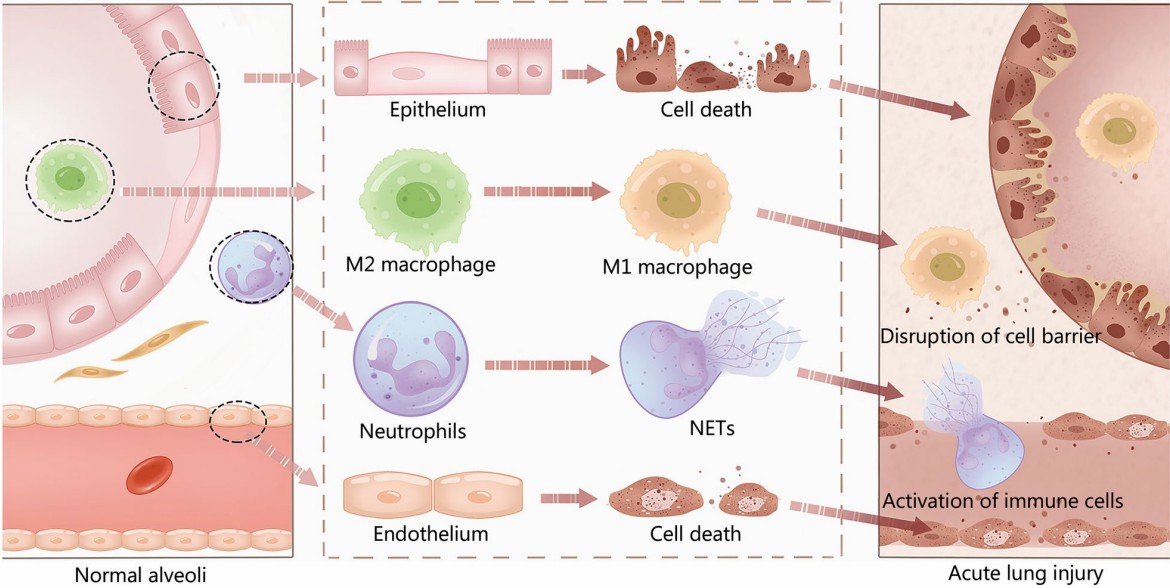 Fig.2 Alveolar cells in lung injury.1, 3
Fig.2 Alveolar cells in lung injury.1, 3
Our Services
We offer specialized services in the isolation and analysis of stem cell-derived exosomes, facilitating their research in exploring the potential of lung injury repair. Our team utilizes advanced techniques to extract and characterize exosomes from various stem cell sources, ensuring high purity and functionality. We provide comprehensive analyses, including molecular profiling and functional assays, to evaluate the therapeutic potential of these exosomes in promoting lung tissue regeneration and mitigating injury.
Features of SC-Exo Promote Lung Repair
After lung injury, the body produces a large number of inflammatory cytokines through alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages, etc., which induce an inflammatory response that leads to lung tissue damage. In contrast, SC-Exo can exert anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, anti-apoptotic and immunomodulatory functions by regulating various key signaling pathways, such as inhibition of inflammatory factors and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases, to promote the repair and regeneration of lung tissue after injury.
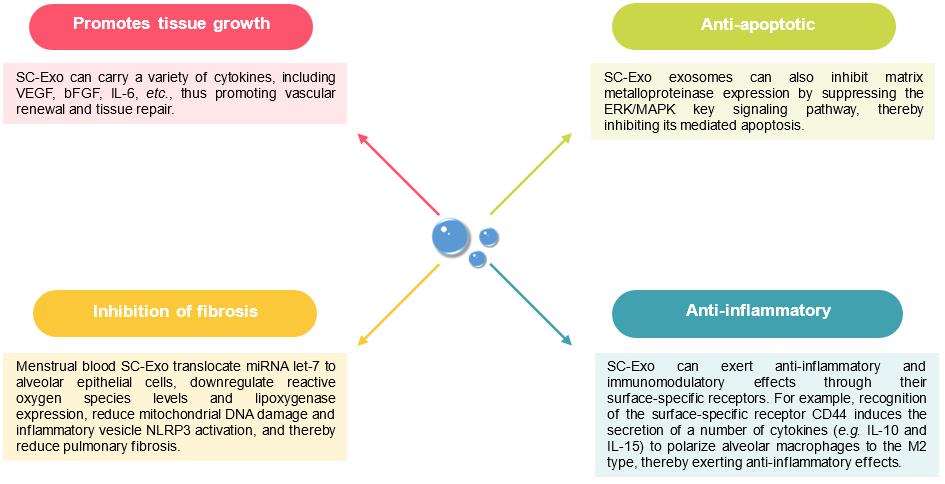 Fig.3 SC-Exo Promotes Lung Tissue Repair.
Fig.3 SC-Exo Promotes Lung Tissue Repair.
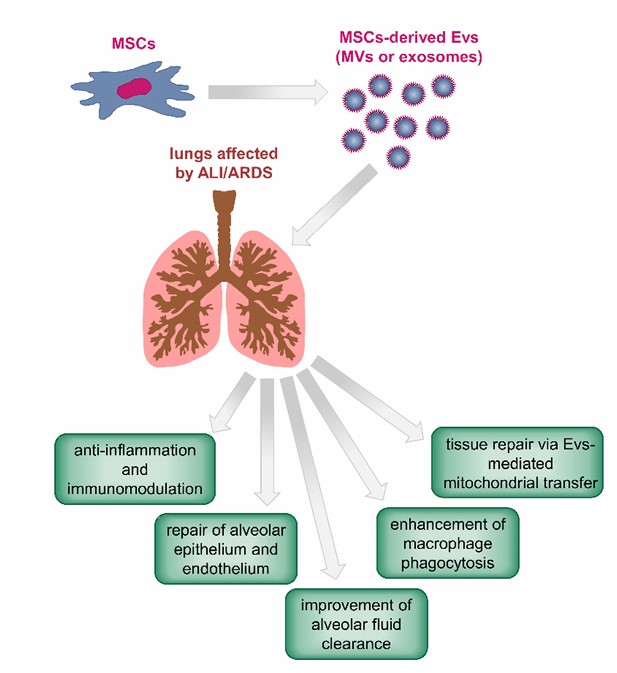 Fig.4 Proposed mechanisms for the beneficial therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs on the lung.2, 3
Fig.4 Proposed mechanisms for the beneficial therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs on the lung.2, 3
SC-Exo carries abundant parental cell-derived proteins, RNA and other biologically active substances and performs similar biological functions, and its transport and preservation conditions are similar to those of proteins, giving it more drug-forming advantages than stem cells. Creative Biolabs provides insights into the role of SC-Exo on a variety of tissue injuries, including lung, and deepens SC-Exo-related research. Please contact us for professional solutions.
FAQs
Q: How do exosomes contribute to lung injury repair?
A: SC-Exo contains bioactive molecules such as lipids, and RNAs that can modulate inflammation, promote cell survival, and enhance tissue regeneration. They play a crucial role in signaling pathways that facilitate the repair of damaged lung tissue.
Q: What specific components of exosomes are involved in lung repair mechanisms?
A: Key components include growth factors, cytokines, and microRNAs that can influence cellular responses in lung epithelial and endothelial cells, promoting healing and reducing fibrosis.
Q: Are there specific types of stem cells that yield more effective exosomes for lung injury repair?
A: Yes, certain stem cell types, such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), have shown enhanced exosomal therapeutic effects due to their unique cargo and regenerative properties.
Q: How can the efficacy of exosomes in lung injury repair be measured?
A: Efficacy can be assessed through in vitro assays measuring cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis, as well as in vivo models evaluating lung function, histological changes, and biomarker levels post-treatment.
Q: What are the challenges in using stem cell-derived exosomes for lung injury repair?
A: Challenges include ensuring consistent exosome production, understanding the mechanisms of action, and addressing potential immunogenicity or off-target effects.
References
Reference
-
Hu, Qian, et al. "Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury." Military Medical Research 9.1 (2022): 61.
-
Gardin, Chiara, et al. "Could Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes be a therapeutic option for critically ill COVID-19 patients?." Journal of clinical medicine 9.9 (2020): 2762.
-
Under open access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Causes of Lung Tissue Damage
Fig.1 Causes of Lung Tissue Damage
 Fig.2 Alveolar cells in lung injury.1, 3
Fig.2 Alveolar cells in lung injury.1, 3
 Fig.3 SC-Exo Promotes Lung Tissue Repair.
Fig.3 SC-Exo Promotes Lung Tissue Repair.
 Fig.4 Proposed mechanisms for the beneficial therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs on the lung.2, 3
Fig.4 Proposed mechanisms for the beneficial therapeutic effects of MSC-EVs on the lung.2, 3









