DMXL1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the DMXL1 gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of DMXL1
First published in 1998, the DmX gene is an evolutionarily highly conserved gene that presents highly similar sequences in a variety of different species, such as insects, nematodes, and mammals. Dmx-like 1 (DMXL1) is one of the human homologs of DmX located on chromosome 5q22. As a member of the WD repeat protein superfamily, the DMXL1 protein consists of 3027 amino acids and contains a large number of WD repeat units. The WD repeat unit consists of almost 40 amino acids ending with a tryptophan-aspartate (WD) dipeptide repeated four to eight times. The WD repeat proteins play an important role in a variety of cellular processes, such as signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, pre-mRNA splicing, cytoskeletal organization, and vesicular fusion. Till now, the WD repeat protein coding gene DmX has been isolated from Drosophila melanogaster.
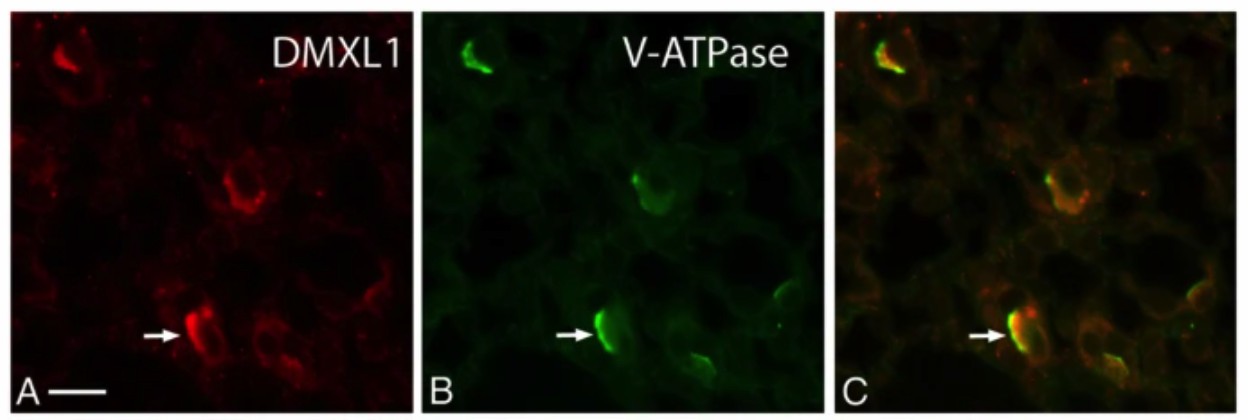 Fig.1 Localization of DMXL1 in proton-secreting cells of mouse kidney by immunocytochemistry. (Merkulova, 2015)
Fig.1 Localization of DMXL1 in proton-secreting cells of mouse kidney by immunocytochemistry. (Merkulova, 2015)
Distribution and Functions of DMXL1
The expression of DMXL protein can be detected in a number of different tissues. Notch signaling is an important pathway to regulate the proliferation, differentiation, and death of cells. The rabconnectin-3 complex is involved in Notch signaling, but its exact mechanism of action is unknown.
DMXL1 in Cancers
The expression of DMXL1 can be detected in a variety of cancers, such as colorectal cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, and liver cancer. Studies have shown that DMXL1 mutations were related to tumor growth. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer and has been the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. There are four major subtypes of HCC, including hepatitis C virus (HCV) associated HCC, hepatitis B virus (HBV) associated HCC, alcohol-associated HCC, as well as HCC with no known etiology. DMXL1 mutations can be identified by aligning the sequences of approximately 18,000 protein-coding genes in HCC patients and normal tissues. Therefore, DMXL1 may serve as a potential target for tumor research and the development of therapeutic methods.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Merkulova, M.; et al. Mapping the H+ (V)-ATPase interactome: identification of proteins involved in trafficking, folding, assembly and phosphorylation. Scientific reports. 2015, 5(1): 1-15. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
