DHX9 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating the development of gene therapy. Based on our understanding of gene therapy and potential target genes, we now describe the DHX9 gene and associated diseases for our clients all over the world.
Overview of DHX9
DHX9, also known as Nuclear DNA Helicase II (NDH II) or RNA Helicase A (RHA), is an NTP-dependent helicase protein that belongs to the DExH-box family of helicases. DHX9 was first isolated from the nuclear part of the calf thymus. Subsequently, the human homologs were obtained from nuclear extracts of HeLa cells. In humans, the DHX9 gene is located on chromosome 1q25 and the active gene consists of 29 exons to encode a protein of 140kDa. Similar to other superfamily 2 helicases, the core region of DHX9 can be divided into two RecA-like domains and there are 2 double-stranded RNA-binding domains (dsRBDs) at its N-terminus.
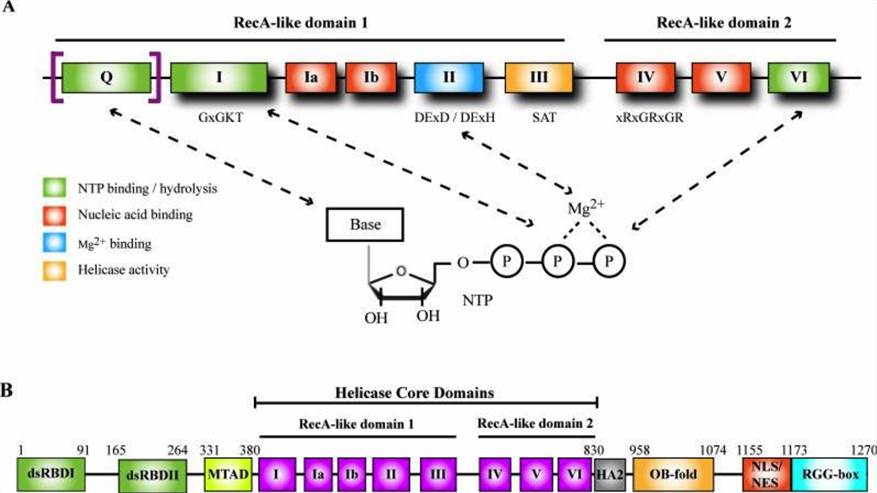 Fig.1 Helicase domain of DExD/H-box helicases and functional domains in DHX9. (Lee, 2016)
Fig.1 Helicase domain of DExD/H-box helicases and functional domains in DHX9. (Lee, 2016)
Distribution and Functions of DHX9
DHX9 is an abundant protein widely expressed in a variety of tissues. According to species, cell type, and environment, the intranuclear localization of DHX9 is dynamic. In human cells, DHX9 is normally localized to the nucleoplasm and can translocate into the nucleolus under certain conditions. As a nuclear protein, DHX9 can shuttle to the cytoplasm and present multiple functions in miRNA processing and translational regulation.
- DHX9 can unravel complex nucleic acid structures and play a role in DNA replication and maintaining genome stability.
- DHX9 can unwind RNA forks, R-loops, and RNA-based tetraplexes to regulate transcription.
- DHX9 is involved in translational regulation.
- DHX9 is associated with microRNA biogenesis and processing.
DHX9 in Cancers
In the past decades, studies have shown that DHX9 is associated with a variety of human diseases, including different types of cancers and a series of viral infections. The multiple roles of DHX9 in cellular processes allow deficiency of DHX9 to have severe effects on cell growth or viability and may lead to a variety of human diseases. Studies have shown that the expression of DHX9 was regulated by the transcription factor SOX4, which was overexpressed in prostate cancer. In this case, DHX9 may be associated with the development of prostate cancer. What’s more, DHX9 is overexpressed in tumor samples compared to normal lung tissue. Recent research showed that DHX9 is also related to osteosarcoma and Wilms' tumor. In summary, DHX9 can be served as a potential chemotherapeutic target against various cancers.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Lee, T.; Pelletier, J. The biology of DHX9 and its potential as a therapeutic target. Oncotarget. 2016, 7(27): 42716. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
