LRP1 and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is a contract research organization focused on the early stages of drug discovery in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. We offer customers customized solutions. We aim to provide high-quality technical services to the research community and adapt to current research trends and needs.
Backgrounds of LRP1
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), a member of the LDL receptor family, is an endocytic receptor for more than 40 structurally diverse ligands. LRP1 is a very large protein, made up of 4,525 amino acids. Structurally, LRP1 consists of two non-covalently bound subunits: an 85 kDa transmembrane β-chain and a 515 kDa extracellular α-chain. LRP1 is a 600 kDa glycosylated precursor protein cleaved by Furin in the Golgi complex. LRP1 has been widely studied due to its pleiotropic roles in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. LRP1 is a ubiquitously expressed transmembrane protein. As a cell surface receptor, it can control the endocytosis of multiple ligands, mediate cell signaling transductions and regulate gene expression through its intracellular domain. In many in vitro and in vivo studies RAP is used as an inhibitor for LRP1. LRP1 is widely expressed in many tissues and has diverse roles in different biological processes. These processes include cell signal transduction, protease degradation, lysosomal enzyme activation, lipoprotein metabolism, or cellular uptake of extracellular ligands, bacterial toxins, and/or viruses through endocytosis.
Functions of LRP1
LRP1 has two known functions :(1) as a scavenger receptor involved in the endocytosis of many of its ligands; (2) as a signal receptor to regulate various cellular processes. LRP1 is found in the somatodendritic compartment of neurons, and it can mediate the endocytosis of extracellular ligands in these cells. LRP1 is involved in the bulk transport, primary production, brain, and systemic clearance of AD toxin Aβ, and therefore plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of AD. In addition, LRP1 has been found to regulate calcium inflow into neurons after stimulation with glutamate receptor agonist N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA).
- LRP1 and the Modulation of Cell Survival Pathways
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that LRP1 signaling is crucial in inhibiting the death pathways and promoting cell survival. In macrophages, LRP1 loss increases apoptotic cell death and inflammation by inhibiting Akt activation.
- Role of LRP1 in Inflammatory Signaling
LRP1 signaling also modulates the inflammatory response. LRP1 ligand is increased in the injured tissue, accelerating the regression of the inflammatory response.
- Role of LRP1 in Acute Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction
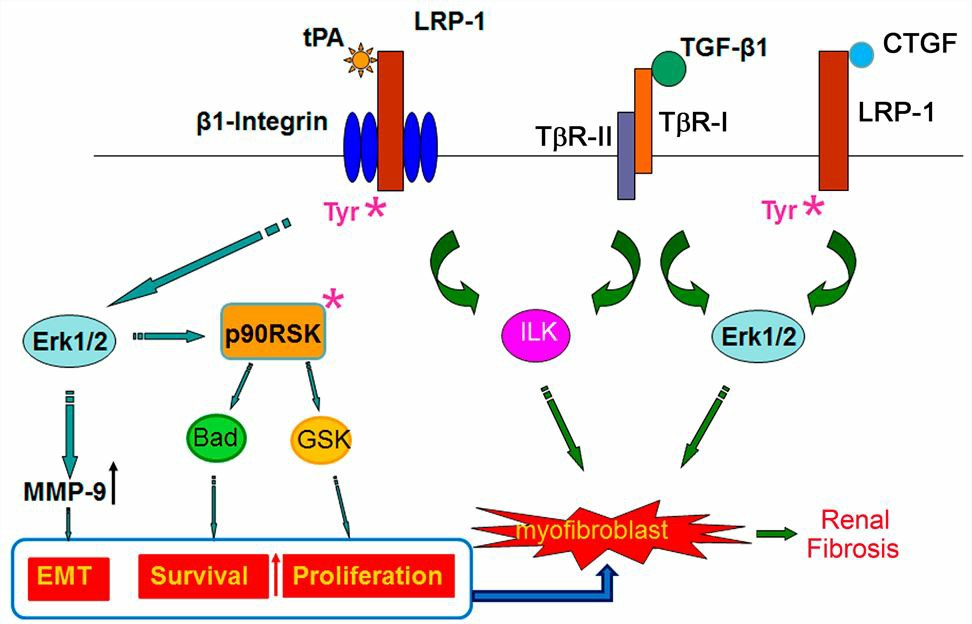 Fig.1 LRP1 signaling in renal fibrogenesis. (Lin, 2014)
Fig.1 LRP1 signaling in renal fibrogenesis. (Lin, 2014)
LRP1 and Associated Diseases
Up-regulation of LRP1 has been reported in numerous human diseases including AD, breast cancer, prostate cancer, multiple sclerosis, proliferative retinopathy, and ischemic cardiomyopathy. LRP1 is essential for normal development in the mouse, as homozygous knockout animals die at day 9 of gestation. Loss of LRP1 in the brain endothelium has a significant effect on the concentration of soluble Aβ in the brain and leads to significant cognitive impairment. LRP1 is locally upregulated in neurons and activated astrocytes surrounding senile plaques in AD patients. Defects in LRP1 function may contribute to an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease. LRP1 expression was correlated with invasiveness, tumor stage, and even clinical outcome. In endometrial cancer, increased LRP1 expression predicts more aggressive tumor behavior and is associated with higher histological grades.
Creative Biolabs is a leading partner in the global biopharmaceutical industry, providing state-of-the-art, integrated and complete solutions in biopharmaceutical development. If you are interested in working with us, please contact us to discuss your ideas.
Reference
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. LRP-1: functions, signaling and implications in kidney and other diseases. International journal of molecular sciences. 2014, 15(12): 22887-22901. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
