NOTCH2 and Associated Diseases
As one of the top life science service companies, Creative Biolabs offers several reliable technologies for your gene therapy studies. To fulfill your needs, our highly qualified scientists can build the best plan of action and manage a wide range of test services.
Overview of NOTCH2
In humans, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 (NOTCH2, also known as notch receptor 2) is a protein encoded by the NOTCH2 gene. As a single-pass transmembrane receptor of the notch family, NOTCH2 has the usual structural features of the type 1 transmembrane protein family, including an intracellular domain with numerous and distinct domains and an extracellular domain containing multiple epidermal growth factor-like repetitions. By controlling cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, NOTCH2 works as a receptor for membrane-bound ligands and is essential for many developmental processes. NOTCH1 is an important paralog of NOTCH2.
NOTCH2 in Disease
Diseases associated with NOTCH2 include Hajdu-Cheney syndrome, thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum, and cancers like nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
- Thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum
NOTCH2 plays an important role in the thoracic ossification of the ligamentum flavum (OLF). The progression of OLF is regarded as endochondral ossification. Upregulated expression of NOTCH2 is observed in ligamentum flavum (LF) sections from OLF patients compared with normal controls. Before osteogenic differentiation of LF cells, the knockdown of NOTCH2 can decelerate osteogenic differentiation with reduced alkaline phosphatase activity, which is enhanced when NOTCH2 is overexpressed. As indicators of osteogenic differentiation, Runx2 and Osterix expression is influenced by the up- or down-regulated expression level of NOTCH2 during osteogenic differentiation of LF cells. Taken together, NOTCH2 may influence OLF via the interactions with Runx2 and Osterix.
- Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Suppression of NOTCH2 can activate the TRAF6/AKT signal and promote metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). NPC is a poorly understood epithelial malignancy and environmental and genetic factors can contribute to the development of NPC. In the NPC tissue from patients with cervical lymph node metastasis, lower NOTCH2 expression can be observed compared with patients without cervical lymph node metastasis. Besides, NOTCH2 expression is lower in the metastatic and poorly differentiated NPC cells. Suppression of NOTCH2 expression can enhance NPC cell metastasis, which is reversed by NOTCH2 overexpression. Low expression of NOTCH2 predicts a poor survival rate. The interaction between the NOTCH2 intracellular domain and TRAF6 can attenuate the TRAF6-AKT signals, inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and eventually suppress NPC metastasis. In summary, NOTCH2 may represent a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of NPC.
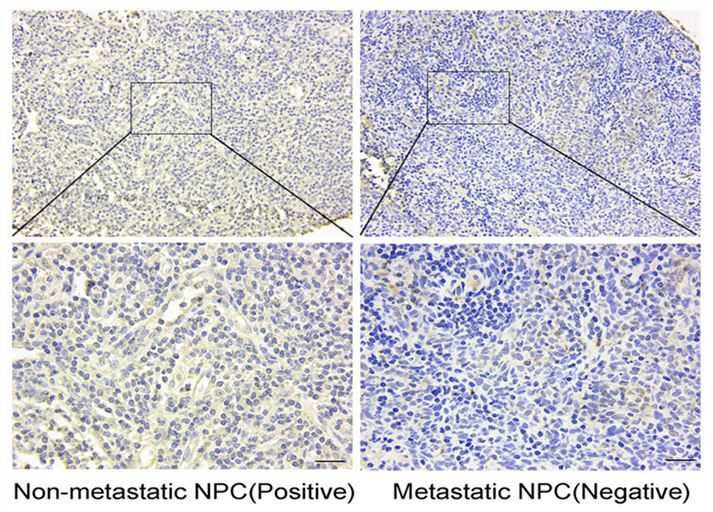 Fig.1 Lower expression of NOTCH2 is observed in non-metastatic NPC. (Zou, 2019)
Fig.1 Lower expression of NOTCH2 is observed in non-metastatic NPC. (Zou, 2019)
Creative Biolabs is a reputable biotechnology company with a large team of highly qualified scientists. Supply chain management and material control are the greatest strengths for us. Please feel free to contact us for more details about your NOTCH2 project since we have cutting-edge platforms and technologies for gene therapy.
Reference
- Zou, Y.; et al. NOTCH2 negatively regulates metastasis and epithelial-Mesenchymal transition via TRAF6/AKT in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019, 38: 456. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
