ACACA and Associated Diseases
Creative Biolabs is well-known in the field of gene therapy and has completed many innovative projects in this field. Our advanced technology platform and years of project experience allow us to provide customers with the most satisfied products and services.
Overview of ACC-alpha
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) refers to a multifunctional enzyme system that catalyzes the carboxylation of acetyl-CoA for the production of malonyl-CoA. There are two forms of ACCs in mammalian cells, alpha and beta, encoded by the ACACA and ACACB genes, respectively. There are three important functional domains for ACC-alpha, which include a biotin carboxylase (BC) domain, a carboxyl transferase (CT) domain, as well as a biotin carboxyl carrier protein (BCCP) domain. Due to the wider spatial dimension, the BC domain and CT domain of the same ACC-alpha molecule is difficult to bind. In this case, the homodimeric form of ACC-alpha molecules can be linked to the cascade of acetyl-CoA carboxylation. Regulation of ACC-alpha homodimer formation will be an important mechanism controlling ACC-alpha acetyl-CoA carboxylation activity.
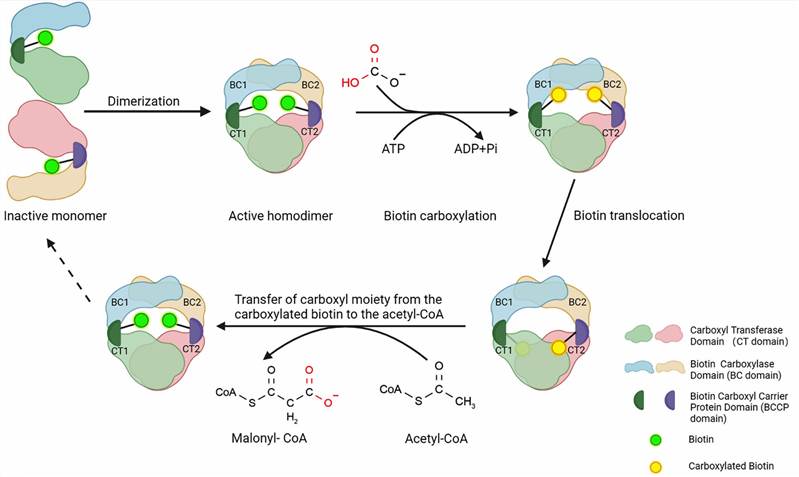 Fig.1 Structure of ACC1 and function of three main domains. (Wang, 2022)
Fig.1 Structure of ACC1 and function of three main domains. (Wang, 2022)
Distribution and Functions of ACC-alpha
ACC-alpha distributes widely in different types of organs and tissues. ACC-alpha is located in the cytosol and is responsible for converting cytosolic acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis. As the first rate-limiting enzyme with a central role in fatty acid synthesis, ACC-alpha is the hub of the fatty acid synthesis-related metabolic network. Studies have shown that the ACC-alpha inhibitor can completely block hepatic de novo lipogenesis. In cancer cells, inhibition of ACC-alpha by Soraphen A renders cells susceptible to oxidative stress and reduces cytoplasmic membrane fluidity. In addition to metabolic functions, ACC-alpha can also regulate protein acetylation by manipulating the availability of acetyl-CoA in cells.
Dysregulation of ACC-alpha in Human Diseases
Fatty acid synthesis is involved in multiple biological processes in life activities. Therefore, dysregulation of ACC-alpha-mediated fatty acid synthesis predisposes the development of diseases, especially cancer and metabolic diseases. When tumor cells are subjected to metabolic stress, ACC-alpha can mediate AMPK-sensed metabolic stress and downstream metabolic reprogramming. Under special conditions, the AMPK/ACC signaling pathway can alternately regulate tumor cell proliferation by maintaining NADPH homeostasis. In summary, ACC-alpha has served as a potential therapeutic target against various diseases, such as cancers and metabolic diseases.
Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on gene therapy development. We can assist you in designing the best research outline customized to meet the requirements of clients’ programs. If you are interested in our services and products, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Wang, Y.; et al. Acetyl-CoA carboxylases and diseases. Frontiers in Oncology. 2022, 12: 836058. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
