RBBP6 and Associated Diseases
RBBP6 is a protein that interacts with tumor suppressors and coordinates the splicing and processing of pre-mRNA 3' end in cells.
Structure of RBBP6
Due to functional and structural similarities, RBBP6 is often compared to a similar molecule in yeast, Mpe1. The full length of RBBP6 and Mpe1 is about 250KD, and there are three highly conserved domains located at their N-terminal. RBBP6 has a unique, longer C-terminal domain that mediates the binding of the RBBP6-domain tumor suppressor p53 and RB1. RS domain mediates the association with SR proteins and the mRNA spliceosome. Furthermore, the ubiquitin-like domain DWNN of RBBP6 mediates its association with processing complexes.
RBBP6 and Pre-mRNA Splicing
In order to ensure the production of transcripts with the correct length and maturity, the mRNA must be cleaved at a specific site. Processing the 3' end of the mature transcript of the pre-nascent mRNA is very important for the stability, localization and translation of the mRNA.
The processing of human mRNA is mostly mediated by cleavage and polyadenylation-specific factors (CPSFs). Early studies demonstrated that RBBP6 is involved in the processing of the 3' end of pre-mRNA in human, but since RBBP6 does not co-purify with endogenous or recombinant CPSF complexes during protein purification, the rule of RBBP6 has been seriously underestimated in early recombination and structure research. However, RBBP6 knockout or interference experiments observed defects in the cellular transcription process and non-functionalization of transcripts, suggesting a critical role of RBBP6 in this process.
Mutation analysis confirmed that RBBP6 interacts with the WDR33 or CPSF73 subunit of CPSF by the N-terminal domain and is recruited in an RNA-dependent manner. The transient nature of RBBP6 and CPSF binding is also suspected to be the reason why human CPSF endonuclease activity is much lower than that of yeast CPF in vitro. In addition, many in vitro experiments have also demonstrated the indispensable role of lytic factor IIm, lytic stimulator and RBBP6 in mRNA 3' end cleavage.
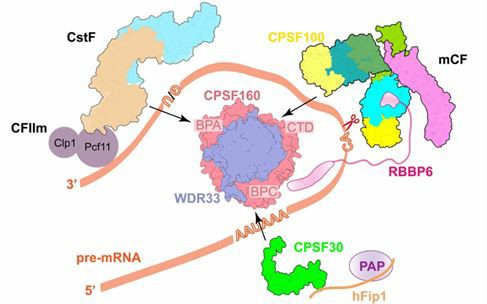 Fig 2. RBBP6 is critical in pre-mRNA splicing. (Liu, 2022)
Fig 2. RBBP6 is critical in pre-mRNA splicing. (Liu, 2022)
RBBP6 in Cancer
RBBP6 is overexpressed in various cancer patients and is directly associated with the cancer suppressor gene p53, in fact, RBBP6 is considered to be one of the key negative regulators of p53. Clinical statistics show that overexpressed RBBP6 is directly related to cancer migration, proliferation as well as its poor prognosis, which seems to be triggered by RBBP-mediated cell cycle arrest.
The role of RBBP6 in cancer has been extensively and intensively studied. The C-terminus of RBBP6 contains a conserved RING finger domain that could work with the multifunctional protein YB-1. The interaction between RBBP6 and YB-1 cause proteasome degradation and ubiquitination of YB126, and functions as an antagonist of p53 and RB1. As an E3 ubiquitin ligase, RBBP6 acts as a scaffold protein to facilitate the interaction between p53 and Hdm2, resulting in the phosphorylation and degradation of p53. RBBP6 also regulates the function of CPSF and DNA replication through the RBBP6/ZBTB38/MCM10 complex. In addition, several studies have demonstrated a significant correlation between NF-κB signaling pathway and RBBP6. RBBP6 degrades the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα to control NF-κB signaling, thereby inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancerous tissues. In summary, RBBP6 may be involved in the regulation of cell cycle, cell differentiation and apoptosis, and its overexpression promotes tumorigenesis by promoting cancer cell proliferation.
Years of experience allow Creative Biolabs to provide our clients with the most reliable services on RBBP6 and associated diseases. We will help you with disease model construction, gene sequencing, protein characterization or perform any molecular biology assay to help you advance your research. Please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Liu, J.; et al. Molecular insights into mRNA polyadenylation and deadenylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022, 23: 10985. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
